India tests new and better restart method for upper stage of its biggest rocket
India’s space agency ISRO has successfully tested new restart method for the engine it uses on the upper stage of its LVM rocket, its biggest rocket that it also intends to use for its manned and interplanetary missions.
For future missions, multiple in-flight restarts of the CE20 engine will be required for mission flexibility towards multi-orbit missions. However, with the present configuration, each restart demands an additional start-up gas bottle and associated systems, leading to a reduction in vehicle payload capability. Hence, achieving boot-strap mode start – where the engine builds up to steady operation without external start-up assistance – is essential.
In this regard, a boot-strap mode start test on the CE20 Cryogenic engine was successfully conducted under vacuum conditions in the High-Altitude Test (HAT) facility at ISRO Propulsion Complex, Mahendragiri on 7th November 2025, for a duration of 10 seconds. A multi-element igniter was employed in both the thrust chamber and gas generator to facilitate boot-strap starting. In this test, following the ignition of the thrust chamber, the gas generator was ignited under tank head conditions, and the turbopumps were started without the use of the start-up system. Subsequently, boot-strap mode build-up and steady-state operation of the engine were successfully demonstrated.
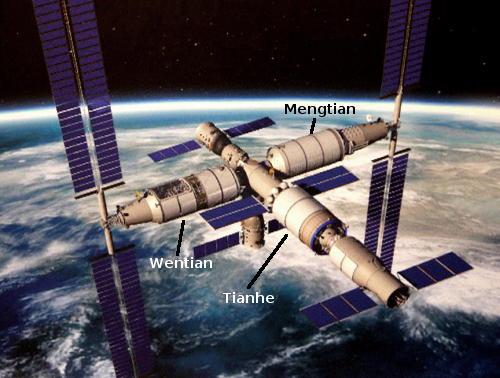
In other words, the engine now be restarted numerous times, giving any payload attached much greater flexibility in positioning and orbital maneuvers. For manned missions this means it can be used to reposition the modules for India’s planned space station, maneuver its manned capsule Gaganyaan, and send interplanetary missions to the Moon and beyond.
India’s space agency ISRO has successfully tested new restart method for the engine it uses on the upper stage of its LVM rocket, its biggest rocket that it also intends to use for its manned and interplanetary missions.
For future missions, multiple in-flight restarts of the CE20 engine will be required for mission flexibility towards multi-orbit missions. However, with the present configuration, each restart demands an additional start-up gas bottle and associated systems, leading to a reduction in vehicle payload capability. Hence, achieving boot-strap mode start – where the engine builds up to steady operation without external start-up assistance – is essential.
In this regard, a boot-strap mode start test on the CE20 Cryogenic engine was successfully conducted under vacuum conditions in the High-Altitude Test (HAT) facility at ISRO Propulsion Complex, Mahendragiri on 7th November 2025, for a duration of 10 seconds. A multi-element igniter was employed in both the thrust chamber and gas generator to facilitate boot-strap starting. In this test, following the ignition of the thrust chamber, the gas generator was ignited under tank head conditions, and the turbopumps were started without the use of the start-up system. Subsequently, boot-strap mode build-up and steady-state operation of the engine were successfully demonstrated.
In other words, the engine now be restarted numerous times, giving any payload attached much greater flexibility in positioning and orbital maneuvers. For manned missions this means it can be used to reposition the modules for India’s planned space station, maneuver its manned capsule Gaganyaan, and send interplanetary missions to the Moon and beyond.