September 12, 2025 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Voyager’s AltiusSpace celebrates winning contract from Maxar to build two robotic arms
These arms are for in-orbit robotic servicing of satellites. UPDATE: This is an old tweet, from three years ago. As of now, there is no sign this work has happened.
- China touts the second successful static fire test of its Long March 10 rocket
The test ran for 320 seconds. The rocket is intended for China’s manned lunar missions. Video can bee seen here.
- China says its Lijian-2 rocket is now being prepped to launch its Qingzhou cargo spacecraft to Tiangong-3
Launch is expected before the end of the year.
- Isar touts its entire manufacturing process making rocketss
Lots of dramatic music and quick cutting. Not a lot of detailed information. Jay notes that he “learned that it is pronounced ‘E-Sar.’ Young Frankenstein joke in there.”
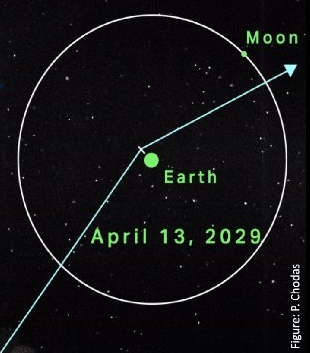
- Another quasi-moon of Earth has been found
Orbital estimates say it has been in this orbit for at least a few decades, and will remain in this orbit for at least a few decades more.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Voyager’s AltiusSpace celebrates winning contract from Maxar to build two robotic arms
These arms are for in-orbit robotic servicing of satellites. UPDATE: This is an old tweet, from three years ago. As of now, there is no sign this work has happened.
- China touts the second successful static fire test of its Long March 10 rocket
The test ran for 320 seconds. The rocket is intended for China’s manned lunar missions. Video can bee seen here.
- China says its Lijian-2 rocket is now being prepped to launch its Qingzhou cargo spacecraft to Tiangong-3
Launch is expected before the end of the year.
- Isar touts its entire manufacturing process making rocketss
Lots of dramatic music and quick cutting. Not a lot of detailed information. Jay notes that he “learned that it is pronounced ‘E-Sar.’ Young Frankenstein joke in there.”
- Another quasi-moon of Earth has been found
Orbital estimates say it has been in this orbit for at least a few decades, and will remain in this orbit for at least a few decades more.