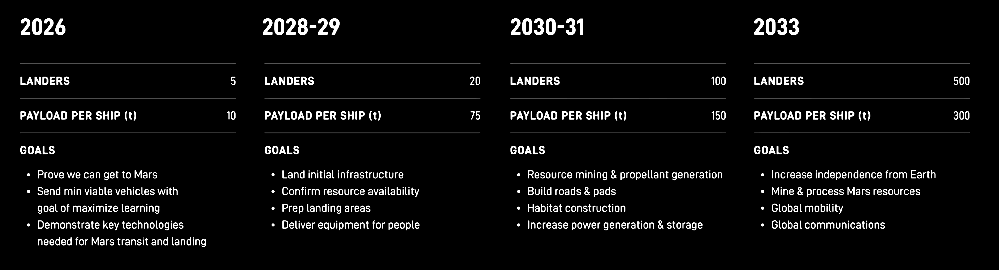
Supreme Court unanimously rules the federal government’s regulatory overuse of environmental impact statements is wrong
In a ruling that will have wide-ranging impacts across multiple industries, including rocketry, the Supreme Court yesterday ruled 8-0 that the mission creep expansion of federal government’s regulatory use of environmental impact statements (EIS) to hinder all new construction projects is incorrect and must stop.
The case involved a planned railroad in Utah, that had gotten all its permits for construction, including approval of its environmental impact statement, but was then stymied by lawsuits by political activist groups that claimed the impact statement, issued under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), had not considered the impact of the industries the railroads would serve, including impacts far from the railroad’s location itself.
This is a perfect example of the broad expansion of NEPA that has been imposed in the last two decades by federal bureaucracy working hand-in-glove with these leftist political groups.
The Supreme Court, including all of the Democratic Party appointees, said enough!
In its majority opinion, authored by Justice Brett Kavanaugh, the Court clarified that under NEPA the STB “did not need to evaluate potential environmental impacts of the separate upstream and downstream projects.” The Court concluded that the “proper judicial approach for NEPA cases is straightforward: Courts should review an agency’s EIS to check that it addresses the environmental effects of the project at hand. The EIS need not address the effects of separate projects.”
This statement “is particularly significant for infrastructure projects, such as pipelines or transmission lines, and should help reduce NEPA’s burdens (at least at the margins),” wrote Jonathan Adler, a law professor at the Case Western Reserve University School of Law, in The Volokh Conspiracy. “The opinion will also likely hamper any future efforts, perhaps by Democratic administrations, to expand or restore more fulsome (and burdensome) NEPA requirements.”
The article notes (and confirms) what I have been writing now for the past five years in connection with the FAA’s demand that rocket companies require new impact statements every time they revise their operations, even when those changes are relatively minor.
This point could reduce one of the largest delays caused by NEPA: litigation. Since its passage in 1969, NEPA has been weaponized by environmental groups to stunt disfavored projects—which has disproportionately impacted clean energy projects. On average, these challenges delay a permitted project’s start time by 4.2 years, according to The Breakthrough Institute.
The increased threat of litigation has forced federal agencies to better cover their bases, leading to longer and more expensive environmental reviews. With courts deferring more to agency decisions, litigation could be settled more quickly.
This ruling is an excellent move in the right direction, but no one should assume it will be followed honestly by the next Democrat who sits in the White House. Just as Biden expanded red tape by simple forcing the FAA to slow-walk its launch licensing process, future presidents could do the same.
Nor should be expect the lawsuits by these luddite leftists to cease. They will find other legal challenges and will push those instead.
The real solution is to reduce the bureaucracy’s size entirely, so there won’t be paper-pushers for these petty dictators to utilize for their authoritarian purposes. Eliminating or simplifying these environmental regulations would help as well, giving the activists fewer handles on which to hang their lawsuits.
In a ruling that will have wide-ranging impacts across multiple industries, including rocketry, the Supreme Court yesterday ruled 8-0 that the mission creep expansion of federal government’s regulatory use of environmental impact statements (EIS) to hinder all new construction projects is incorrect and must stop.
The case involved a planned railroad in Utah, that had gotten all its permits for construction, including approval of its environmental impact statement, but was then stymied by lawsuits by political activist groups that claimed the impact statement, issued under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), had not considered the impact of the industries the railroads would serve, including impacts far from the railroad’s location itself.
This is a perfect example of the broad expansion of NEPA that has been imposed in the last two decades by federal bureaucracy working hand-in-glove with these leftist political groups.
The Supreme Court, including all of the Democratic Party appointees, said enough!
In its majority opinion, authored by Justice Brett Kavanaugh, the Court clarified that under NEPA the STB “did not need to evaluate potential environmental impacts of the separate upstream and downstream projects.” The Court concluded that the “proper judicial approach for NEPA cases is straightforward: Courts should review an agency’s EIS to check that it addresses the environmental effects of the project at hand. The EIS need not address the effects of separate projects.”
This statement “is particularly significant for infrastructure projects, such as pipelines or transmission lines, and should help reduce NEPA’s burdens (at least at the margins),” wrote Jonathan Adler, a law professor at the Case Western Reserve University School of Law, in The Volokh Conspiracy. “The opinion will also likely hamper any future efforts, perhaps by Democratic administrations, to expand or restore more fulsome (and burdensome) NEPA requirements.”
The article notes (and confirms) what I have been writing now for the past five years in connection with the FAA’s demand that rocket companies require new impact statements every time they revise their operations, even when those changes are relatively minor.
This point could reduce one of the largest delays caused by NEPA: litigation. Since its passage in 1969, NEPA has been weaponized by environmental groups to stunt disfavored projects—which has disproportionately impacted clean energy projects. On average, these challenges delay a permitted project’s start time by 4.2 years, according to The Breakthrough Institute.
The increased threat of litigation has forced federal agencies to better cover their bases, leading to longer and more expensive environmental reviews. With courts deferring more to agency decisions, litigation could be settled more quickly.
This ruling is an excellent move in the right direction, but no one should assume it will be followed honestly by the next Democrat who sits in the White House. Just as Biden expanded red tape by simple forcing the FAA to slow-walk its launch licensing process, future presidents could do the same.
Nor should be expect the lawsuits by these luddite leftists to cease. They will find other legal challenges and will push those instead.
The real solution is to reduce the bureaucracy’s size entirely, so there won’t be paper-pushers for these petty dictators to utilize for their authoritarian purposes. Eliminating or simplifying these environmental regulations would help as well, giving the activists fewer handles on which to hang their lawsuits.