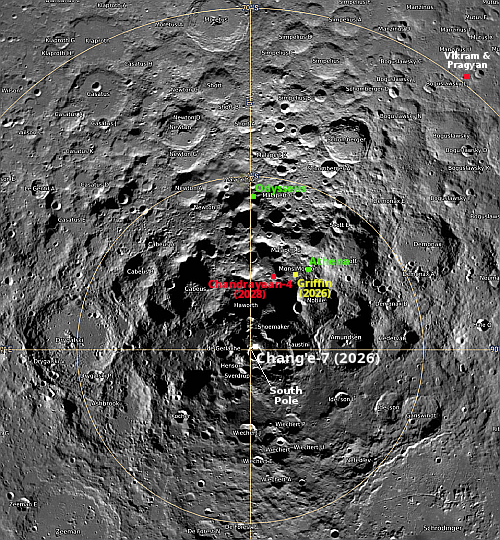
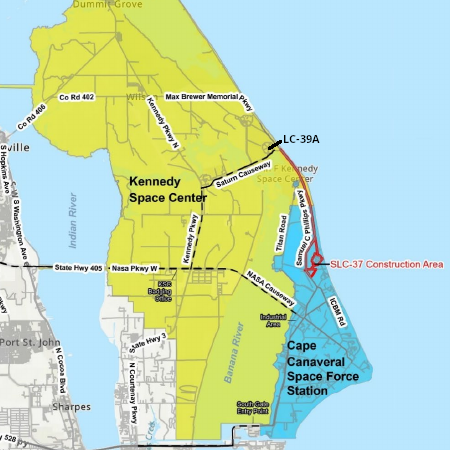
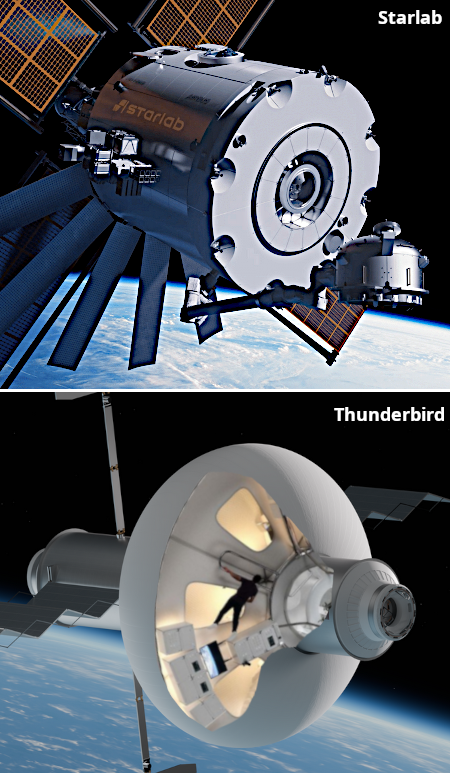
A lava tube on Venus?
The uncertainty of science: Scientists in Italy have reanalyzed the radar data of Venus by the Magellan orbiter from 1990 to 1992 and concluded that at least one open pit on the side of a shield volcano might be the entrance to a underground lava tube.
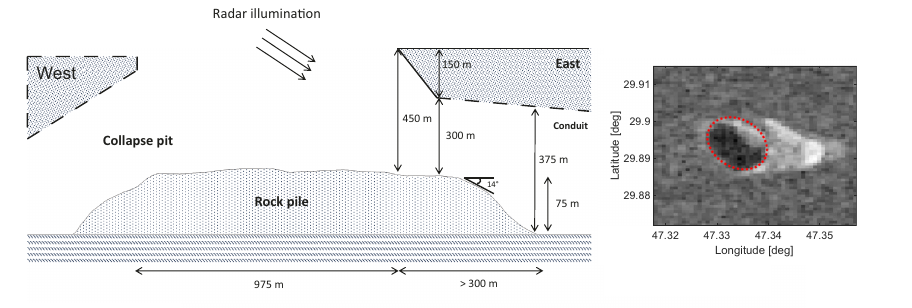
You can read their paper here [pdf]. The graphic above comes from figures 2 and 3 of their paper, with the radar image of the pit to the right, and the cartoon to the left their interpretation of that radar data. From the abstract:
Between 1990 and 1992, the Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) instrument on board the Magellan spacecraft mapped the Venusian surface. By leveraging a SAR imaging technique developed for detecting and characterizing accessible subsurface conduits in the proximity of skylights, we analysed
the Magellan radar images in locations where there is evidence of localized surface collapses. Our analyses reveal the existence of a large and open subsurface conduit in the Nyx Mons region. This feature is hypothesized to be a pyroduct, characterized by a diameter of about 1 km, a roof thickness of at least 150 m and an empty void height of no less than 375 m. The conduit extends in the subsurface for at least 300 meters from the skylight.
To strengthen their conclusions, which are based on a LOT of assumptions, the scientists also compared this radar data with radar data taken of similar-sized lava tube skylights on Earth.
Their conclusion is reasonable, as Venus is a planet of volcanoes, with more than a million detected in radar data. Lava tubes should exist. Nonetheless, their interpretation of the radar data is very uncertain, and must be viewed with a great deal of skepticism.

The uncertainty of science: Scientists in Italy have reanalyzed the radar data of Venus by the Magellan orbiter from 1990 to 1992 and concluded that at least one open pit on the side of a shield volcano might be the entrance to a underground lava tube.
You can read their paper here [pdf]. The graphic above comes from figures 2 and 3 of their paper, with the radar image of the pit to the right, and the cartoon to the left their interpretation of that radar data. From the abstract:
Between 1990 and 1992, the Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) instrument on board the Magellan spacecraft mapped the Venusian surface. By leveraging a SAR imaging technique developed for detecting and characterizing accessible subsurface conduits in the proximity of skylights, we analysed
the Magellan radar images in locations where there is evidence of localized surface collapses. Our analyses reveal the existence of a large and open subsurface conduit in the Nyx Mons region. This feature is hypothesized to be a pyroduct, characterized by a diameter of about 1 km, a roof thickness of at least 150 m and an empty void height of no less than 375 m. The conduit extends in the subsurface for at least 300 meters from the skylight.
To strengthen their conclusions, which are based on a LOT of assumptions, the scientists also compared this radar data with radar data taken of similar-sized lava tube skylights on Earth.
Their conclusion is reasonable, as Venus is a planet of volcanoes, with more than a million detected in radar data. Lava tubes should exist. Nonetheless, their interpretation of the radar data is very uncertain, and must be viewed with a great deal of skepticism.