Anonymous sources: Starship will need a major rebuild after two consecutive failures

Starship just before loss of signal on March 6, 2025
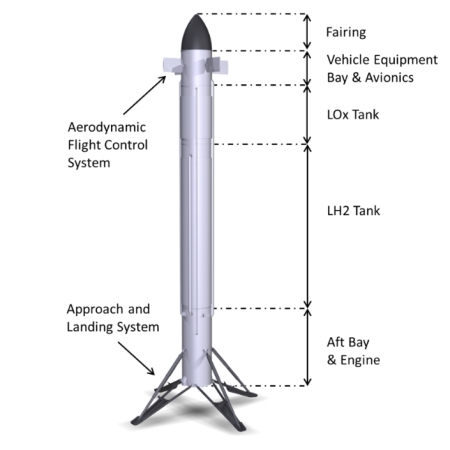
According to information at this tweet from anonymous sources, parts of Starship will likely require a major redesign due to the spacecraft’s break-up shortly after stage separation on its last two test flights.
These are the key take-aways, most of which focus on the redesign of the first version of Starship (V1) to create the V2 that flew unsuccessfully on those flights:
- Hot separation also aggravates the situation in the compartment.
- Not related to the flames from the Super Heavy during the booster turn.
- This is a fundamental miscalculation in the design of the Starship V2 and the engine section.
- The fuel lines, wiring for the engines and the power unit will be urgently redone.
- The fate of S35 and S36 is still unclear. Either revision or scrap.
- For the next ships, some processes may be paused in production until a decision on the design is made.
- The team was rushed with fixes for S34, hence the nervous start. There was no need to rush.
- The fixes will take much longer than 4-6 weeks.
- Comprehensive ground testing with long-term fire tests is needed. [emphasis mine]
It must be emphasized that this information comes from leaks from anonymous sources, and could be significantly incorrect. It does however fit the circumstances, and suggests that the next test flight will not occur in April but will be delayed for an unknown period beyond.
I think the tweet however is much too pessimistic. If the problems are all within the fuel lines, engine wiring, and the power unit, they are well localized. Moreover, the design of these components on version 1 of Starship apparently worked reasonably well, which gives them a good basis for that redesign. Nonetheless, if these facts are correct, my guess is the next test flight won’t occur before June.
The one saving grace is that FAA red tape is clearly no longer an additional obstacle. It is very clear now that with the change from Biden to Trump it is letting SpaceX lead all investigations, and immediately accepting its conclusions and fixes, rather than sitting on those conclusions as it retyped them for weeks or months in its own report.
Hat tip to reader Richard M.

Starship just before loss of signal on March 6, 2025
According to information at this tweet from anonymous sources, parts of Starship will likely require a major redesign due to the spacecraft’s break-up shortly after stage separation on its last two test flights.
These are the key take-aways, most of which focus on the redesign of the first version of Starship (V1) to create the V2 that flew unsuccessfully on those flights:
- Hot separation also aggravates the situation in the compartment.
- Not related to the flames from the Super Heavy during the booster turn.
- This is a fundamental miscalculation in the design of the Starship V2 and the engine section.
- The fuel lines, wiring for the engines and the power unit will be urgently redone.
- The fate of S35 and S36 is still unclear. Either revision or scrap.
- For the next ships, some processes may be paused in production until a decision on the design is made.
- The team was rushed with fixes for S34, hence the nervous start. There was no need to rush.
- The fixes will take much longer than 4-6 weeks.
- Comprehensive ground testing with long-term fire tests is needed. [emphasis mine]
It must be emphasized that this information comes from leaks from anonymous sources, and could be significantly incorrect. It does however fit the circumstances, and suggests that the next test flight will not occur in April but will be delayed for an unknown period beyond.
I think the tweet however is much too pessimistic. If the problems are all within the fuel lines, engine wiring, and the power unit, they are well localized. Moreover, the design of these components on version 1 of Starship apparently worked reasonably well, which gives them a good basis for that redesign. Nonetheless, if these facts are correct, my guess is the next test flight won’t occur before June.
The one saving grace is that FAA red tape is clearly no longer an additional obstacle. It is very clear now that with the change from Biden to Trump it is letting SpaceX lead all investigations, and immediately accepting its conclusions and fixes, rather than sitting on those conclusions as it retyped them for weeks or months in its own report.
Hat tip to reader Richard M.