Scientists: X-rays from the Helix Nebula caused by the destruction of a planet

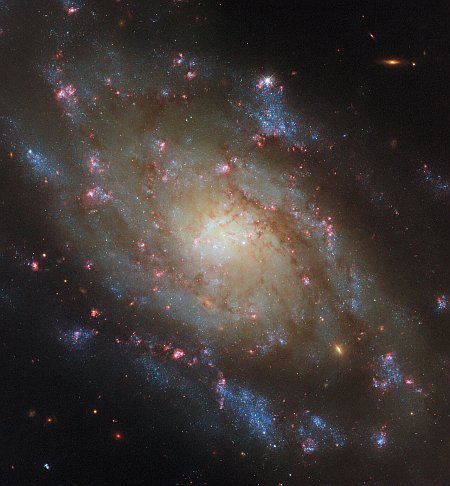
A composite image of the Helix Nebula, combining data
from multiple ground- and space-based telescopes.
Click for original image.
Using data collected by multiple ground-bases and space telescopes over decades, scientists now think the previously unexplained high energy X-rays coming from the white dwarf star at the center of the Helix Nebula are caused by the destruction of a Jupiter-sized exoplanet.
The besieged planet could have initially been a considerable distance from the white dwarf but then migrated inwards by interacting with the gravity of other planets in the system. Once it approached close enough to the white dwarf, the gravity of the star would have partially or completely torn the planet apart. “The mysterious signal we’ve been seeing could be caused by the debris from the shattered planet falling onto the white dwarf’s surface, and being heated to glow in X-rays,” said co-author Martin Guerrero of The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia in Spain. “If confirmed, this would be the first case of a planet seen to be destroyed by the central star in a planetary nebula.”
The study shows that the X-ray signal from the white dwarf has remained approximately constant in brightness between 1992, 1999, and 2002 (with observations by ROSAT, Chandra and XMM respectively). The data, however, suggests there may be a subtle, regular change in the X-ray signal every 2.9 hours, providing evidence for the remains of a planet exceptionally close to the white dwarf.
You can read the original paper here. The Helix Nebula is about 650 light years away, and is one of the most studied planetary nebula, believed to have formed when the central star collapsed into a white dwarf.

A composite image of the Helix Nebula, combining data
from multiple ground- and space-based telescopes.
Click for original image.
Using data collected by multiple ground-bases and space telescopes over decades, scientists now think the previously unexplained high energy X-rays coming from the white dwarf star at the center of the Helix Nebula are caused by the destruction of a Jupiter-sized exoplanet.
The besieged planet could have initially been a considerable distance from the white dwarf but then migrated inwards by interacting with the gravity of other planets in the system. Once it approached close enough to the white dwarf, the gravity of the star would have partially or completely torn the planet apart. “The mysterious signal we’ve been seeing could be caused by the debris from the shattered planet falling onto the white dwarf’s surface, and being heated to glow in X-rays,” said co-author Martin Guerrero of The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia in Spain. “If confirmed, this would be the first case of a planet seen to be destroyed by the central star in a planetary nebula.”
The study shows that the X-ray signal from the white dwarf has remained approximately constant in brightness between 1992, 1999, and 2002 (with observations by ROSAT, Chandra and XMM respectively). The data, however, suggests there may be a subtle, regular change in the X-ray signal every 2.9 hours, providing evidence for the remains of a planet exceptionally close to the white dwarf.
You can read the original paper here. The Helix Nebula is about 650 light years away, and is one of the most studied planetary nebula, believed to have formed when the central star collapsed into a white dwarf.