Another cool hiking location on Mars
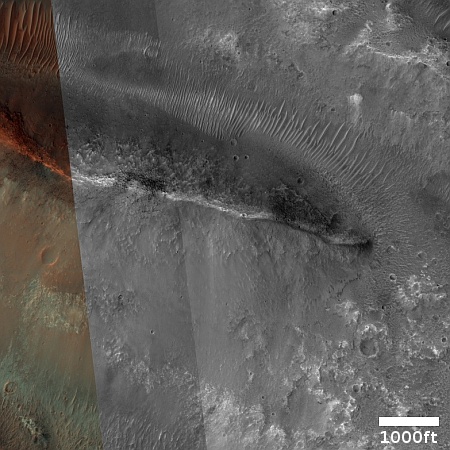
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on August 10, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
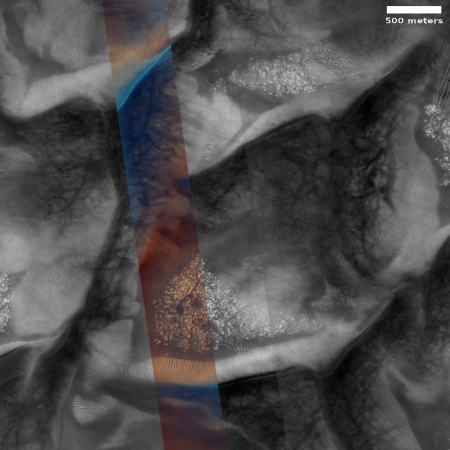
My reason to posting this I admit is selfish and tourist-oriented. This narrow ridge, about a mile long and about 300 to 600 feet high, appeals directly to my hiking passions. A trail along its length would provide any hiker some really spectactular views.
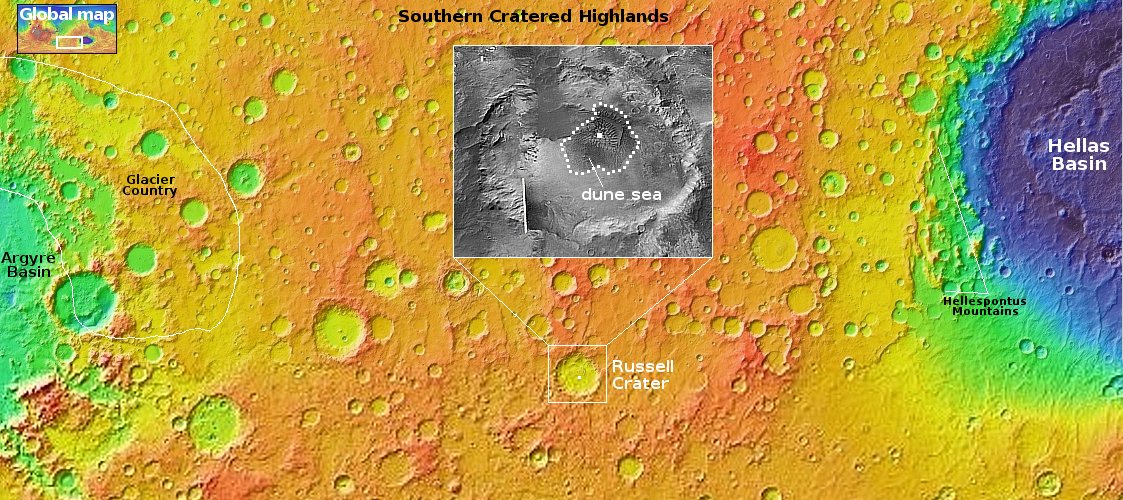
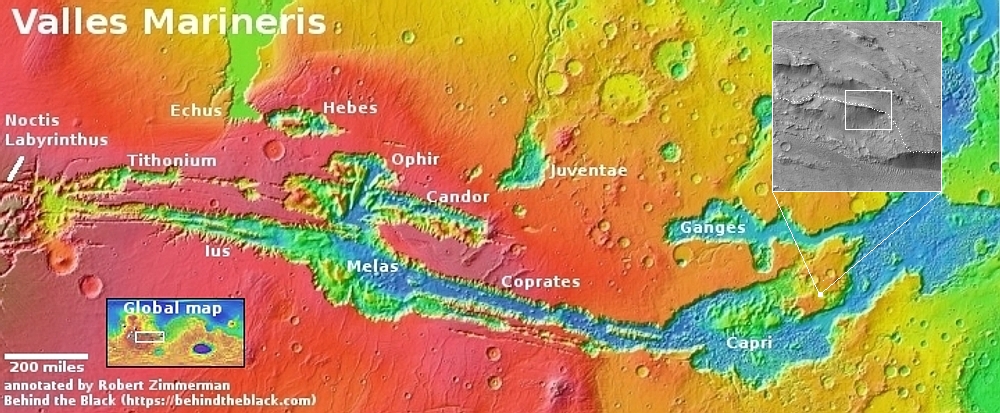
The scientists took the picture because of the geology. The white dot on the overview map above marks the location, a short channel dubbed Daga Vallis that connects two major canyons in the eastern part of Valles Marineris, the largest known canyon system in the solar system. This ridge and several nearby parallel ridges were apparently made of something, possibly lava, that was resistent to the theorized ancient catastrophic floods that scientists presently believe carved out these channels and canyons.
In the inset the dotted line indicates one possible hiking trail route that travels the full length of the ridge but then heads south to continue along the rim of a 1,200-foot-high cliff face. For future Martian colonists, I offer this site as a great place to set up a bed-and-breakfast, surrounded by many potential hikes of incredible stark beauty.

Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on August 10, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
My reason to posting this I admit is selfish and tourist-oriented. This narrow ridge, about a mile long and about 300 to 600 feet high, appeals directly to my hiking passions. A trail along its length would provide any hiker some really spectactular views.
The scientists took the picture because of the geology. The white dot on the overview map above marks the location, a short channel dubbed Daga Vallis that connects two major canyons in the eastern part of Valles Marineris, the largest known canyon system in the solar system. This ridge and several nearby parallel ridges were apparently made of something, possibly lava, that was resistent to the theorized ancient catastrophic floods that scientists presently believe carved out these channels and canyons.
In the inset the dotted line indicates one possible hiking trail route that travels the full length of the ridge but then heads south to continue along the rim of a 1,200-foot-high cliff face. For future Martian colonists, I offer this site as a great place to set up a bed-and-breakfast, surrounded by many potential hikes of incredible stark beauty.