Crazily eroded rock on Mars
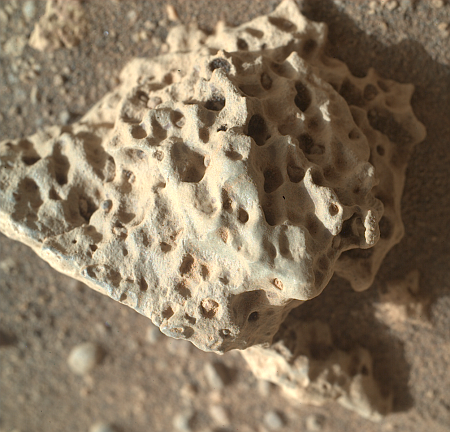
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken today by the Perseverance Mars rover, using its SHERLOC-WATSON close-up camera at the end of its robot arm.
The size of this rock is tiny, no more than a few inches across. The many holes remind me of surface limestone on Earth. When it rains, the water dissolves the limestone, and so holes will develop and grow over time. You can see this process if you spray very hot water on top of a block of ice.
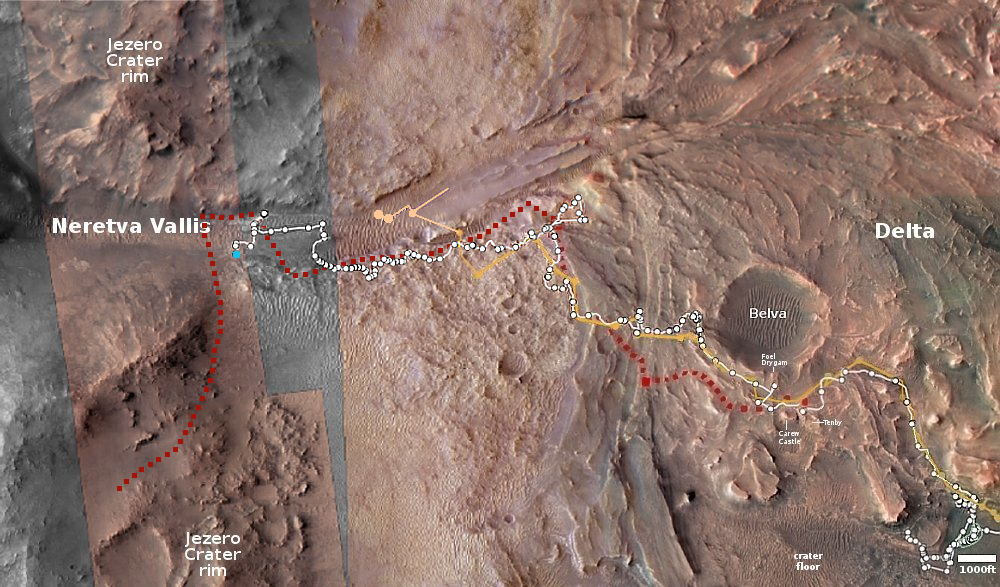
The problem is that it doesn’t rain on Mars. Lava can sometimes freeze and look this way, but is it lava? The blue dot on the overview map above shows where Perseverance was two days earlier. The rover team has not updated that map so it is not known exactly where the rover was when it snapped this picture today. Nor has the science team posted an update on their activities since June 27th.
These strange features however mirror somewhat the same surface features seen back in June, when the rover was on the north side of Neretva Vallis, so it is likely this rock was produced by the same geological processes. I will however not guess what those processes were.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken today by the Perseverance Mars rover, using its SHERLOC-WATSON close-up camera at the end of its robot arm.
The size of this rock is tiny, no more than a few inches across. The many holes remind me of surface limestone on Earth. When it rains, the water dissolves the limestone, and so holes will develop and grow over time. You can see this process if you spray very hot water on top of a block of ice.
The problem is that it doesn’t rain on Mars. Lava can sometimes freeze and look this way, but is it lava? The blue dot on the overview map above shows where Perseverance was two days earlier. The rover team has not updated that map so it is not known exactly where the rover was when it snapped this picture today. Nor has the science team posted an update on their activities since June 27th.
These strange features however mirror somewhat the same surface features seen back in June, when the rover was on the north side of Neretva Vallis, so it is likely this rock was produced by the same geological processes. I will however not guess what those processes were.