NASA initiates new program to grab talent from the private sector

Where new talent will now go to wither.
As part of NASA administrator’s effort to remake NASA into a cutting edge agency, “the global leader in space,” the agency in partnership with the federal Office of Personnel Management (OPM) has initiated a new program, dubbed NASA Force, to recruit talent from the private sector for two-year terms, after which they can then try to get a full time job either with NASA or a private aerospace company.
NASA Force will identify and place high-impact technical talent into mission-critical roles supporting NASA’s exploration, research, and advanced technology priorities, ensuring the agency has the cutting-edge expertise needed to maintain U.S. leadership in space.
Tech Force, led by OPM, was established to recruit elite technical professionals into federal service, embed them at partner agencies to modernize systems, accelerate innovation, and strengthen mission delivery. NASA Force represents a focused expansion of that effort, tailored to the unique technical demands of space exploration and aerospace research.
“America’s leadership in space depends on extraordinary talent,” said NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman. “NASA Force will help us attract the next generation of innovators and technical experts who are ready to solve the toughest challenges in exploration, science, and aerospace technology. This partnership strengthens our workforce and helps ensure the United States remains the global leader in space.”
This program however has things entirely backwards. The last thing any engineer who has just graduated college should do is get a short two-year job at NASA. He or she will learn all the wrong lessons, working for a government agency not interested in efficiency or profit.
Instead, it is essential the first job new engineers get is in the private sector, to learn how to do things fast and efficiently. It Isaacman had the right priorities, he would use this money to fund these jobs in the private sector, so that new graduates will get the right training. Unfortunately, that is not Isaacman’s priority. He wants the government to lead.
Moreover, NASA’s job was never intended to be “the global leader in space.” Its job was to formulate the federal government’s needs in space, and then ask the private sector — the American people — to get the job done. Isaacman instead wants to have NASA do the job, as it did for a half century after Apollo, quite poorly. Only after the agency began relying on private enterprise beginning in 2008, the capitalism model, did things finally start happening again.
The worst aspect of this program is that it will take talent away from the private sector. A lot of good and talented young engineers will gravitate to these NASA positions for the high pay, relatively easy good hours, and prestige. They won’t accomplish much there, and their training will be wrong-headed. Meanwhile, the private sector will lose that talent and have to find it elsewhere, assuming it is available at all.

Where new talent will now go to wither.
As part of NASA administrator’s effort to remake NASA into a cutting edge agency, “the global leader in space,” the agency in partnership with the federal Office of Personnel Management (OPM) has initiated a new program, dubbed NASA Force, to recruit talent from the private sector for two-year terms, after which they can then try to get a full time job either with NASA or a private aerospace company.
NASA Force will identify and place high-impact technical talent into mission-critical roles supporting NASA’s exploration, research, and advanced technology priorities, ensuring the agency has the cutting-edge expertise needed to maintain U.S. leadership in space.
Tech Force, led by OPM, was established to recruit elite technical professionals into federal service, embed them at partner agencies to modernize systems, accelerate innovation, and strengthen mission delivery. NASA Force represents a focused expansion of that effort, tailored to the unique technical demands of space exploration and aerospace research.
“America’s leadership in space depends on extraordinary talent,” said NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman. “NASA Force will help us attract the next generation of innovators and technical experts who are ready to solve the toughest challenges in exploration, science, and aerospace technology. This partnership strengthens our workforce and helps ensure the United States remains the global leader in space.”
This program however has things entirely backwards. The last thing any engineer who has just graduated college should do is get a short two-year job at NASA. He or she will learn all the wrong lessons, working for a government agency not interested in efficiency or profit.
Instead, it is essential the first job new engineers get is in the private sector, to learn how to do things fast and efficiently. It Isaacman had the right priorities, he would use this money to fund these jobs in the private sector, so that new graduates will get the right training. Unfortunately, that is not Isaacman’s priority. He wants the government to lead.
Moreover, NASA’s job was never intended to be “the global leader in space.” Its job was to formulate the federal government’s needs in space, and then ask the private sector — the American people — to get the job done. Isaacman instead wants to have NASA do the job, as it did for a half century after Apollo, quite poorly. Only after the agency began relying on private enterprise beginning in 2008, the capitalism model, did things finally start happening again.
The worst aspect of this program is that it will take talent away from the private sector. A lot of good and talented young engineers will gravitate to these NASA positions for the high pay, relatively easy good hours, and prestige. They won’t accomplish much there, and their training will be wrong-headed. Meanwhile, the private sector will lose that talent and have to find it elsewhere, assuming it is available at all.
On Christmas Eve 1968 three Americans became the first humans to visit another world. What they did to celebrate was unexpected and profound, and will be remembered throughout all human history. Genesis: the Story of Apollo 8, Robert Zimmerman's classic history of humanity's first journey to another world, tells that story, and it is now available as both an ebook and an audiobook, both with a foreword by Valerie Anders and a new introduction by Robert Zimmerman.
The print edition can be purchased at Amazon or any other book seller. If you want an autographed copy the price is $60 for the hardback and $45 for the paperback, plus $8 shipping for each. Go here for purchasing details. The ebook is available everywhere for $5.99 (before discount) at amazon, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
The audiobook is also available at all these vendors, and is also free with a 30-day trial membership to Audible.
"Not simply about one mission, [Genesis] is also the history of America's quest for the moon... Zimmerman has done a masterful job of tying disparate events together into a solid account of one of America's greatest human triumphs."--San Antonio Express-News
March 4, 2026 Quick space links
As BtB’s stringer Jay is on vacation, here are a few links I spotted that don’t deserve full posts. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Redwire touts its new solar array available for sale to spacecraft and satellites
The company says it produces 50% more power while being smaller and lighter.
- China successfully conducts laser communications between a geosynchronous satellite and ground station
According to China’s state-run press, it did “two-way data transmission at 1 gigabit per second over a distance exceeding 40,000 kilometers.”
As BtB’s stringer Jay is on vacation, here are a few links I spotted that don’t deserve full posts. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Redwire touts its new solar array available for sale to spacecraft and satellites
The company says it produces 50% more power while being smaller and lighter.
- China successfully conducts laser communications between a geosynchronous satellite and ground station
According to China’s state-run press, it did “two-way data transmission at 1 gigabit per second over a distance exceeding 40,000 kilometers.”
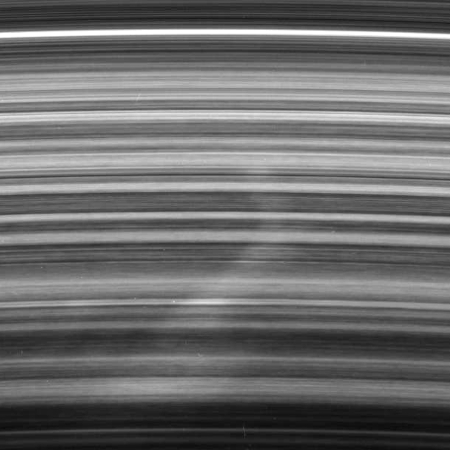
The mysterious spokes in Saturn’s rings
Cool image time! When Voyager-1 did its fly-by of Saturn in December 1980, its cameras captured something in the gas giant’s rings that no one had predicted or expected, spokes of brightness pointing outward along the surface of the rings at right angles to the planet. Even more puzzling, these spokes actually appeared to rotate around Saturn, always pointing away from it.
The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on March 7, 2007 by the Saturn orbiter Cassini. It shows a close-up of one such spoke, though in this case it is bent. From the press release:
A bright spoke extends across the unilluminated side of Saturn’s B ring about the same distance as that from London to Cairo. The background ring material displays some azimuthal (i.e., left to right) asymmetry. The radial (outward from Saturn) direction is up in this view. A noticeable kink in the spoke occurs very close to the radius where ring particles orbit the planet at the speed of Saturn’s magnetic field. Such a connection is most intriguing to scientists studying these ghostly ring phenomena.
If gravity alone were affecting the spoke material, there would be no kink and the entire spoke would be angled toward right, like the bottom portion. That it bends to the left above the kink indicates that some other force, possibly related to the magnetic field, is acting on the spoke material. The shape might also indicate that the spoke did not form in a radial orientation, thus challenging scientists’ assumptions about these features.
In other words, the spokes exist because of multiple factors, some still unknown, that cause these streaks of brightness in the rings. For some reason, the millions of tiny ice particles that comprise the rings are brightened along these spokes, and it isn’t just gravity that is causing it.
Cool image time! When Voyager-1 did its fly-by of Saturn in December 1980, its cameras captured something in the gas giant’s rings that no one had predicted or expected, spokes of brightness pointing outward along the surface of the rings at right angles to the planet. Even more puzzling, these spokes actually appeared to rotate around Saturn, always pointing away from it.
The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here, was taken on March 7, 2007 by the Saturn orbiter Cassini. It shows a close-up of one such spoke, though in this case it is bent. From the press release:
A bright spoke extends across the unilluminated side of Saturn’s B ring about the same distance as that from London to Cairo. The background ring material displays some azimuthal (i.e., left to right) asymmetry. The radial (outward from Saturn) direction is up in this view. A noticeable kink in the spoke occurs very close to the radius where ring particles orbit the planet at the speed of Saturn’s magnetic field. Such a connection is most intriguing to scientists studying these ghostly ring phenomena.
If gravity alone were affecting the spoke material, there would be no kink and the entire spoke would be angled toward right, like the bottom portion. That it bends to the left above the kink indicates that some other force, possibly related to the magnetic field, is acting on the spoke material. The shape might also indicate that the spoke did not form in a radial orientation, thus challenging scientists’ assumptions about these features.
In other words, the spokes exist because of multiple factors, some still unknown, that cause these streaks of brightness in the rings. For some reason, the millions of tiny ice particles that comprise the rings are brightened along these spokes, and it isn’t just gravity that is causing it.
Now available in hardback and paperback as well as ebook!
From the press release: In this ground-breaking new history of early America, historian Robert Zimmerman not only exposes the lie behind The New York Times 1619 Project that falsely claims slavery is central to the history of the United States, he also provides profound lessons about the nature of human societies, lessons important for Americans today as well as for all future settlers on Mars and elsewhere in space.
Conscious Choice: The origins of slavery in America and why it matters today and for our future in outer space, is a riveting page-turning story that documents how slavery slowly became pervasive in the southern British colonies of North America, colonies founded by a people and culture that not only did not allow slavery but in every way were hostile to the practice.
Conscious Choice does more however. In telling the tragic history of the Virginia colony and the rise of slavery there, Zimmerman lays out the proper path for creating healthy societies in places like the Moon and Mars.
“Zimmerman’s ground-breaking history provides every future generation the basic framework for establishing new societies on other worlds. We would be wise to heed what he says.” —Robert Zubrin, founder of the Mars Society.
All editions are available at Amazon, Barnes & Noble, and all book vendors, with the ebook priced at $5.99 before discount. All editions can also be purchased direct from the ebook publisher, ebookit, in which case you don't support the big tech companies and the author gets a bigger cut much sooner.
Autographed printed copies are also available at discount directly from the author (hardback $29.95; paperback $14.95; Shipping cost for either: $6.00). Just send an email to zimmerman @ nasw dot org.
South Korean rocket startup Innospace signs another spaceport launch deal

Proposed Canadian spaceports
The South Korean rocket startup Innospace, which has attempted one launch of its Hanbit-Nano rocket (a failure), has now signed a launch deal with the proposed Spaceport Nova Scotia, run by Maritime Launch Services.
Maritime Launch Services announced a strategic partnership with South Korean rocket developer Innospace. Under a new Letter of Intent (LOI), the two companies will evaluate hosting the HANBIT launch system at Spaceport Nova Scotia, potentially transforming the Atlantic coast into a primary North American hub for the South Korean firm.
Innospace’s first launch was from Brazil’s long unused Alcantera spaceport on its northeast coast. The company has also signed deals with Portugal’s proposed Santa Maria spaceport, two spaceports in Australia (Southern Launch and Equatorial Launch), and Norway’s Andoya spaceport.
This new deal in Nova Scotia is still preliminary, with the two companies having until the end of the year to finalize the specifics. For Innospace, it appears the company its trying to give itself as many spaceport options as possible. It can also launch from the government spaceport in South Korea, but that provides much more limited orbital flight paths, and presents scheduling difficulties.
For Maritime, this deal might finally get this spaceport off the ground. It was first proposed in 2016, offering satellite companies both a launch site and a Ukrainian-built rocket. That plan fell through when Russia invaded the Ukraine and the rocket became unavailable. Since then Maritime has struggled to convince rocket companies to use the spaceport, all to no avail. It signed some deals, but none has gone anywhere. This deal is its first with a rocket startup that has actually attempted a launch, though that launch was a failure.

Proposed Canadian spaceports
The South Korean rocket startup Innospace, which has attempted one launch of its Hanbit-Nano rocket (a failure), has now signed a launch deal with the proposed Spaceport Nova Scotia, run by Maritime Launch Services.
Maritime Launch Services announced a strategic partnership with South Korean rocket developer Innospace. Under a new Letter of Intent (LOI), the two companies will evaluate hosting the HANBIT launch system at Spaceport Nova Scotia, potentially transforming the Atlantic coast into a primary North American hub for the South Korean firm.
Innospace’s first launch was from Brazil’s long unused Alcantera spaceport on its northeast coast. The company has also signed deals with Portugal’s proposed Santa Maria spaceport, two spaceports in Australia (Southern Launch and Equatorial Launch), and Norway’s Andoya spaceport.
This new deal in Nova Scotia is still preliminary, with the two companies having until the end of the year to finalize the specifics. For Innospace, it appears the company its trying to give itself as many spaceport options as possible. It can also launch from the government spaceport in South Korea, but that provides much more limited orbital flight paths, and presents scheduling difficulties.
For Maritime, this deal might finally get this spaceport off the ground. It was first proposed in 2016, offering satellite companies both a launch site and a Ukrainian-built rocket. That plan fell through when Russia invaded the Ukraine and the rocket became unavailable. Since then Maritime has struggled to convince rocket companies to use the spaceport, all to no avail. It signed some deals, but none has gone anywhere. This deal is its first with a rocket startup that has actually attempted a launch, though that launch was a failure.
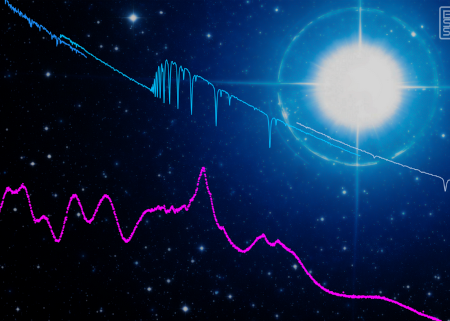
The first orbiting private space telescope releases “first light” image
The first orbiting private space telescope, owned by Blue Skies Space and dubbed Mauve, has successfully taken its first image and data, a 5 second long exposure of a single star.
That image is to the right, with the spectroscopic data shown by the magenta line. The Hubble Space Telescope’s spectroscopic data is shown in blue and while for comparison.
As part of early commissioning, Mauve was pointed at its first calibration target, eta Ursae Majoris (eta UMa), a bright star in the constellation Ursa Major, approximately 104 light-years from Earth, for a 5-second observation. Eta UMa is a hot, blue-white star, much hotter than our Sun. Eta UMa shines brightly in ultraviolet light, making it an ideal calibration target for a UV observatory like Mauve.
The telescope has a 5-inch mirror, so its resolution is far lower than Hubble’s 94-inch mirror, but because it is above the atmosphere its view is far better than larger ground-based telescopes. Mauve is intended as a three-year-long demonstration project, during which it will study flares from nearby stars that are thought to have exoplanets, as well as binary star systems and variable stars. It is also making this data available to scientists, for a subscription fee. It already has almost a dozen universities signed up.
Blue Skies hopes Mauve’s success will help it raise the capital to build Twinkle, a space telescope with an 18-inch primary mirror. If that succeeds, the company plans to scale up to even bigger orbiting telescopes.
This private sector astronomy model is how the U.S. did things routinely prior to World War II. Then, for many reasons, the government took over for the next three-quarters of a century. It now appears the pendulum is shifting back to the private sector.
The first orbiting private space telescope, owned by Blue Skies Space and dubbed Mauve, has successfully taken its first image and data, a 5 second long exposure of a single star.
That image is to the right, with the spectroscopic data shown by the magenta line. The Hubble Space Telescope’s spectroscopic data is shown in blue and while for comparison.
As part of early commissioning, Mauve was pointed at its first calibration target, eta Ursae Majoris (eta UMa), a bright star in the constellation Ursa Major, approximately 104 light-years from Earth, for a 5-second observation. Eta UMa is a hot, blue-white star, much hotter than our Sun. Eta UMa shines brightly in ultraviolet light, making it an ideal calibration target for a UV observatory like Mauve.
The telescope has a 5-inch mirror, so its resolution is far lower than Hubble’s 94-inch mirror, but because it is above the atmosphere its view is far better than larger ground-based telescopes. Mauve is intended as a three-year-long demonstration project, during which it will study flares from nearby stars that are thought to have exoplanets, as well as binary star systems and variable stars. It is also making this data available to scientists, for a subscription fee. It already has almost a dozen universities signed up.
Blue Skies hopes Mauve’s success will help it raise the capital to build Twinkle, a space telescope with an 18-inch primary mirror. If that succeeds, the company plans to scale up to even bigger orbiting telescopes.
This private sector astronomy model is how the U.S. did things routinely prior to World War II. Then, for many reasons, the government took over for the next three-quarters of a century. It now appears the pendulum is shifting back to the private sector.
Leaving Earth: Space Stations, Rival Superpowers, and the Quest for Interplanetary Travel, can be purchased as an ebook everywhere for only $3.99 (before discount) at amazon, Barnes & Noble, all ebook vendors, or direct from my ebook publisher, ebookit.
If you buy it from ebookit you don't support the big oppressive tech companies and I get a bigger cut much sooner.
Winner of the 2003 Eugene M. Emme Award of the American Astronautical Society.
"Leaving Earth is one of the best and certainly the most comprehensive summary of our drive into space that I have ever read. It will be invaluable to future scholars because it will tell them how the next chapter of human history opened." -- Arthur C. Clarke
ESA asks for proposals on building its own space station

The European Space Agency (ESA) last week issued an open call for proposals outlining the construction of its own space station, independent of the five American stations presently in development to replace ISS.
On 27 February, ESA published an intended call for tenders for two Pre-Phase A studies under Scenario 3. According to the call, the studies will consolidate the “feasibility, architecture, utilisation, and technology requirements of a European-led LEO outpost” and propose cooperation with the Canadian Space Agency, Japan’s national space agency JAXA, and “additional partners.” The results of the two parallel studies will be used to enable ESA decision-making for its post-ISS transition by the end of 2026.
Do not expect these “studies” to produce a European-led space station any time soon. It is the ESA way to do lots of studies, and then after reading these to do more detailed follow-up studies outlining what they will do. Then, after years of review, it might finally get started on construction, which always proceeds somewhat slowly.
In the meantime, ESA has signed agreements with three of the five American space station projects (Axiom, Starlab, Vast), with its deal with the Starlab station the most extensive. All three deals leave open the possibility that Europe will rent time at each station to fly experiments and astronauts there.

The European Space Agency (ESA) last week issued an open call for proposals outlining the construction of its own space station, independent of the five American stations presently in development to replace ISS.
On 27 February, ESA published an intended call for tenders for two Pre-Phase A studies under Scenario 3. According to the call, the studies will consolidate the “feasibility, architecture, utilisation, and technology requirements of a European-led LEO outpost” and propose cooperation with the Canadian Space Agency, Japan’s national space agency JAXA, and “additional partners.” The results of the two parallel studies will be used to enable ESA decision-making for its post-ISS transition by the end of 2026.
Do not expect these “studies” to produce a European-led space station any time soon. It is the ESA way to do lots of studies, and then after reading these to do more detailed follow-up studies outlining what they will do. Then, after years of review, it might finally get started on construction, which always proceeds somewhat slowly.
In the meantime, ESA has signed agreements with three of the five American space station projects (Axiom, Starlab, Vast), with its deal with the Starlab station the most extensive. All three deals leave open the possibility that Europe will rent time at each station to fly experiments and astronauts there.
Spanish rocket startup PLD raises $209 million in new investment capital
The Spanish rocket startup PLD, which hopes to launch its orbital Miura-5 rocket this year, has now raised an additional $209 million in new investment capital, bringing the total capital it has raised to more than $400 million.
PLD Space, an international space transportation company, has closed a €180 million Series C equity funding round led by the renowned Japanese manufacturer Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, alongside with other investors.
The Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, through the Centre for the Development of Technology and Innovation (CDTI) and its INNVIERTE fund, and the Spanish public funds management company COFIDES, through its FOCO investment fund, have co-invested in this round. Ultimately, the European renowned Spanish fund Nazca Capital, via Nazca Aeroespacial y Defensa INNIVERTE I FCR Fund, close the round.
The company hopes to ramp up its launch pace to as many as 30 launches per year by 2030, though these numbers are clearly aspirational. It has already won two launch contracts, and it is building its own launchpad in French Guiana, where that first launch will take place, and has also signed a deal with Oman to launch from its proposed spaceport in Duqm. PLD has also said it is in negotiations for a third launch site, not yet named.
The Spanish rocket startup PLD, which hopes to launch its orbital Miura-5 rocket this year, has now raised an additional $209 million in new investment capital, bringing the total capital it has raised to more than $400 million.
PLD Space, an international space transportation company, has closed a €180 million Series C equity funding round led by the renowned Japanese manufacturer Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, alongside with other investors.
The Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, through the Centre for the Development of Technology and Innovation (CDTI) and its INNVIERTE fund, and the Spanish public funds management company COFIDES, through its FOCO investment fund, have co-invested in this round. Ultimately, the European renowned Spanish fund Nazca Capital, via Nazca Aeroespacial y Defensa INNIVERTE I FCR Fund, close the round.
The company hopes to ramp up its launch pace to as many as 30 launches per year by 2030, though these numbers are clearly aspirational. It has already won two launch contracts, and it is building its own launchpad in French Guiana, where that first launch will take place, and has also signed a deal with Oman to launch from its proposed spaceport in Duqm. PLD has also said it is in negotiations for a third launch site, not yet named.
Varda rents new 200K-square-foot facility in California
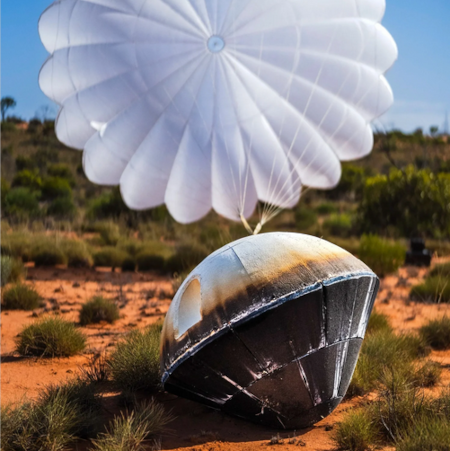

Varda’s fifth capsule after landing on January 29, 2026
The startup Varda, which launches returnable capsules for manufacturing products in space, has now rented a large building in California to build those capsules.
In an expansion of its business of processing pharmaceuticals in Earth’s orbit, Varda Space Industries is renting a large El Segundo plant where toy manufacturer Mattel used to design Hot Wheels and Barbie dolls. The plant in El Segundo’s aerospace corridor will be an extension of Varda Space Industries’ headquarters in a much smaller building on nearby Aviation Boulevard.
Varda will occupy a 205,443-square-foot industrial and office campus at 2031 E. Mariposa Ave., which will give it additional capacity to manufacture spacecraft at scale, the company said
The company will take control of the building in December, and will then need another four to eight months to install its production facilities.
Varda has launched and recovered five capsules so far. Some produced pharmaceuticals for sale on Earth, others other products, while two did hypersonic tests for the Pentagon during re-entry. It has a deal in Australia to land as many as 20 more capsules, and presently has ten more missions scheduled on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket.

Varda’s fifth capsule after landing on January 29, 2026
The startup Varda, which launches returnable capsules for manufacturing products in space, has now rented a large building in California to build those capsules.
In an expansion of its business of processing pharmaceuticals in Earth’s orbit, Varda Space Industries is renting a large El Segundo plant where toy manufacturer Mattel used to design Hot Wheels and Barbie dolls. The plant in El Segundo’s aerospace corridor will be an extension of Varda Space Industries’ headquarters in a much smaller building on nearby Aviation Boulevard.
Varda will occupy a 205,443-square-foot industrial and office campus at 2031 E. Mariposa Ave., which will give it additional capacity to manufacture spacecraft at scale, the company said
The company will take control of the building in December, and will then need another four to eight months to install its production facilities.
Varda has launched and recovered five capsules so far. Some produced pharmaceuticals for sale on Earth, others other products, while two did hypersonic tests for the Pentagon during re-entry. It has a deal in Australia to land as many as 20 more capsules, and presently has ten more missions scheduled on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket.
SpaceX launches 29 more Starlink satellites
SpaceX early this morning successfully placed another 29 Starlink satellites in orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
The first stage completed its 25th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
The 2026 launch race:
28 SpaceX
8 China
2 Rocket Lab
2 Russia
1 ULA
1 Europe (Arianespace)
Not only is SpaceX this year leading the entire world combined in total launches — as it did in both ’24 and ’25 — at the moment it has launched twice as much as the rest of the globe.
SpaceX early this morning successfully placed another 29 Starlink satellites in orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
The first stage completed its 25th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
The 2026 launch race:
28 SpaceX
8 China
2 Rocket Lab
2 Russia
1 ULA
1 Europe (Arianespace)
Not only is SpaceX this year leading the entire world combined in total launches — as it did in both ’24 and ’25 — at the moment it has launched twice as much as the rest of the globe.
Engineers locate helium flow issue on SLS upper stage
NASA last evening posted an update on the status of its SLS rocket, noting that engineers had located the seal that had caused the helium flow issue in the upper stage during unfueling after the wet dress rehearsal two weeks ago.
Engineers determined a seal in the quick disconnect, through which helium flows from the ground systems to the rocket, was obstructing the pathway. The team removed the quick disconnect, reassembled the system, and began validating the repairs to the upper stage by running a reduced flow rate of helium through the mechanism to ensure the issue was resolved. Engineers are assessing what allowed the seal to become dislodged to prevent the issue from recurring.
Though this information is somewhat vague, it strongly suggests the seal with the problem was in the upper stage, not the umbilical line that is part of the ground systems.
Before they can return the rocket to the launchpad, they need to make sure they identified the exact issue that caused the seal to not work properly. They also are replacing the batteries in the rocket’s self-destruct system as well as flight batteries in the upper stage, core stage, and two strap-on solid-fueled boosters. It also appears they are replacing another seal the oxygen feed line for the core stage.
Once this work is finished and confirmed, they will still need to roll SLS back to the launchpad and likely do another wet dress rehearsal countdown, though that rehearsal might be condensed to focus on these issues specifically.
The present launch window closes on April 6th, so the timeline is very tight. NASA management is reviewing later windows in late April as well as May and June.
Despite the major reshaping of the later missions in the Artemis program that NASA administrator Jared Isaacman announced last week, this upcoming Artemis-2 mission remains the same, a ten-mission carrying four astronauts around the Moon using an Orion capsule with a questionable heat shield and an untested life support system.
NASA last evening posted an update on the status of its SLS rocket, noting that engineers had located the seal that had caused the helium flow issue in the upper stage during unfueling after the wet dress rehearsal two weeks ago.
Engineers determined a seal in the quick disconnect, through which helium flows from the ground systems to the rocket, was obstructing the pathway. The team removed the quick disconnect, reassembled the system, and began validating the repairs to the upper stage by running a reduced flow rate of helium through the mechanism to ensure the issue was resolved. Engineers are assessing what allowed the seal to become dislodged to prevent the issue from recurring.
Though this information is somewhat vague, it strongly suggests the seal with the problem was in the upper stage, not the umbilical line that is part of the ground systems.
Before they can return the rocket to the launchpad, they need to make sure they identified the exact issue that caused the seal to not work properly. They also are replacing the batteries in the rocket’s self-destruct system as well as flight batteries in the upper stage, core stage, and two strap-on solid-fueled boosters. It also appears they are replacing another seal the oxygen feed line for the core stage.
Once this work is finished and confirmed, they will still need to roll SLS back to the launchpad and likely do another wet dress rehearsal countdown, though that rehearsal might be condensed to focus on these issues specifically.
The present launch window closes on April 6th, so the timeline is very tight. NASA management is reviewing later windows in late April as well as May and June.
Despite the major reshaping of the later missions in the Artemis program that NASA administrator Jared Isaacman announced last week, this upcoming Artemis-2 mission remains the same, a ten-mission carrying four astronauts around the Moon using an Orion capsule with a questionable heat shield and an untested life support system.
MIT – Quicker than a Wink
An evening pause: This 1940 short film won an Academy Award for best one-reel short. It provides a nice and witty demonstration of the first technology that allowed very high speed slow motion movies to be made.
Hat tip Wayne DeVette.
March 3, 2026 Quick space links
As BtB’s stringer Jay is on vacation, here are a few links I spotted that don’t deserve full posts. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- ESA develops carbon-fiber material that can self-heal
As with too many European research projects, this one is not tied to any profit-making operation, and has a somewhat leisurely schedule.
- Blue Origin buys 20 acres near Cape Canaveral for $11.5 million
It appears the company wants to accelerate its launch operation in Florida, an excellent development.
As BtB’s stringer Jay is on vacation, here are a few links I spotted that don’t deserve full posts. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- ESA develops carbon-fiber material that can self-heal
As with too many European research projects, this one is not tied to any profit-making operation, and has a somewhat leisurely schedule.
- Blue Origin buys 20 acres near Cape Canaveral for $11.5 million
It appears the company wants to accelerate its launch operation in Florida, an excellent development.
Charon’s surface, completely unlike Pluto
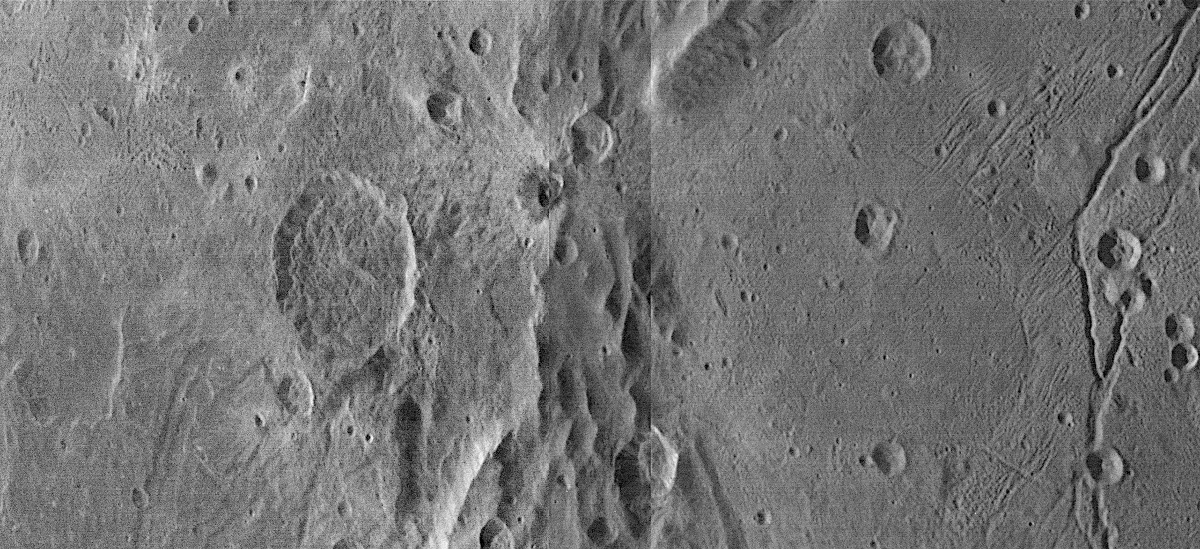

Click for full resolution. For original images go here, here, and here.

Cool image time! The panorama above, created from three images taken by New Horizons as it began its July 14, 2015 fly-by of the Pluto-Charon double planet system (found here, here, and here), show in close-up one specific swath of Charon cutting across its equatorial regions.
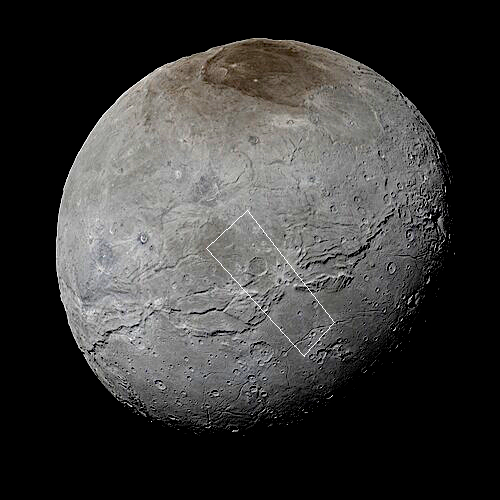
The true color global image of Charon to the right shows the approximate area covered by the panorama above. For scale, Charon has a diameter of about 750 miles, about half that of Pluto. For clarity I have rotated the panorama so that it more closely aligns with the rectangle of global image.
One of the most remarkable discoveries made during New Horizons’ fly-by was how completely different Pluto and Charon appeared, despite their likely formation together at the same time and in the same location of the early solar system. While Pluto had frozen nitrogen seas and water ice mountains floating at the shores, Charon more resembled Mercury, cratered with many large ridges and canyons criss-crossing its service. Both planets appear to be icy, but somehow Charon appears to lack the large differentiated variety of materials seen on Pluto.

Click for full resolution. For original images go here, here, and here.

Cool image time! The panorama above, created from three images taken by New Horizons as it began its July 14, 2015 fly-by of the Pluto-Charon double planet system (found here, here, and here), show in close-up one specific swath of Charon cutting across its equatorial regions.
The true color global image of Charon to the right shows the approximate area covered by the panorama above. For scale, Charon has a diameter of about 750 miles, about half that of Pluto. For clarity I have rotated the panorama so that it more closely aligns with the rectangle of global image.
One of the most remarkable discoveries made during New Horizons’ fly-by was how completely different Pluto and Charon appeared, despite their likely formation together at the same time and in the same location of the early solar system. While Pluto had frozen nitrogen seas and water ice mountains floating at the shores, Charon more resembled Mercury, cratered with many large ridges and canyons criss-crossing its service. Both planets appear to be icy, but somehow Charon appears to lack the large differentiated variety of materials seen on Pluto.
While Democrats rage against the American/Israel war on Iran, the PEOPLE celebrate
Without doubt there remain great risks and real constitutional issues involved the present military campaign by both the United States and Israel to destroy the Islamic leadership in Iran. First, it is almost impossible to force a change in power solely by air power. This has been tried numerous times, with little success. Killing the leaders of this terrorist Iranian government is a positive step, but it remains entirely unclear whether this war can produce a better government there.
Second, as much as there might be legal precedents that allow President Trump to initiate this action without direct congressional approval, it continues a dangerous trend ceding power away from Congress and to the presidency, in direct opposition to the intentions of the Founding Fathers in their writing of the Constitution. They very much were opposed to giving any president the power to start a war unilaterally.

Click here and here for original videos.
Having stated the reasonable objections to this military action, however, we must now take a look at the two images to the right to see its immediate and very positive consequences. Both pictures are from videos of very spontaneous demonstrations on February 28, 2026 by Iranian refugees celebrating the American/Israeli attacks against Iran.
The top picture is a screen capture from a demonstration in Georgetown, DC. The bottom picture is a screen capture from a demonstration in Austin, Texas.
Note the flags in both pictures. There are numerous flags of Iran (the version during the Shah’s rule, not the version from the Islamic Revolution). There are many American flags, of course, since these demonstrations are in America.
What is most revealing however are the Israeli flags, being enthusiastically waved by Iranians. Clearly the decades of hate against Israel and Jews by the mullahs in Iran has not had any impact on these Iranian refugees. In fact, in the video of the bottom picture they are chanting “Thank you, Bibi!”, referring to Israel’s leader Benjamin Netanyahu as the camera pans across the crowd.
Moreover, these demonstrations took place in two Democratic Party strongholds, cities where pro-Hamas demonstrations have been routine, including rioting and violence against Jews and anyone who dared suggest Israel’s actions in Gaza might be justified.
Nor are these two demonstrations an exception. They have been the rule across the United States and Europe, as well as in Iran itself. The public — the ordinary people for whom governments are meant to serve — seem very much in favor of what President Trump and Netanyahu are doing in Iran. And they are expressing that support of both America and Israel quite unequivocally. If this doesn’t indicate to the world that Israel and the rest of the Middle East can live together in peace and mutual cooperation, nothing can.
This conclusion is further supported by the response by almost every Arab nation in the Middle East, most of whom started off quite willing to let the U.S. and Israel do this deed, with no opposition or with covert support. Now, because of Iran’s indiscriminate attacks on Arab nations, they have all publicly joined the war, allying themselves not with the Islamic nation of Iran but with the U.S. and Israel.
I would not be surprised if Saudi Arabia soon signs the Abraham Accords. Nor would I be surprised if most of the last remaining Arab nations that have not yet done so join Saudi Arabia.
We could very well be seeing a major realignment of alliances in the Middle East that could really really harbinger the beginnings of real peace in that region. Imagine: Israel at peace with all its neighbors, because the Arabs have finally recognized that it is to their own best interest to do so as well.
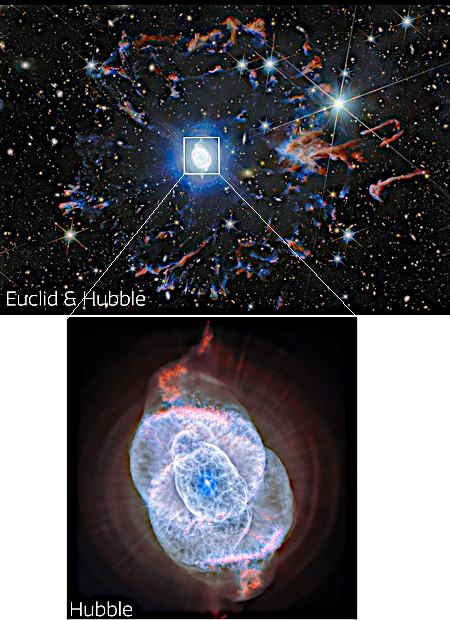
Old and new optical space telescopes team up to view the Cat’s Eye
Astronomers using both NASA’s long established Hubble Space Telescope and Europe’s new Euclid space telescope have produced new optical/infrared images of the Cat’s Eye planetary nebula.
Those images are to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here. The Hubble image at bottom shows the complex structure of the nebula itself, located about 4,400 light years away and believed created by the inner orbital motions of a binary star system that act almost like the blades in a blender, mixing the material thrown off by one or both of the stars as they erupt in their latter stages of life.
In Euclid’s wide, near-infrared, and visible light view, the arcs and filaments of the nebula’s bright central region are situated within a halo of colorful fragments of gas zooming away from the star. This ring was ejected from the star at an earlier stage, before the main nebula at the center formed. The whole nebula stands out against a backdrop teeming with distant galaxies, demonstrating how local astrophysical beauty and the farthest reaches of the cosmos can be seen together with Euclid.
Euclid has a primary mirror 1.2 meters in diameter, about half that of Hubble. Though it can’t zoom in with the same resolution, its view is as sharp since it is in space above the atmosphere. It thus provides a wider view, which in this case helps provide a larger context to the detailed close-up view provided by Hubble.
In many ways Euclid is Hubble’s replacement, produced by the European Space Agency, as NASA and the American astronomy community has not been able to get together to build their own new optical orbiting telescope.
Astronomers using both NASA’s long established Hubble Space Telescope and Europe’s new Euclid space telescope have produced new optical/infrared images of the Cat’s Eye planetary nebula.
Those images are to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here. The Hubble image at bottom shows the complex structure of the nebula itself, located about 4,400 light years away and believed created by the inner orbital motions of a binary star system that act almost like the blades in a blender, mixing the material thrown off by one or both of the stars as they erupt in their latter stages of life.
In Euclid’s wide, near-infrared, and visible light view, the arcs and filaments of the nebula’s bright central region are situated within a halo of colorful fragments of gas zooming away from the star. This ring was ejected from the star at an earlier stage, before the main nebula at the center formed. The whole nebula stands out against a backdrop teeming with distant galaxies, demonstrating how local astrophysical beauty and the farthest reaches of the cosmos can be seen together with Euclid.
Euclid has a primary mirror 1.2 meters in diameter, about half that of Hubble. Though it can’t zoom in with the same resolution, its view is as sharp since it is in space above the atmosphere. It thus provides a wider view, which in this case helps provide a larger context to the detailed close-up view provided by Hubble.
In many ways Euclid is Hubble’s replacement, produced by the European Space Agency, as NASA and the American astronomy community has not been able to get together to build their own new optical orbiting telescope.
Japan to do vertical tests of its own Grasshopper-type demo stage this month
Japan’s space agency is about to attempt two test vertical take-off-and-landing test flights of of its own Grasshopper-type demo stage, dubbed RV-X later this month.
First flight of a small experimental version of a reusable launch vehicle has been scheduled for March 6 by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The 24-ft.-tall vertical-takeoff-and-vertical-landing (VTVL) RV-X is planned to make a short hop at the agency’s Noshiro Rocket Testing Center on the Sea of Japan coast.
RV-X is the first of two flight experiments planned by JAXA on the path to development of a reusable first stage for a next-generation launch vehicle. A second vehicle is planned to fly in 2027 under the multinational Callisto program.
Callisto is being developed jointly with the European Space Agency. Both it and RV-X have been in development for about a decade. Both were initiated in response to SpaceX’s successful reuse of its Falcon 9 first stage. Both projects however appeared stalled until the last two years or so, with little happening.
The JAXA engine on RV-X is apparently the engine it is providing for Callisto. If the flight tests are successful this March, it will be the be transferred to French Guiana for Callisto tests planned no sooner than ’27.
Japan’s space agency is about to attempt two test vertical take-off-and-landing test flights of of its own Grasshopper-type demo stage, dubbed RV-X later this month.
First flight of a small experimental version of a reusable launch vehicle has been scheduled for March 6 by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The 24-ft.-tall vertical-takeoff-and-vertical-landing (VTVL) RV-X is planned to make a short hop at the agency’s Noshiro Rocket Testing Center on the Sea of Japan coast.
RV-X is the first of two flight experiments planned by JAXA on the path to development of a reusable first stage for a next-generation launch vehicle. A second vehicle is planned to fly in 2027 under the multinational Callisto program.
Callisto is being developed jointly with the European Space Agency. Both it and RV-X have been in development for about a decade. Both were initiated in response to SpaceX’s successful reuse of its Falcon 9 first stage. Both projects however appeared stalled until the last two years or so, with little happening.
The JAXA engine on RV-X is apparently the engine it is providing for Callisto. If the flight tests are successful this March, it will be the be transferred to French Guiana for Callisto tests planned no sooner than ’27.
Russia completes repairs to Soyuz-2 launchpad at Baikonur
According to Roscosmos, it has completed the repairs to Soyuz-2 launchpad at Baikonur, and will do launch a Progress freighter to ISS on March 22, 2026.
According to the State Corporation, a total of 150 workers from four contractor organizations prepared and painted 2,350 square meters of structures, replaced all the attachment devices, replaced and tuned up electric equipment and inspected or serviced all the systems and mechanisms of the service platform. The team also made 250 welding lines.
The most complex task was the installation of the platform elements, some of which had a length of 19 meters and mass of 17 tons, which required a development of special methodic, Roskosmos said.
The State Corporation confirmed that the first mission departing from the repaired launch pad at Site 31 was scheduled for March 22, 2026, carrying the Progress MS-33 cargo ship to the ISS.
For Russia, this repair was completed remarkably fast. But then, the Russians generally get things done fast when it is absolutely essential to do so. Without that pad, Russia had no way to launch any astronauts in space. Nor could it send supplies to ISS. A delay would have been very public and embarrassing.
If there is no immediate need, however, its projects drag on endlessly.
According to Roscosmos, it has completed the repairs to Soyuz-2 launchpad at Baikonur, and will do launch a Progress freighter to ISS on March 22, 2026.
According to the State Corporation, a total of 150 workers from four contractor organizations prepared and painted 2,350 square meters of structures, replaced all the attachment devices, replaced and tuned up electric equipment and inspected or serviced all the systems and mechanisms of the service platform. The team also made 250 welding lines.
The most complex task was the installation of the platform elements, some of which had a length of 19 meters and mass of 17 tons, which required a development of special methodic, Roskosmos said.
The State Corporation confirmed that the first mission departing from the repaired launch pad at Site 31 was scheduled for March 22, 2026, carrying the Progress MS-33 cargo ship to the ISS.
For Russia, this repair was completed remarkably fast. But then, the Russians generally get things done fast when it is absolutely essential to do so. Without that pad, Russia had no way to launch any astronauts in space. Nor could it send supplies to ISS. A delay would have been very public and embarrassing.
If there is no immediate need, however, its projects drag on endlessly.
Glen Campbell – Galveston
March 2, 2026 Quick space links
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay, who is off on a two week vacation, so no quick links for awhile. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Video of Iranian ballistic missile being destroyed by American technology in the stratosphere, mid-arc, outside Earth’s atmosphere
It is amazing how effective the U.S. military has suddenly become, simply because it now has good and firm leadership focused on defeating tyrants.
- On this day in 2002, the fourth servicing mission to Hubble was launched
Astronauts installed the Advanced Camera for Surveys, improving its imaging capability 10-fold. The camera is still working, almost a quarter of a century later.
- On this day in 2007, New Horizons captured a 200-mile-high plume erupting on Jupiter’s moon Io
The spacecraft was on its long journey to Pluto, using Jupiter to slingshot it on its way.
Courtesy of BtB’s stringer Jay, who is off on a two week vacation, so no quick links for awhile. This post is also an open thread. I welcome my readers to post any comments or additional links relating to any space issues, even if unrelated to the links below.
- Video of Iranian ballistic missile being destroyed by American technology in the stratosphere, mid-arc, outside Earth’s atmosphere
It is amazing how effective the U.S. military has suddenly become, simply because it now has good and firm leadership focused on defeating tyrants.
- On this day in 2002, the fourth servicing mission to Hubble was launched
Astronauts installed the Advanced Camera for Surveys, improving its imaging capability 10-fold. The camera is still working, almost a quarter of a century later.
- On this day in 2007, New Horizons captured a 200-mile-high plume erupting on Jupiter’s moon Io
The spacecraft was on its long journey to Pluto, using Jupiter to slingshot it on its way.
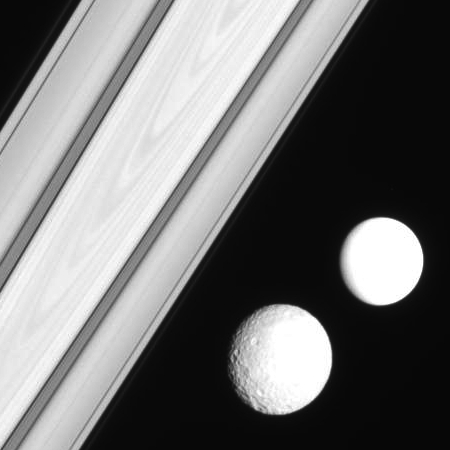
Two moons of Saturn against its majestic rings
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and enhanced to post here, was taken on December 23, 2005 by Cassini as it orbited Saturn.
The larger cratered moon is Mimas, known best for the single giant crater that dominates one hemisphere. I have not been able to identify the brighter but smaller moon.
Note the pattern within the largest bright central ring in the background. It is possible this is an optical illusion, but it is also possible this pattern is inherent in the ring itself. Other images show similar patterns that scientists have concluded were real.
This image was part of a set of eight images all taken in the space of less than two minutes, as the smaller moon moved from the lower left to the upper right and was eclipsed by Minas as it did so. Below are four of those pictures, showing the sequence.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and enhanced to post here, was taken on December 23, 2005 by Cassini as it orbited Saturn.
The larger cratered moon is Mimas, known best for the single giant crater that dominates one hemisphere. I have not been able to identify the brighter but smaller moon.
Note the pattern within the largest bright central ring in the background. It is possible this is an optical illusion, but it is also possible this pattern is inherent in the ring itself. Other images show similar patterns that scientists have concluded were real.
This image was part of a set of eight images all taken in the space of less than two minutes, as the smaller moon moved from the lower left to the upper right and was eclipsed by Minas as it did so. Below are four of those pictures, showing the sequence.
» Read more
Sunspot update: Sunspot activity tumbles in February, including the 1st blank days since ’22
The uncertainty of science! It is the start of the month, and thus time for another sunspot update, using NOAA’s monthly graph of the sunspot activity on the Earth-facing hemisphere, updated by NOAA to include the activity in February but annotated with extra information by me to illustrate the larger scientific context.
Last month I lambasted NOAA’s solar science panel for its consistently failed predictions, and made a tentative prediction of my own, suggesting the ramp down to solar minimum might not be occurring as they had predicted in April 2025.
This month I can lambast myself, because the Sun in February saw a significant drop in sunspots, including three consecutive days in which the Sun was blank of spots, for the first time since 2022. This drop supports the NOAA panel prediction and makes my prediction look foolish, but it also suggests the ramp down is continuing to go faster than predicted.
» Read more
Indian rocket startup Agnikul completes static fire test of three-engine cluster
The Indian rocket startup Agnikul has now released a video of a 40-second static fire test of three-engine cluster it hopes to use on its Agnibaan orbital rocket.
The engines, powered by electric motor-driven pumps, were designed and manufactured in-house at Agnikul’s Rocket Factory-1. All three were fully 3D-printed as single-piece hardware units, reflecting the startup’s focus on advanced manufacturing and indigenous engineering.
Co-founder and chief executive Srinath Ravichandran said that increasing the number of engines improves rocket performance and that a three-engine system is required for commercial missions. The clustered test involved calibrating six pumps and six motors and fine-tuning six independent speed control algorithms to function in synchronisation. The goal was to achieve uniform startup, steady-state operation and shutdown performance across all three engines, a technically complex process given the precision required in semi-cryogenic propulsion systems.
The company has completed one suborbital test launch in May 2024, and in September 2025 said its orbital rocket’s first stage will land vertically and be reused.
Agnikul however has not released any schedule for launch, and based on this static fire test appears years from a first launch. It is making progress, but slowly. At the same time, it says it has raised $500 million in private investment capital, giving it the resources to build the rocket.
Based on testing and published progress, Agnikul appears to be trailing India’s other rocket startup Skyroot, though this could change in the coming year.
The Indian rocket startup Agnikul has now released a video of a 40-second static fire test of three-engine cluster it hopes to use on its Agnibaan orbital rocket.
The engines, powered by electric motor-driven pumps, were designed and manufactured in-house at Agnikul’s Rocket Factory-1. All three were fully 3D-printed as single-piece hardware units, reflecting the startup’s focus on advanced manufacturing and indigenous engineering.
Co-founder and chief executive Srinath Ravichandran said that increasing the number of engines improves rocket performance and that a three-engine system is required for commercial missions. The clustered test involved calibrating six pumps and six motors and fine-tuning six independent speed control algorithms to function in synchronisation. The goal was to achieve uniform startup, steady-state operation and shutdown performance across all three engines, a technically complex process given the precision required in semi-cryogenic propulsion systems.
The company has completed one suborbital test launch in May 2024, and in September 2025 said its orbital rocket’s first stage will land vertically and be reused.
Agnikul however has not released any schedule for launch, and based on this static fire test appears years from a first launch. It is making progress, but slowly. At the same time, it says it has raised $500 million in private investment capital, giving it the resources to build the rocket.
Based on testing and published progress, Agnikul appears to be trailing India’s other rocket startup Skyroot, though this could change in the coming year.
Rocket Lab completes in-space commissioning of two Escapade Mars orbiters
Built by Rocket Lab for NASA and launched in November 2025, the company has now completed the in-space commissioning of two Escapade Mars orbiters and is about to hand operations over to the University of California Berkeley Space Sciences Laboratory (UC-Berkeley).
With both spacecraft now fully commissioned and successfully operating at the Earth–Sun Lagrange Point 2 (L2), Rocket Lab is preparing to hand over operational control to [UC-Berkeley], who will lead science operations at L2 and prepare the mission for its cruise to Mars.
Under contract from [UC-Berkeley], Rocket Lab was selected to design, build, and provide commissioning operations of the two high delta-V Explorer-class interplanetary spacecraft for ESCAPADE. Rocket Lab moved from concept to launch readiness in just over three years, proving commercial collaboration can deliver important science key to supporting future human and robotic exploration of Mars on ambitious schedules and for significantly smaller budgets than typical interplanetary missions. This speed was made possible through Rocket Lab’s vertically integrated spacecraft production, with key components including solar arrays, reaction wheels, propellant tanks, star trackers, radios, avionics, and flight software designed and built in-house.
Launched from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in November 2025, the twin ESCAPADE spacecraft, known as Blue and Gold, completed spacecraft commissioning and executed two precise trajectory correction maneuvers, placing both spacecraft into their loiter trajectory near L2, approximately 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
Both spacecraft will be sent on their way to Mars in December 2026 when orbital mechanics between the Red Planet and Earth are right for the journey. Once in Mars orbit the two orbiters will allow for a three-dimensional study of the interaction between the solar wind and Mars’ atmosphere.
Though this is a NASA-funded mission, note that it was built a commercial company and operated not by NASA but by a university. For this reason, it was not only built fast and at a low cost, it uses an innovative flight path that allowed it to be launched anytime and wait in orbit for the right moment to go to Mars. This last innovation provides for a lot more flexibility.
Built by Rocket Lab for NASA and launched in November 2025, the company has now completed the in-space commissioning of two Escapade Mars orbiters and is about to hand operations over to the University of California Berkeley Space Sciences Laboratory (UC-Berkeley).
With both spacecraft now fully commissioned and successfully operating at the Earth–Sun Lagrange Point 2 (L2), Rocket Lab is preparing to hand over operational control to [UC-Berkeley], who will lead science operations at L2 and prepare the mission for its cruise to Mars.
Under contract from [UC-Berkeley], Rocket Lab was selected to design, build, and provide commissioning operations of the two high delta-V Explorer-class interplanetary spacecraft for ESCAPADE. Rocket Lab moved from concept to launch readiness in just over three years, proving commercial collaboration can deliver important science key to supporting future human and robotic exploration of Mars on ambitious schedules and for significantly smaller budgets than typical interplanetary missions. This speed was made possible through Rocket Lab’s vertically integrated spacecraft production, with key components including solar arrays, reaction wheels, propellant tanks, star trackers, radios, avionics, and flight software designed and built in-house.
Launched from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in November 2025, the twin ESCAPADE spacecraft, known as Blue and Gold, completed spacecraft commissioning and executed two precise trajectory correction maneuvers, placing both spacecraft into their loiter trajectory near L2, approximately 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
Both spacecraft will be sent on their way to Mars in December 2026 when orbital mechanics between the Red Planet and Earth are right for the journey. Once in Mars orbit the two orbiters will allow for a three-dimensional study of the interaction between the solar wind and Mars’ atmosphere.
Though this is a NASA-funded mission, note that it was built a commercial company and operated not by NASA but by a university. For this reason, it was not only built fast and at a low cost, it uses an innovative flight path that allowed it to be launched anytime and wait in orbit for the right moment to go to Mars. This last innovation provides for a lot more flexibility.
SpaceX completes its second Starlink launch today; Firefly scrubs launch
SpaceX successfully placed another 29 Starlink satellites in orbit this evening during its second launch today, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
The first stage completed its 26th launch, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
Firefly meanwhile scrubbed its launch of its Alpha rocket due to high winds. No new launch date as yet been scheduled. This would be Firefly’s first launch since it had a launch failure in April 2025, followed by a static fire test explosion in September 2025. According to the company, this Alpha launch will be the last of this version before it begins flying an upgraded rocket.
The 2026 launch race:
27 SpaceX
8 China
2 Rocket Lab
2 Russia
1 ULA
1 Europe (Arianespace)
As it did in both ’24 and ’25, SpaceX in ’26 so far has more launches than the entire rest of the world combined.
SpaceX successfully placed another 29 Starlink satellites in orbit this evening during its second launch today, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
The first stage completed its 26th launch, landing on a drone ship in the Atlantic.
Firefly meanwhile scrubbed its launch of its Alpha rocket due to high winds. No new launch date as yet been scheduled. This would be Firefly’s first launch since it had a launch failure in April 2025, followed by a static fire test explosion in September 2025. According to the company, this Alpha launch will be the last of this version before it begins flying an upgraded rocket.
The 2026 launch race:
27 SpaceX
8 China
2 Rocket Lab
2 Russia
1 ULA
1 Europe (Arianespace)
As it did in both ’24 and ’25, SpaceX in ’26 so far has more launches than the entire rest of the world combined.
SpaceX launches 25 more Starlink satellites
SpaceX early this morning successfully placed another 25 Starlink satellites in orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
The first stage completed its 20th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific.
The 2026 launch race:
26 SpaceX
8 China
2 Rocket Lab
2 Russia
1 ULA
1 Europe (Arianespace)
As it did in both ’24 and ’25, SpaceX in ’26 so far has more launches than the entire rest of the world combined.
Both SpaceX and Firefly have launches scheduled for later today. The Japanese rocket startup Space One has now rescheduled the third launch attempt of its Kairos rocket for March 3, 2026.
SpaceX early this morning successfully placed another 25 Starlink satellites in orbit, its Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
The first stage completed its 20th flight, landing on a drone ship in the Pacific.
The 2026 launch race:
26 SpaceX
8 China
2 Rocket Lab
2 Russia
1 ULA
1 Europe (Arianespace)
As it did in both ’24 and ’25, SpaceX in ’26 so far has more launches than the entire rest of the world combined.
Both SpaceX and Firefly have launches scheduled for later today. The Japanese rocket startup Space One has now rescheduled the third launch attempt of its Kairos rocket for March 3, 2026.
Cargo Dragon successfully returns to Earth
A cargo Dragon capsule successfully splashed down in the Pacific late Thursday, February 26, 2026, bringing back several thousand pounds of hardware and experiments.
The ship had been docked at ISS for the past six months, during which it used its engines six different times to raise the station’s orbit. That capability has traditionally been done by Russian Progress freighters, but NASA has been testing other options as they are unsure Russia will remain with the station after 2028. Furthermore, there are risks using Progress to do these reboosts, as the burns take place when Progress is docked to its Zvezda module port, and the hull of the Zvezda module has been developing stress fractures in the past five years that could catastrophically fail.
Not only has Dragon now demonstrated this boost capability, so has Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus capsule.
I strongly expect Russia to stick with ISS for as long as it can, mainly because its own proposed new space station is not likely to launch as presently scheduled later this decade. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, Roscosmos has consistently been unable to complete almost any new proposed projects, and the few it has completed launched literally decades late.
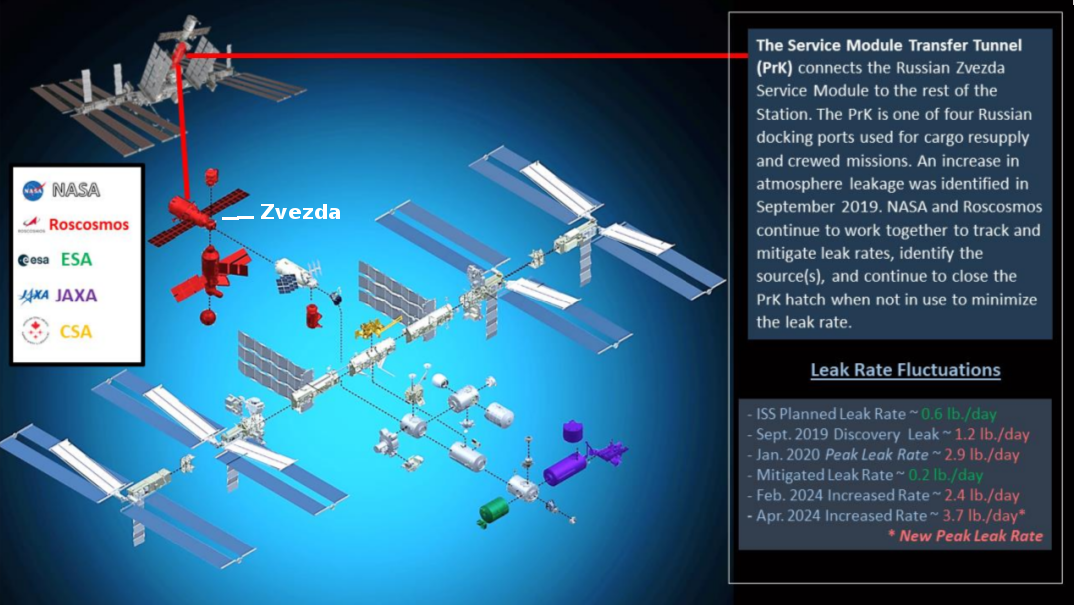
Figure 3 from September 2024 Inspector General report, showing Zvezda’s location on ISS, as well as the station’s leak rate at that time. The leaks in Zvezda now appear to have been sealed, but there is no guarantee more stress fractures will not appear as dockings continue at its port.
A cargo Dragon capsule successfully splashed down in the Pacific late Thursday, February 26, 2026, bringing back several thousand pounds of hardware and experiments.
The ship had been docked at ISS for the past six months, during which it used its engines six different times to raise the station’s orbit. That capability has traditionally been done by Russian Progress freighters, but NASA has been testing other options as they are unsure Russia will remain with the station after 2028. Furthermore, there are risks using Progress to do these reboosts, as the burns take place when Progress is docked to its Zvezda module port, and the hull of the Zvezda module has been developing stress fractures in the past five years that could catastrophically fail.
Not only has Dragon now demonstrated this boost capability, so has Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus capsule.
I strongly expect Russia to stick with ISS for as long as it can, mainly because its own proposed new space station is not likely to launch as presently scheduled later this decade. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, Roscosmos has consistently been unable to complete almost any new proposed projects, and the few it has completed launched literally decades late.

Figure 3 from September 2024 Inspector General report, showing Zvezda’s location on ISS, as well as the station’s leak rate at that time. The leaks in Zvezda now appear to have been sealed, but there is no guarantee more stress fractures will not appear as dockings continue at its port.
Rocket Lab completes another HASTE suborbital mission
Rocket Lab late yesterday successfully completed its seven HASTE suborbital mission, using the first stage of its Electron rocket to do a hypersonic test mission for the War Department.
In this case, the test vehicle was from the Australian company Hypersonix, and it lifted off from Rocket Lab’s Electron launchpad at Wallops Island in Virginia.
This was Rocket Lab’s second flight for this particular military agency in the past three months, and its eleventh overall launch from Wallops Island. The company’s quick reconfiguration of Electron for hypersonic suborbital testing made it possible for it to capture a bulk of the military’s suborbital hypersonic testing business that others, such as Stratolaunch, had hoped to win.
Rocket Lab late yesterday successfully completed its seven HASTE suborbital mission, using the first stage of its Electron rocket to do a hypersonic test mission for the War Department.
In this case, the test vehicle was from the Australian company Hypersonix, and it lifted off from Rocket Lab’s Electron launchpad at Wallops Island in Virginia.
This was Rocket Lab’s second flight for this particular military agency in the past three months, and its eleventh overall launch from Wallops Island. The company’s quick reconfiguration of Electron for hypersonic suborbital testing made it possible for it to capture a bulk of the military’s suborbital hypersonic testing business that others, such as Stratolaunch, had hoped to win.
February 27, 2026 Zimmerman/Batchelor podcast
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more
Embedded below the fold in two parts.
To listen to all of John Batchelor’s podcasts, go here.
» Read more