ISS study suggests that weightlessness impacts the eyes of men more than women
Astronauts who experienced changes in their
eyes (SANS) while on long missions in space
The uncertainty of science: A recent study of 30 astronauts during long term stays on ISS suggests that weightlessness impacts the shape of the eyes more in men than in women.
You can read the paper here.
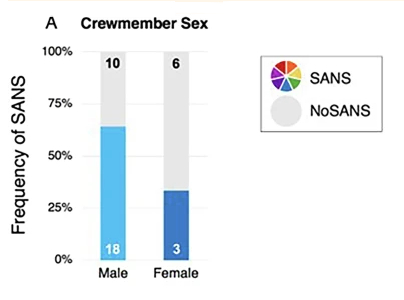
In addition to changes in fluid around the brain, the team also found that a form of eye compression, a hallmark of Spaceflight Associated Neuro-ocular Syndrome known as globe flattening, was the most consistent eye change among crew members. “By far the most prevalent sign of eye changes that we observed was globe flattening, suggesting that this should be the primary monitoring target for ocular health,” Seidler said. “Interestingly, eye changes were more prevalent in males than females.”
Globe flattening, when the back of the eyeball becomes slightly indented or pushed inward, might sound minor, but it can have significant effects on vision and raise concerns for long-duration space missions.
Surprisingly, there was no strong link between brain structural changes and eye changes, suggesting that the effects on the eyes and brain may arise from distinct mechanisms rather than shared physiological cause
For the eye research, the sample was so small, 28 individuals of which only 9 were females, the researchers readily admit in their abstract that and “interpretation of these findings should be tempered by the fact that our sample included a relatively small number of females.” Nonetheless, the research did suggest that, regardless of sex, about half of all humans will experience these eye issues during long missions in weightlessness.
The results underscore the need to do artificial gravity experiments in orbit, to find out the minimum amount of gravity needed to mitigate or even eliminate these health issues. Otherwise, interplanetary travel is going to be seriously hampered, if not impossible.

Astronauts who experienced changes in their
eyes (SANS) while on long missions in space
The uncertainty of science: A recent study of 30 astronauts during long term stays on ISS suggests that weightlessness impacts the shape of the eyes more in men than in women.
You can read the paper here.
In addition to changes in fluid around the brain, the team also found that a form of eye compression, a hallmark of Spaceflight Associated Neuro-ocular Syndrome known as globe flattening, was the most consistent eye change among crew members. “By far the most prevalent sign of eye changes that we observed was globe flattening, suggesting that this should be the primary monitoring target for ocular health,” Seidler said. “Interestingly, eye changes were more prevalent in males than females.”
Globe flattening, when the back of the eyeball becomes slightly indented or pushed inward, might sound minor, but it can have significant effects on vision and raise concerns for long-duration space missions.
Surprisingly, there was no strong link between brain structural changes and eye changes, suggesting that the effects on the eyes and brain may arise from distinct mechanisms rather than shared physiological cause
For the eye research, the sample was so small, 28 individuals of which only 9 were females, the researchers readily admit in their abstract that and “interpretation of these findings should be tempered by the fact that our sample included a relatively small number of females.” Nonetheless, the research did suggest that, regardless of sex, about half of all humans will experience these eye issues during long missions in weightlessness.
The results underscore the need to do artificial gravity experiments in orbit, to find out the minimum amount of gravity needed to mitigate or even eliminate these health issues. Otherwise, interplanetary travel is going to be seriously hampered, if not impossible.