Chinese astronauts provide their perspective on the cracked Shenzhou-20 window
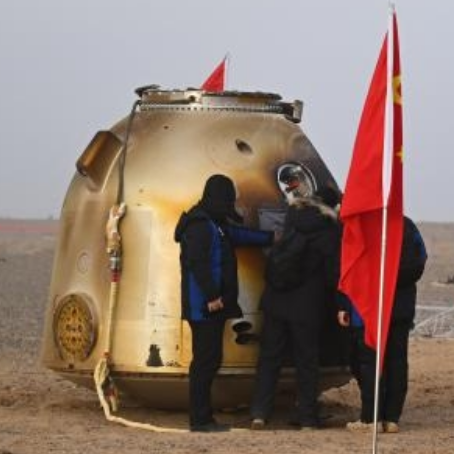

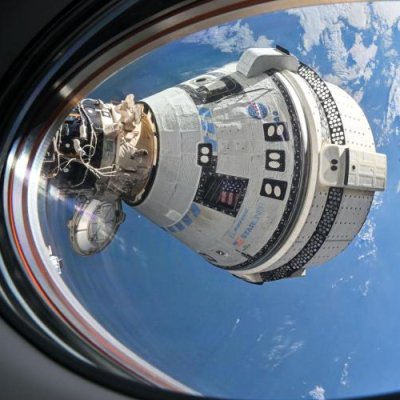
Shenzhou-20 after its return to Earth. The damaged
window can be seen on the right. Click for original image.
The Chinese Shenzhou-20 crew this week gave a detailed interview describing their discovery and inspection of the cracks in the window of their Shenzhou-20 capsule.
Chen Dong, commander of the Shenzhou-20 crew, first noticed the damage to the window while conducting final checks on the return capsule. The believed culprit: space debris striking the window. …As mission commander for Shenzhou-20, Chen said he was the one who went for checking out the return craft. During that work, “I spotted something like a triangular on the viewport,” he said. “My first thought was whether a small leaf had somehow stuck to the outside of the window,” said Chen. “But then I quickly realized that couldn’t happen because we were in space. How could there possibly be a fallen leaf there?”
Chen pointed out the window anomaly to his two other colleagues also in ready mode for the return trek to Earth. Wang, who served as the flight engineer on the Shenzhou-20 mission, had previously worked as an aerospace technician involved in the construction of China’s space station before becoming an astronaut. “I wasn’t really nervous, actually. The outermost layer of the viewport is a protective layer, and inside it there are two pressure-bearing layers, and we are safe as long as the cabin pressure doesn’t change,” said Wang.
Using a 40x microscope, they determined that some of the cracks had penetrated through the window’s outermost layer.
As of today however China has yet to release images of the cracks, or if they have, no western media source has found and released them.

Shenzhou-20 after its return to Earth. The damaged
window can be seen on the right. Click for original image.
The Chinese Shenzhou-20 crew this week gave a detailed interview describing their discovery and inspection of the cracks in the window of their Shenzhou-20 capsule.
Chen Dong, commander of the Shenzhou-20 crew, first noticed the damage to the window while conducting final checks on the return capsule. The believed culprit: space debris striking the window. …As mission commander for Shenzhou-20, Chen said he was the one who went for checking out the return craft. During that work, “I spotted something like a triangular on the viewport,” he said. “My first thought was whether a small leaf had somehow stuck to the outside of the window,” said Chen. “But then I quickly realized that couldn’t happen because we were in space. How could there possibly be a fallen leaf there?”
Chen pointed out the window anomaly to his two other colleagues also in ready mode for the return trek to Earth. Wang, who served as the flight engineer on the Shenzhou-20 mission, had previously worked as an aerospace technician involved in the construction of China’s space station before becoming an astronaut. “I wasn’t really nervous, actually. The outermost layer of the viewport is a protective layer, and inside it there are two pressure-bearing layers, and we are safe as long as the cabin pressure doesn’t change,” said Wang.
Using a 40x microscope, they determined that some of the cracks had penetrated through the window’s outermost layer.
As of today however China has yet to release images of the cracks, or if they have, no western media source has found and released them.