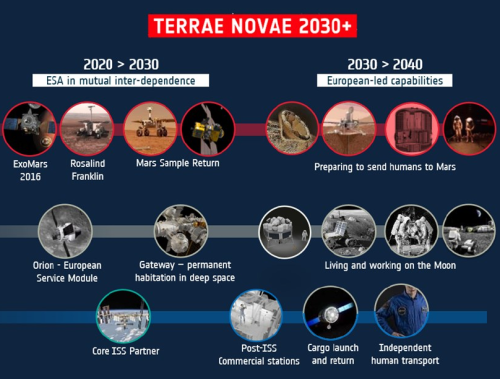
Chinese university tests hypersonic space plane

According to social media reports, a Chinese university, Northwestern Polytechnical University (NPU), successfully tested on July 4, 2022 a prototype hypersonic prototype that uses both rocket and scramjet engines, as explained at this report:
What is particularly interesting about the launch of Feitian-1 is that it uses an RBCC [Rocket-Based Combined Cycle] engine to propel it to speeds in excess of Mach 5. An RBCC engine is a combination of an air-breathing ramjet, air-breathing scramjet, and ducted rocket. As the vehicle accelerates, the engine transfers from one mode to the next, allowing it to cope with air hitting the intake at greater and greater speed, and then becoming a pure rocket at top speed and very high altitudes.
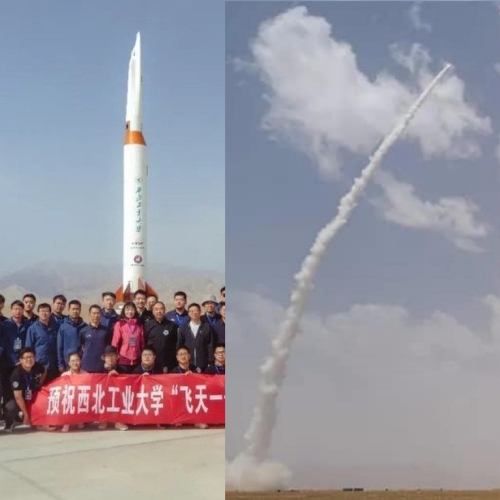
The two images shown above are an attempt to get a sense of scale for this rocket. I think it is smaller than the Chinese wish us to believe, probably less than fifty feet tall, as stacked. Note the buildings in the right image. Other images showed no tower or strongback, also suggesting a small rocket. Moreover, all the released images hide the base of the rocket, suggesting there are attachments there the Chinese do not wish us to see, probably fuel and communications lines, all of which would help determine scale.
Finally, the upper stage, which I estimate to be no more than fifteen feet long, is purposely photographed from the side to hide its likely spaceplane appearance. This spaceplane look suggests this particular engineering research is at least superficially commercial and not military, connected more with the effort in China to develop hypersonic planes. That the Chinese government allowed this much information to be released also tells us that this particular prototype is not specifically military in nature.
This is not to say that the technology will not be adapted for military use. It certainly will be. NPU and its Institute of Spaceplanes and Hypersonic Technologies is also sanctioned by the U.S. government because of its ties to China’s military.
The US sanctions list frequently includes Northwestern Polytechnical University among the sanctioned entities from China. The University’s staff and students are not allowed to purchase or use commodities made in the US, including mathematical software.
Despite being a space plane test of the small prototype hypersonic rocket, this is the first reliable report from China that I have seen of such a suborbital test. Previous reports, despite being heavily touted by the U.S. military and accepted without question by the mainstream press, were unconfirmed and appeared untrustworthy. This report, showing proof of a suborbital test of what looks like a smaller scaled prototype I think gives us a more accurate picture of China’s present capabilities in this technology. They are moving fast, but are not there yet.

According to social media reports, a Chinese university, Northwestern Polytechnical University (NPU), successfully tested on July 4, 2022 a prototype hypersonic prototype that uses both rocket and scramjet engines, as explained at this report:
What is particularly interesting about the launch of Feitian-1 is that it uses an RBCC [Rocket-Based Combined Cycle] engine to propel it to speeds in excess of Mach 5. An RBCC engine is a combination of an air-breathing ramjet, air-breathing scramjet, and ducted rocket. As the vehicle accelerates, the engine transfers from one mode to the next, allowing it to cope with air hitting the intake at greater and greater speed, and then becoming a pure rocket at top speed and very high altitudes.
The two images shown above are an attempt to get a sense of scale for this rocket. I think it is smaller than the Chinese wish us to believe, probably less than fifty feet tall, as stacked. Note the buildings in the right image. Other images showed no tower or strongback, also suggesting a small rocket. Moreover, all the released images hide the base of the rocket, suggesting there are attachments there the Chinese do not wish us to see, probably fuel and communications lines, all of which would help determine scale.
Finally, the upper stage, which I estimate to be no more than fifteen feet long, is purposely photographed from the side to hide its likely spaceplane appearance. This spaceplane look suggests this particular engineering research is at least superficially commercial and not military, connected more with the effort in China to develop hypersonic planes. That the Chinese government allowed this much information to be released also tells us that this particular prototype is not specifically military in nature.
This is not to say that the technology will not be adapted for military use. It certainly will be. NPU and its Institute of Spaceplanes and Hypersonic Technologies is also sanctioned by the U.S. government because of its ties to China’s military.
The US sanctions list frequently includes Northwestern Polytechnical University among the sanctioned entities from China. The University’s staff and students are not allowed to purchase or use commodities made in the US, including mathematical software.
Despite being a space plane test of the small prototype hypersonic rocket, this is the first reliable report from China that I have seen of such a suborbital test. Previous reports, despite being heavily touted by the U.S. military and accepted without question by the mainstream press, were unconfirmed and appeared untrustworthy. This report, showing proof of a suborbital test of what looks like a smaller scaled prototype I think gives us a more accurate picture of China’s present capabilities in this technology. They are moving fast, but are not there yet.