A slew of propaganda today from China’s state-run press attempts to hide the delays in its manned lunar program
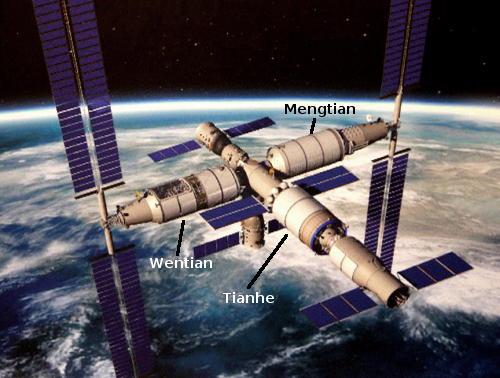
The Tiangong-3 station, as presently configured
Generally China’s state-run news agency Xinhua posts no more than one to two short space-related articles per day, with most confined to simply announcing the launch of a rocket.
Today however that state-run agency posted a dozen short articles, linked it appeared to the two press conferences held in connection with tomorrow’s launch of a new crew to China’s Tiangong-3 space station.
- China to launch Shenzhou-21 crewed spaceship on Oct. 31
- Astronauts of China’s Shenzhou-21 mission meet press
- China discloses new space mission tasks, highlighting mice experiment
- New extravehicular spacesuits offer astronauts greater comfort, convenience: official
- Hong Kong, Macao astronauts in good health after completing rigorous training
- Pakistani astronaut to enter Chinese space station as payload specialist
- China targets manned moon landing by 2030, outlines testing tasks ahead
The list above is not complete, leaving out a few other short propaganda pieces. Some of these stories — such as those directly related to that new crew launch tomorrow — could have easily been folded into one report. They were not, however, in order to create a large number of separate reports, which in turn hides the fact that there is only one news outlet reporting anything from those two press conferences.
Out of this plethora of stories, two news items stand out however. One, China has now agreed to fly a Pakistani to Tiangong-3. Negotiations for that mission began in 2018. Training has now finally begun. China is also moving forward on flying astronauts from Hong Kong and Macao, two places formally run by western powers that China now controls, quite oppressively. Like the Soviet Union, it is using its space program for propaganda stunts to distract those regions from its iron rule.
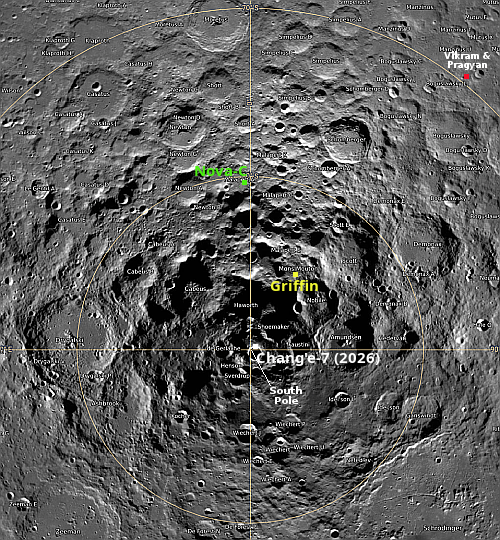
Second and more important, Chinese officials claim their program to do a manned lunar landing is still on schedule for a 2030 launch.
» Read more

The Tiangong-3 station, as presently configured
Generally China’s state-run news agency Xinhua posts no more than one to two short space-related articles per day, with most confined to simply announcing the launch of a rocket.
Today however that state-run agency posted a dozen short articles, linked it appeared to the two press conferences held in connection with tomorrow’s launch of a new crew to China’s Tiangong-3 space station.
- China to launch Shenzhou-21 crewed spaceship on Oct. 31
- Astronauts of China’s Shenzhou-21 mission meet press
- China discloses new space mission tasks, highlighting mice experiment
- New extravehicular spacesuits offer astronauts greater comfort, convenience: official
- Hong Kong, Macao astronauts in good health after completing rigorous training
- Pakistani astronaut to enter Chinese space station as payload specialist
- China targets manned moon landing by 2030, outlines testing tasks ahead
The list above is not complete, leaving out a few other short propaganda pieces. Some of these stories — such as those directly related to that new crew launch tomorrow — could have easily been folded into one report. They were not, however, in order to create a large number of separate reports, which in turn hides the fact that there is only one news outlet reporting anything from those two press conferences.
Out of this plethora of stories, two news items stand out however. One, China has now agreed to fly a Pakistani to Tiangong-3. Negotiations for that mission began in 2018. Training has now finally begun. China is also moving forward on flying astronauts from Hong Kong and Macao, two places formally run by western powers that China now controls, quite oppressively. Like the Soviet Union, it is using its space program for propaganda stunts to distract those regions from its iron rule.
Second and more important, Chinese officials claim their program to do a manned lunar landing is still on schedule for a 2030 launch.
» Read more