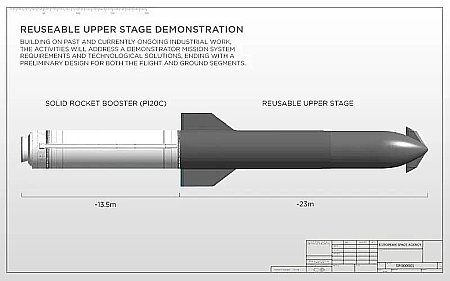
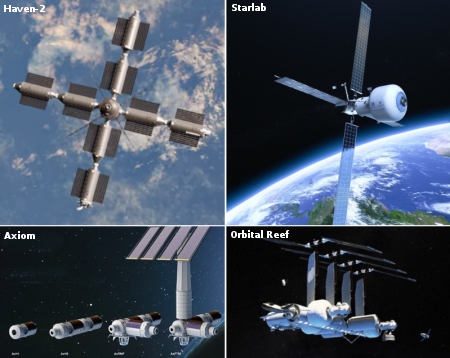
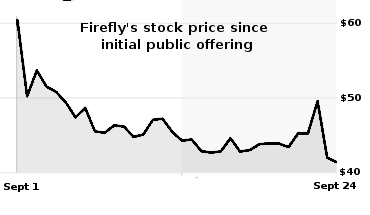
Varda signs deal for more capsule landings in Australia
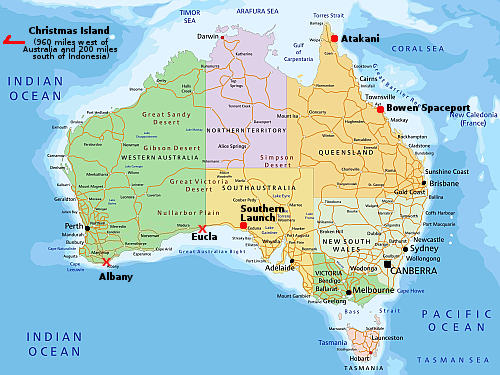
Australian spaceports: operating (red dot) and proposed (red “X”)
Click for original image.
The recoverable capsule company Varda has now signed a new deal that will allow it to land up to 20 more capsules at the commercial spaceport/range Southern Launch in Australia through 2028.
It has already landed capsules there twice. This new contract suggests that Varda has enough expected customers and products to place in its capsules to pay for about six or seven capsules launched per year. If so, this manufacturing model in space is going to bloom very quickly, and will likely become a major profit center for the commercial space stations now under development.
The deal also illustrates the utter failure of the U.S. government’s red tape, especially during the Biden administration.
The company landed its first mission, W-1, at the Utah Test and Training Range in February 2024. But difficulties securing licenses and other approvals for that mission prompted Varda to look elsewhere. “Through that experience, it became pretty clear that the U.S. was not going to be the location for high-cadence reentry operations in the near term,” Eric Lasker, Varda’s chief revenue officer, said at an IAC event announcing the new agreement.
Hopefully the anti-regulatory policies of Trump will change this, but for the moment our government has driven this American company away from the U.S.

Australian spaceports: operating (red dot) and proposed (red “X”)
Click for original image.
The recoverable capsule company Varda has now signed a new deal that will allow it to land up to 20 more capsules at the commercial spaceport/range Southern Launch in Australia through 2028.
It has already landed capsules there twice. This new contract suggests that Varda has enough expected customers and products to place in its capsules to pay for about six or seven capsules launched per year. If so, this manufacturing model in space is going to bloom very quickly, and will likely become a major profit center for the commercial space stations now under development.
The deal also illustrates the utter failure of the U.S. government’s red tape, especially during the Biden administration.
The company landed its first mission, W-1, at the Utah Test and Training Range in February 2024. But difficulties securing licenses and other approvals for that mission prompted Varda to look elsewhere. “Through that experience, it became pretty clear that the U.S. was not going to be the location for high-cadence reentry operations in the near term,” Eric Lasker, Varda’s chief revenue officer, said at an IAC event announcing the new agreement.
Hopefully the anti-regulatory policies of Trump will change this, but for the moment our government has driven this American company away from the U.S.