German rocket startup Isar Aerospace opens new rocket testing facility at Esrange spaceport

Proposed or active spaceports in North Europe
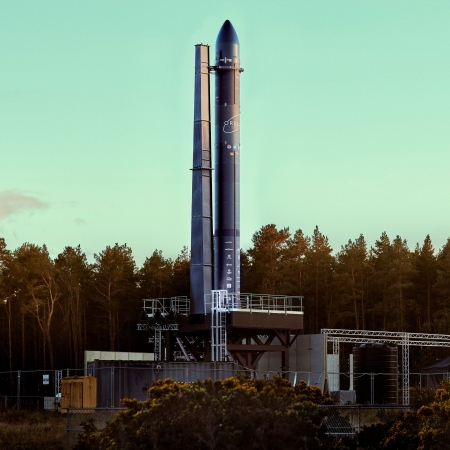
Though the German rocket startup Isar Aerospace is using Norway’s Andoya spaceport to launch its Spectrum rocket, it is now expanding significantly its testing facilities at Sweden’s Esrange spaceport to the east.
European space company Isar Aerospace is significantly expanding their testing operations with SSC Space at Esrange Space Center in Sweden, opening a second test site to support the development and production of its ‘Spectrum’ rocket. The new facility will enable testing of 30+ engines per month, along with expanded integrated stage testing capabilities, increasing testing capacity and enabling faster development.
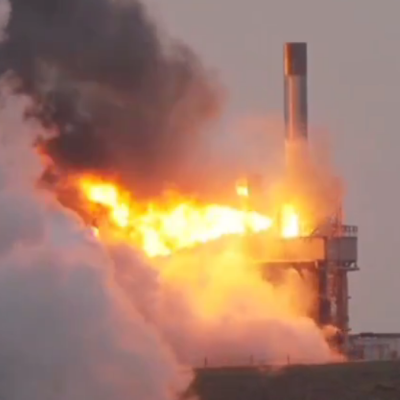
Launching from Esrange is a problem because of its interior location, but testing engines there, close to Germany and the Andoya spaceport makes great sense.
Isar had hoped to make its second attempt to complete the first orbital launch of Spectrum in January, but postponed the launch until March to deal with a valve issue.
Hat tip to BtB’s stringer Jay.

Proposed or active spaceports in North Europe
Though the German rocket startup Isar Aerospace is using Norway’s Andoya spaceport to launch its Spectrum rocket, it is now expanding significantly its testing facilities at Sweden’s Esrange spaceport to the east.
European space company Isar Aerospace is significantly expanding their testing operations with SSC Space at Esrange Space Center in Sweden, opening a second test site to support the development and production of its ‘Spectrum’ rocket. The new facility will enable testing of 30+ engines per month, along with expanded integrated stage testing capabilities, increasing testing capacity and enabling faster development.
Launching from Esrange is a problem because of its interior location, but testing engines there, close to Germany and the Andoya spaceport makes great sense.
Isar had hoped to make its second attempt to complete the first orbital launch of Spectrum in January, but postponed the launch until March to deal with a valve issue.
Hat tip to BtB’s stringer Jay.