Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander now targeting mid-January launch window

According to a media update from NASA yesterday, Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander now targeting mid-January launch window for its unmanned mission to the Moon.
A six-day launch window opens no earlier than mid-January 2025 for the first Firefly Aerospace launch to the lunar surface.
The Blue Ghost flight, carrying 10 NASA science and technology instruments, will launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Media prelaunch and launch activities will take place at NASA Kennedy.
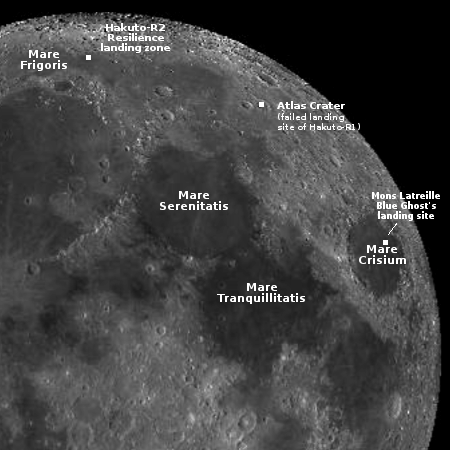
The first quarter of 2025 will be a busy time for unmanned missions to the Moon. In addition to Firefly’s mission, the American startup Intuitive Machines also hopes to launch its Athena lander to the Moon’s south pole in February. Though it will launch after Blue Ghost, it will get to the Moon first, as it is taking a more direct week-long route compared to Blue Ghost’s 45-day journey. In addition, the Japanese company Ispace is targeting its own January launch for its Resilience lander.
If all three lift off as planned, there will be three landers heading for the Moon in early 2025.

According to a media update from NASA yesterday, Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander now targeting mid-January launch window for its unmanned mission to the Moon.
A six-day launch window opens no earlier than mid-January 2025 for the first Firefly Aerospace launch to the lunar surface.
The Blue Ghost flight, carrying 10 NASA science and technology instruments, will launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Media prelaunch and launch activities will take place at NASA Kennedy.
The first quarter of 2025 will be a busy time for unmanned missions to the Moon. In addition to Firefly’s mission, the American startup Intuitive Machines also hopes to launch its Athena lander to the Moon’s south pole in February. Though it will launch after Blue Ghost, it will get to the Moon first, as it is taking a more direct week-long route compared to Blue Ghost’s 45-day journey. In addition, the Japanese company Ispace is targeting its own January launch for its Resilience lander.
If all three lift off as planned, there will be three landers heading for the Moon in early 2025.