French startup gets another space station cargo contract
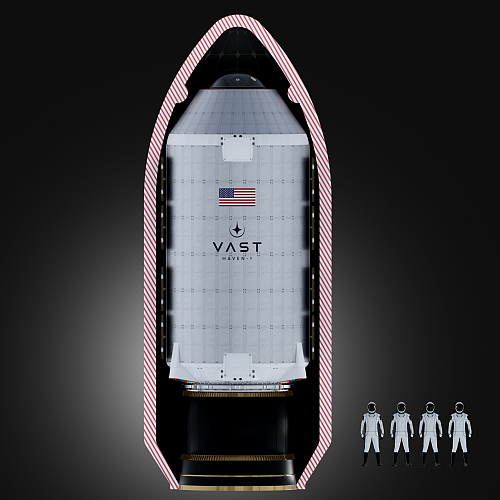
The French startup The Exploration Company has gotten its fourth contract for its proposed Nyx unmanned reusable cargo capsule, signing a deal with Vast to fly one freighter mission to its proposed second Haven station.
This startup, which has not yet flown anything, already had contracts to fly one cargo mission to ISS (a demo mission for the European Space Agency), one to Axiom’s space station, and three to Voyager Space’s Starlab station. This new contract means The Exploration Company already has a manifest of six missions.
These contracts pose a puzzle. Why is this startup getting all these deals, but not Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus or SpaceX’s Dragon capsules? Or have these two American companies signed deals without the same PR splash?
The French startup The Exploration Company has gotten its fourth contract for its proposed Nyx unmanned reusable cargo capsule, signing a deal with Vast to fly one freighter mission to its proposed second Haven station.
This startup, which has not yet flown anything, already had contracts to fly one cargo mission to ISS (a demo mission for the European Space Agency), one to Axiom’s space station, and three to Voyager Space’s Starlab station. This new contract means The Exploration Company already has a manifest of six missions.
These contracts pose a puzzle. Why is this startup getting all these deals, but not Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus or SpaceX’s Dragon capsules? Or have these two American companies signed deals without the same PR splash?