China: Quequiao-2 is successfully operating in lunar orbit
China’s state-run press today announced that its Quequiao-2 communications relay satellite in lunar orbit has successfully completed its initial in-orbit tests, and is functioning as planned.
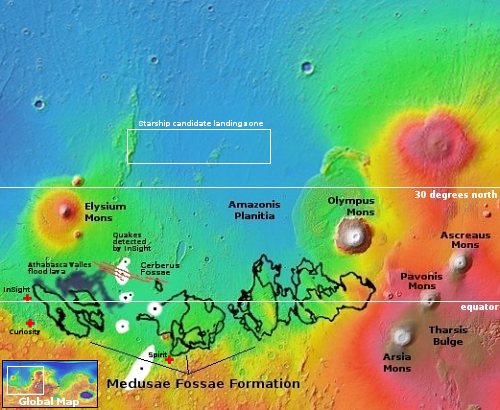
The satellite successfully completed a communication test on April 6 with Chang’e-4, which is now carrying out an exploration mission on the far side of the moon. From April 8 to 9, it conducted communication tests with the Chang’e-6 probe, which is yet to be launched. Queqiao-2 was launched on March 20 and entered its target highly elliptical orbit on April 2 after midway correction, near-moon braking and orbital maneuver around the moon.
Two communication and navigation technology test satellites, Tiandu-1 and Tiandu-2, were sent into space together with Queqiao-2. They entered their target circumlunar orbits on March 29 and separated with each other on April 3. They are now conducting a series of tests on communication and navigation technology.
According to the article, Quequiao-2’s orbit is relatively stable for a lunar orbit and requires less fuel to maintain. The spacecraft thus should be able to operate for a very long time. The orbit “has also significantly improved its communication coverage on the south pole region of the moon.” It will be used for all of China’s future unmanned and manned lunar missions, and will provide China the ability to do farside missions routinely.
China’s state-run press today announced that its Quequiao-2 communications relay satellite in lunar orbit has successfully completed its initial in-orbit tests, and is functioning as planned.
The satellite successfully completed a communication test on April 6 with Chang’e-4, which is now carrying out an exploration mission on the far side of the moon. From April 8 to 9, it conducted communication tests with the Chang’e-6 probe, which is yet to be launched. Queqiao-2 was launched on March 20 and entered its target highly elliptical orbit on April 2 after midway correction, near-moon braking and orbital maneuver around the moon.
Two communication and navigation technology test satellites, Tiandu-1 and Tiandu-2, were sent into space together with Queqiao-2. They entered their target circumlunar orbits on March 29 and separated with each other on April 3. They are now conducting a series of tests on communication and navigation technology.
According to the article, Quequiao-2’s orbit is relatively stable for a lunar orbit and requires less fuel to maintain. The spacecraft thus should be able to operate for a very long time. The orbit “has also significantly improved its communication coverage on the south pole region of the moon.” It will be used for all of China’s future unmanned and manned lunar missions, and will provide China the ability to do farside missions routinely.