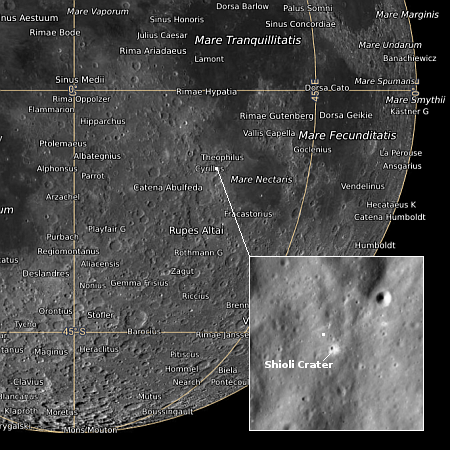
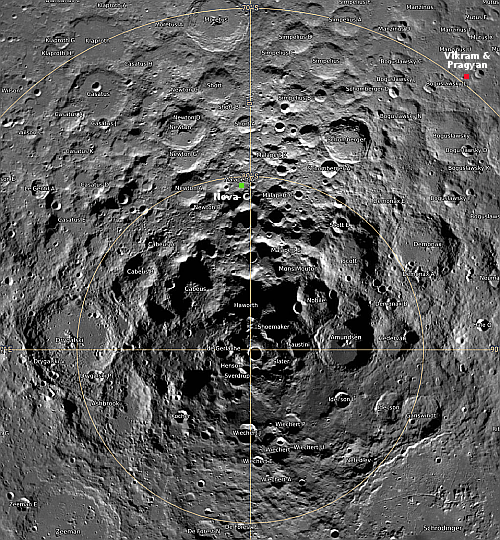
Record-setting Falcon 9 1st stage booster lost after landing
The SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage booster that launched on December 23, 2023 for a record-setting nineteenth time was damaged beyond repair when, after landing on its drone ship successfully, experienced rough seas that caused it to fall over.
The picture at the link shows the crushed booster on its side on the drone ship. SpaceX noted the spectacular history of this booster in a separate tweet:
This one reusable rocket booster alone launched to orbit 2 astronauts and more than 860 satellites — totaling 260+ metric tons — in ~3.5 years.
In a sense, it actually put more mass into orbit that a Saturn 5 rocket, for significant less money though over a much longer period of time.
For SpaceX the loss of this booster is hardly a set back, because it has several other boosters with only a few less total launches in its fleet. Expect one to exceed twenty launches in the near future.
Hat tip to out stringer Jay as well as several readers.
The SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage booster that launched on December 23, 2023 for a record-setting nineteenth time was damaged beyond repair when, after landing on its drone ship successfully, experienced rough seas that caused it to fall over.
The picture at the link shows the crushed booster on its side on the drone ship. SpaceX noted the spectacular history of this booster in a separate tweet:
This one reusable rocket booster alone launched to orbit 2 astronauts and more than 860 satellites — totaling 260+ metric tons — in ~3.5 years.
In a sense, it actually put more mass into orbit that a Saturn 5 rocket, for significant less money though over a much longer period of time.
For SpaceX the loss of this booster is hardly a set back, because it has several other boosters with only a few less total launches in its fleet. Expect one to exceed twenty launches in the near future.
Hat tip to out stringer Jay as well as several readers.