Click for full image.
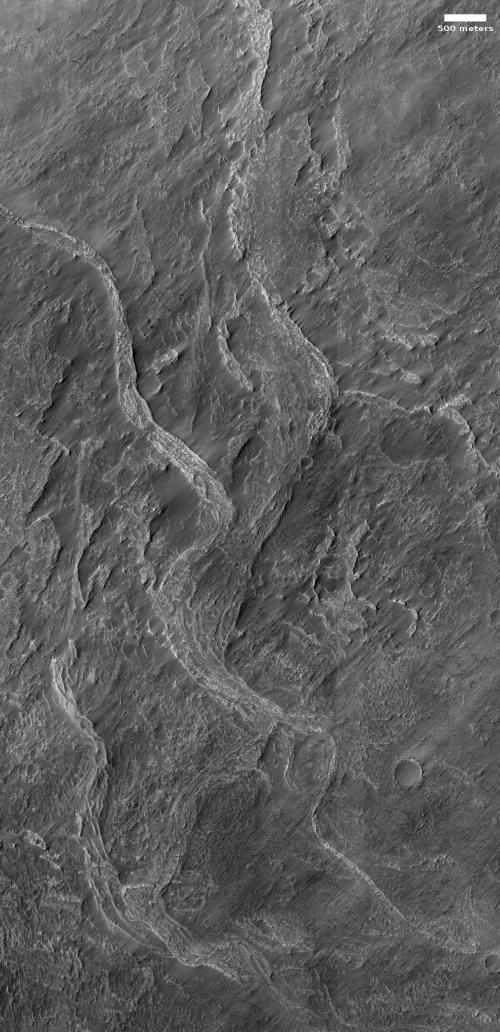
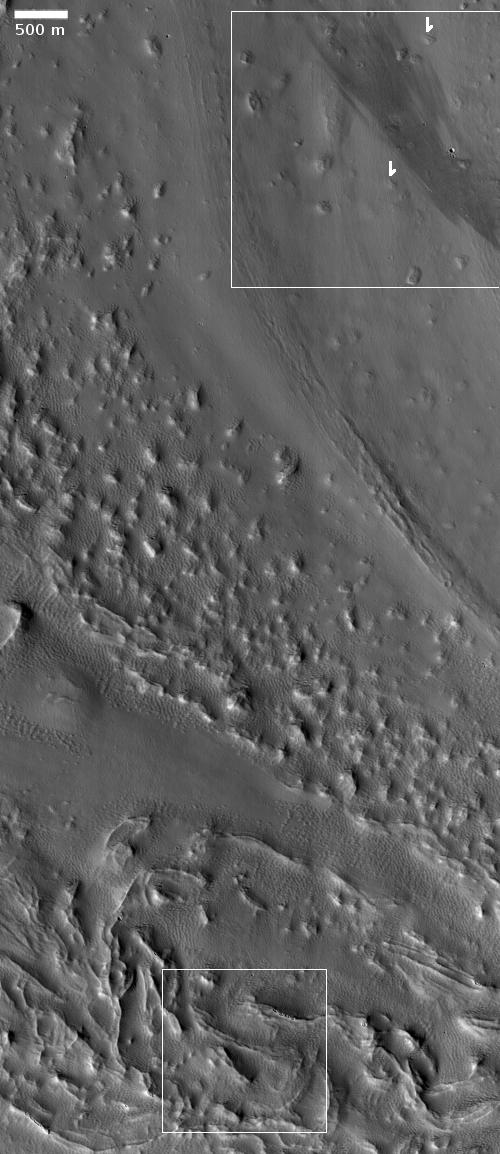
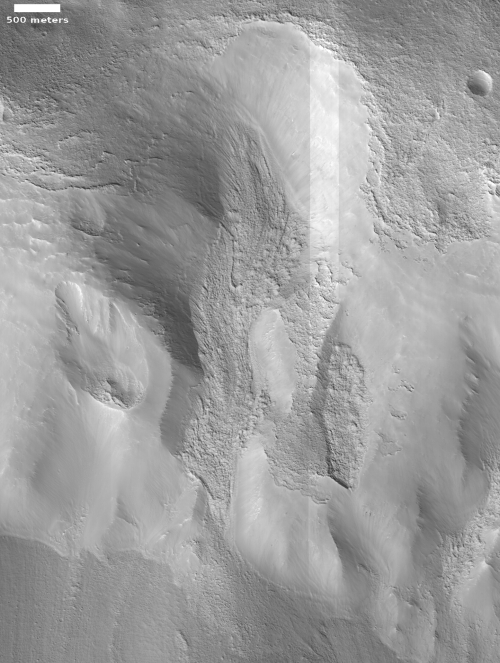
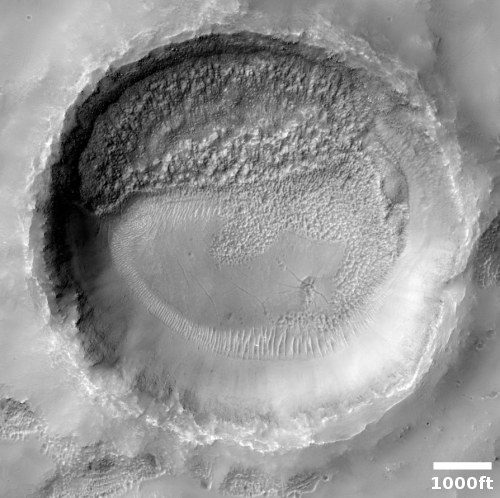
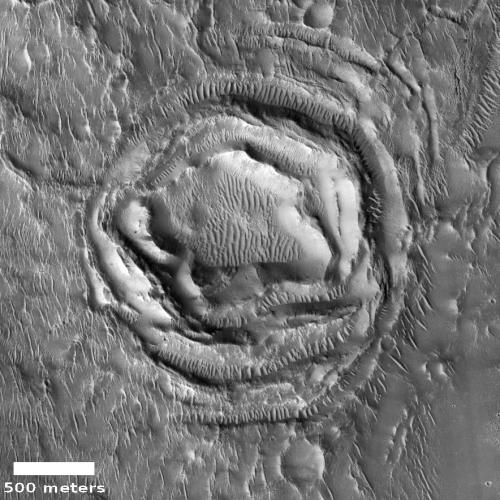
Time for some more cool but mysterious Martian images! The photo to the right, rotated, cropped, and reduced to post here, is the first of two images today, both of which show the ridges but of a completely different nature. Both are located in Hellas Basin in Mars southern hemisphere.
This first picture was taken on September 4, 2020 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), and shows a sinuous complex that resembles to a remarkable extent a set of river tributaries, but is instead a set of raised ridges rather than a canyon system.
Scientists have found more than 10,000 miles of such ridges in the northern hemisphere in Arabia Terra, the most extensive transition zone between the southern highlands and the northern lowlands, and have dubbed them fossilized rivers. From a 2016 press release:
The inverted channels are similar to those found elsewhere on Mars and Earth. They are made of sand and gravel deposited by a river and when the river becomes dry, the channels are left upstanding as the surrounding material erodes. On Earth, inverted channels often occur in dry, desert environments like Oman, Egypt, or Utah, where erosion rates are low – in most other environments, the channels are worn away before they can become inverted. “The networks of inverted channels in Arabia Terra are about 30m high and up to 1–2km wide, so we think they are probably the remains of giant rivers that flowed billions of years ago. Arabia Terra was essentially one massive flood plain bordering the highlands and lowlands of Mars. We think the rivers were active 3.9–3.7 billion years ago, but gradually dried up before being rapidly buried and protected for billions of years, potentially preserving any ancient biological material that might have been present,” added Joel Davis.
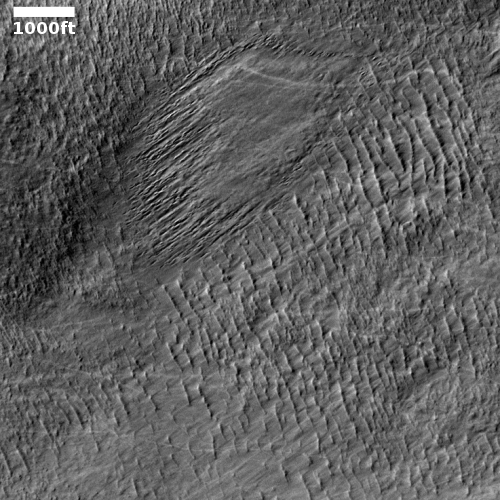
Nor are such features on Mars limited to Hellas and Arabia Terra. For a particularly spectacular feature in the cratered highlands see this 2019 post.
The origin of these sinuous ridges in Hellas might have a similar origin as these other fossilized rivers. At present the bottom of Hellas, the deepest basin on Mars, is a place with little signs of ice. In the past there is evidence that lakes once existed here, so we cannot rule out water as a cause.
At the same time, Hellas was formed by a gigantic impact. One cannot dismiss the possibility of a volcanic origin, impact melt left over from the heat of that crash.
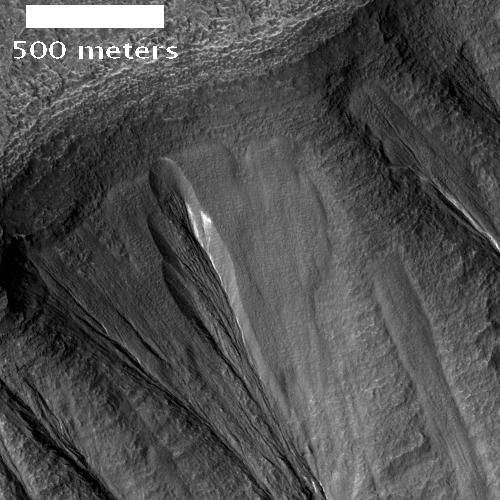
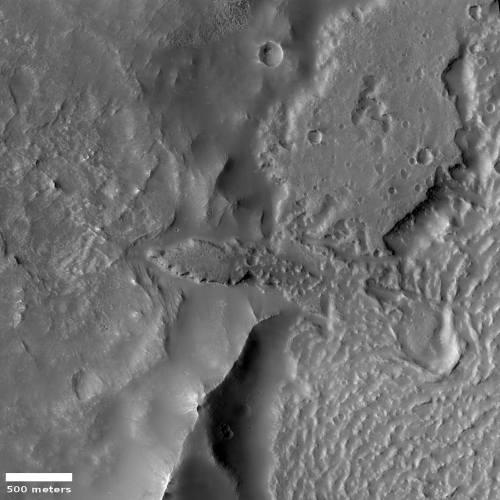
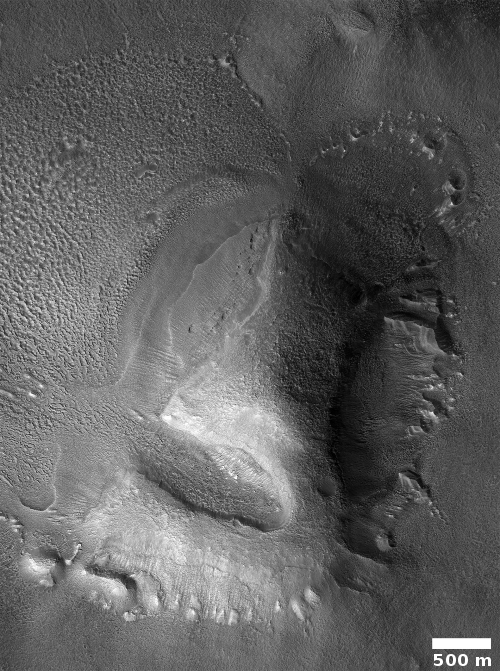
Today’s second ridge complex in Hellas looks far different.
» Read more