An exposed dry waterfall on Mars

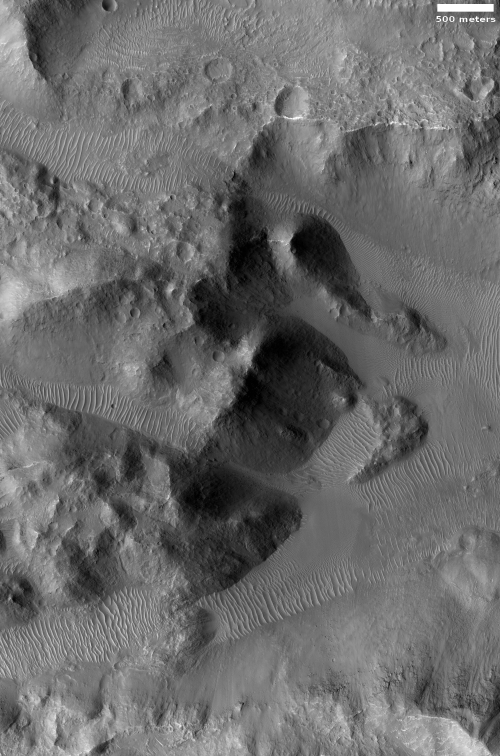
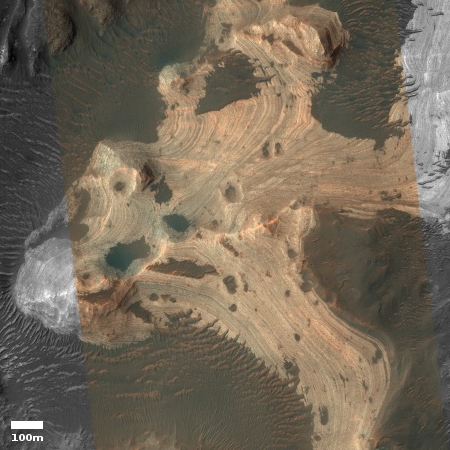
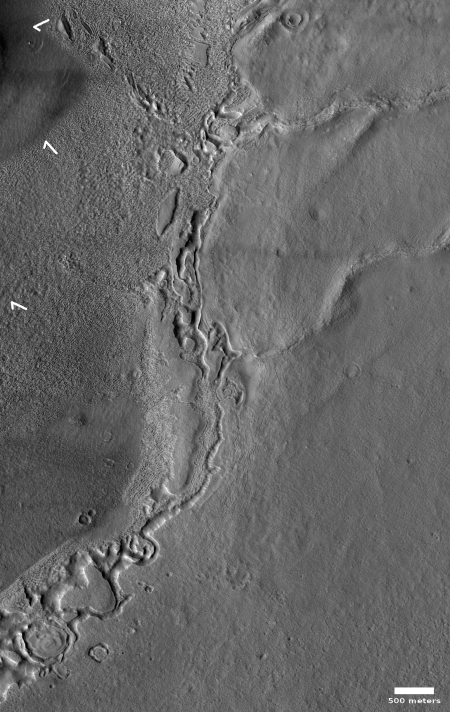
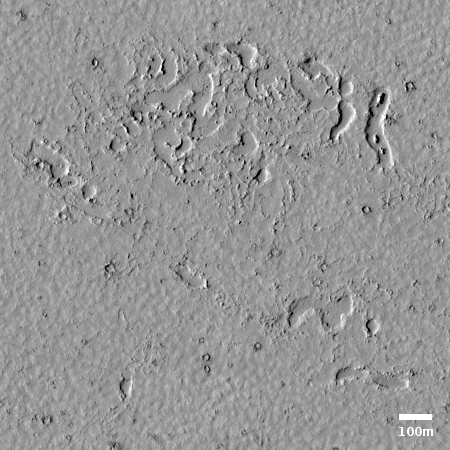
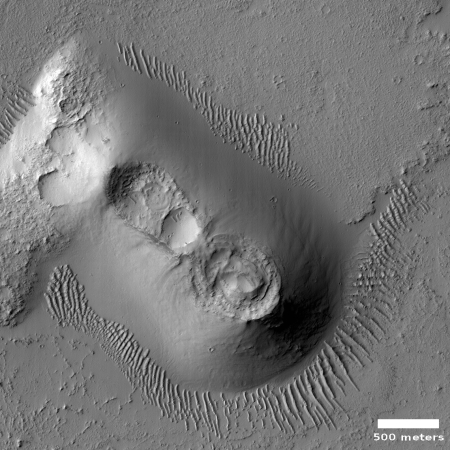
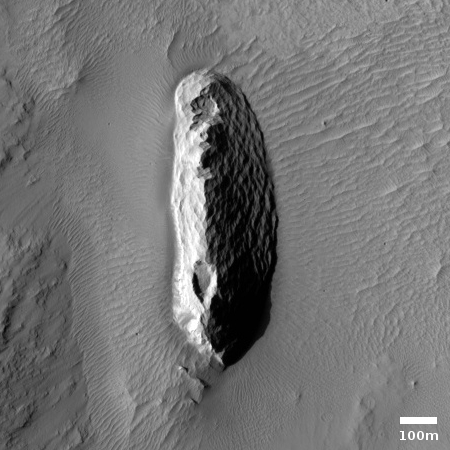
Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on April 30, 2020 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Uncaptioned, the science team titled the release as a “Cataract in Osuga Valles.”
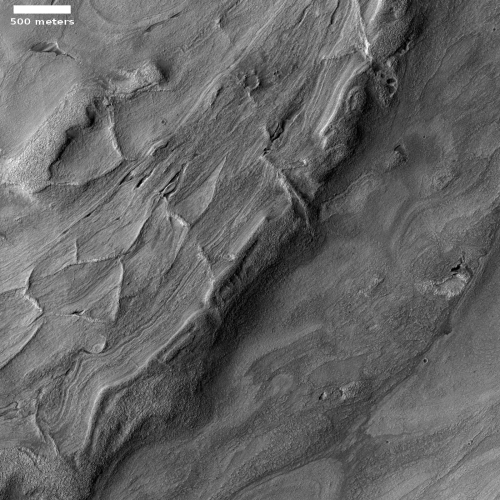
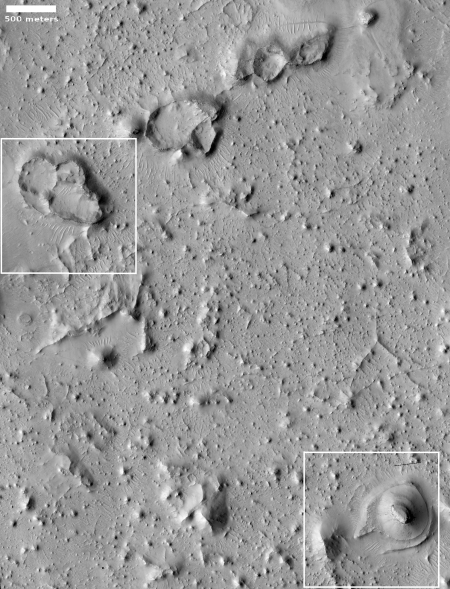
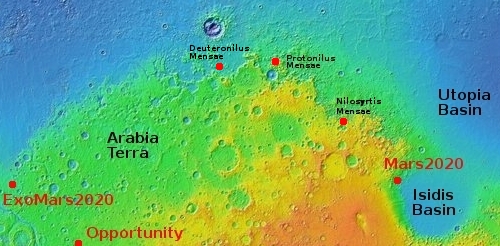
To understand what we are looking at it is necessary to also see a wider view, as provided by the context map below and to the right. As you can see, this image straddles across the canyon called Osuga Valles, and heads downstream to the east. It also shows a point where the grade of that canyon suddenly drops. If water ever flowed here this place would have been the location of a truly spectacular waterfall.
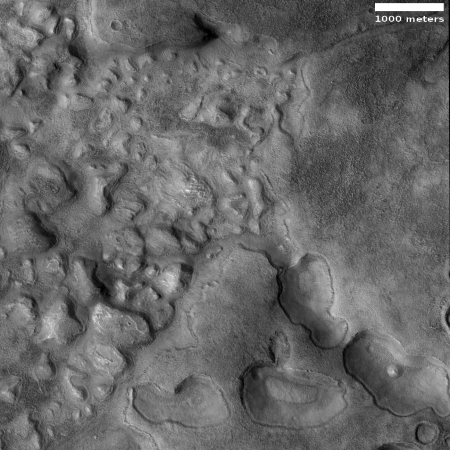
More likely, these cataracts mark the location where sometime in the past a glacier had flowed down this valley, cutting a path until it broke out into the large and wide dead end area that appears to have no clear outlet. For some reason at this point the downhill grade of this canyon suddenly dropped, with the glacier following that sudden steep drop.
There is no glaciers here now, as this location is at 14 degrees south latitude, too close to the equator for any ice to remain close to the surface. Instead, dust dunes remain as the only feature flowing down through these cataracts.
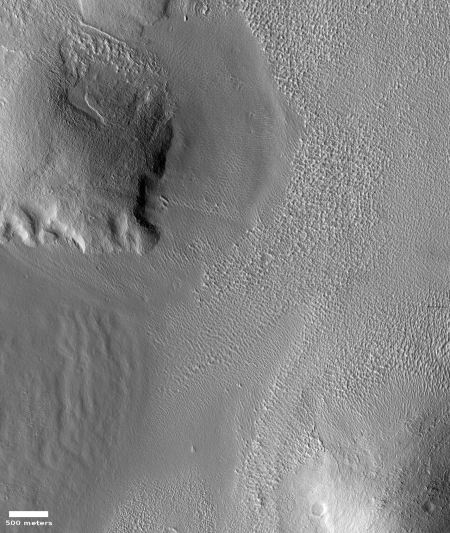
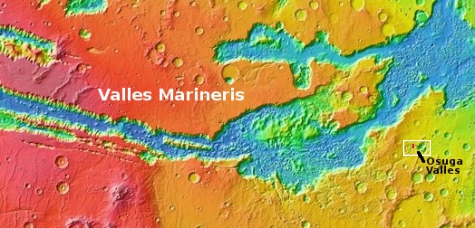
The second overview map provides further context, showing the location of Osuga Valles relative to nearby Valles Marineris, the largest known canyon system in the solar system. Whatever process formed that gigantic canyon system certainly was a factor in forming Osuga Valles. The details however are not yet understood with any certainty. All we presently have are theories.


Cool image time! The photo to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on April 30, 2020 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Uncaptioned, the science team titled the release as a “Cataract in Osuga Valles.”
To understand what we are looking at it is necessary to also see a wider view, as provided by the context map below and to the right. As you can see, this image straddles across the canyon called Osuga Valles, and heads downstream to the east. It also shows a point where the grade of that canyon suddenly drops. If water ever flowed here this place would have been the location of a truly spectacular waterfall.
More likely, these cataracts mark the location where sometime in the past a glacier had flowed down this valley, cutting a path until it broke out into the large and wide dead end area that appears to have no clear outlet. For some reason at this point the downhill grade of this canyon suddenly dropped, with the glacier following that sudden steep drop.
There is no glaciers here now, as this location is at 14 degrees south latitude, too close to the equator for any ice to remain close to the surface. Instead, dust dunes remain as the only feature flowing down through these cataracts.
The second overview map provides further context, showing the location of Osuga Valles relative to nearby Valles Marineris, the largest known canyon system in the solar system. Whatever process formed that gigantic canyon system certainly was a factor in forming Osuga Valles. The details however are not yet understood with any certainty. All we presently have are theories.