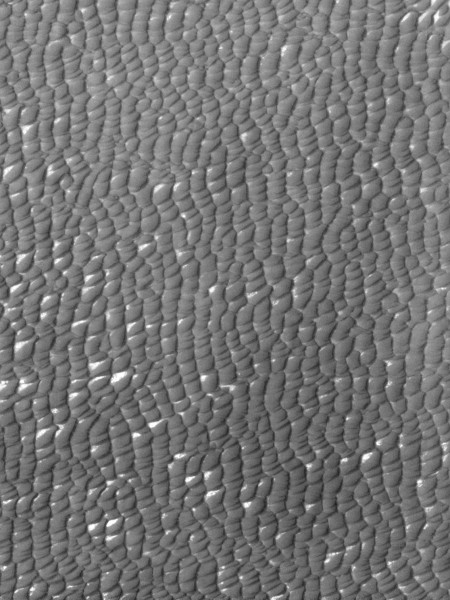
Curiosity’s wheels handling rough terrain
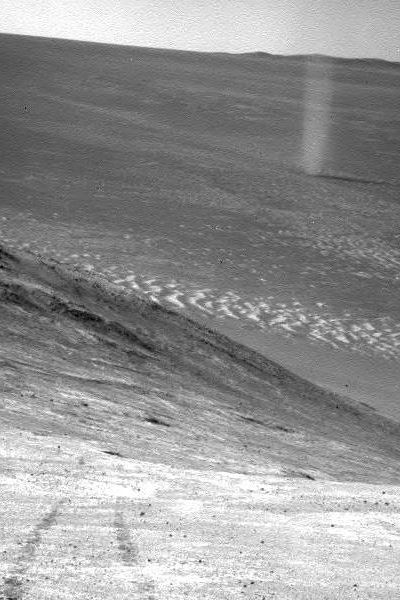
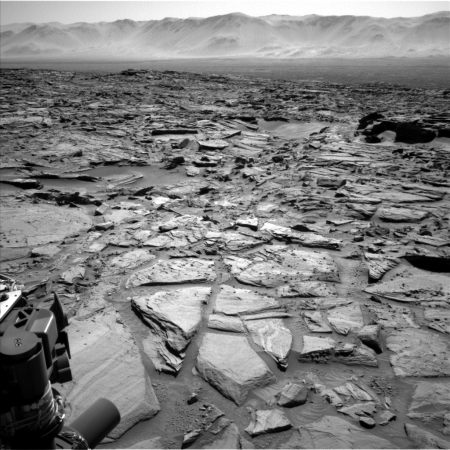
Good news: The Curiosity engineering team has found that the rough and fractured rocky terrain the rover has been recently traveling across on Naukluft Plateau has not significantly increased the wear & tear on the rover’s wheels.
The rover team closely monitors wear and tear on Curiosity’s six wheels. “We carefully inspect and trend the condition of the wheels,” said Steve Lee, Curiosity’s deputy project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. “Cracks and punctures have been gradually accumulating at the pace we anticipated, based on testing we performed at JPL. Given our longevity projections, I am confident these wheels will get us to the destinations on Mount Sharp that have been in our plans since before landing.”
Inspection of the wheels after crossing most of the Naukluft Plateau has indicated that, while the terrain presented challenges for navigation, driving across it did not accelerate damage to the wheels.
Good news: The Curiosity engineering team has found that the rough and fractured rocky terrain the rover has been recently traveling across on Naukluft Plateau has not significantly increased the wear & tear on the rover’s wheels.
The rover team closely monitors wear and tear on Curiosity’s six wheels. “We carefully inspect and trend the condition of the wheels,” said Steve Lee, Curiosity’s deputy project manager at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. “Cracks and punctures have been gradually accumulating at the pace we anticipated, based on testing we performed at JPL. Given our longevity projections, I am confident these wheels will get us to the destinations on Mount Sharp that have been in our plans since before landing.”
Inspection of the wheels after crossing most of the Naukluft Plateau has indicated that, while the terrain presented challenges for navigation, driving across it did not accelerate damage to the wheels.