India to do 19 launches through March 2025
According to India’s space bureaucracy IN-SPACe, that nation has planned as many as 19 launches through March 2025.
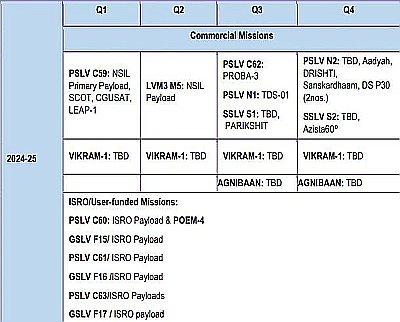
The image to the right shows the manifest that IN-SPACe released. That agency is tasked with encouraging India’s private and independnt space industry, and it claims that 30 missions in total are planned, with half by commercial companies. This number however includes payloads and suborbital test missions, not just orbital launches. Based on the manifest to the right it appears that 19 of these missions are launches, with six being entirely private launches. One of those private launches, the first of Agnikul’s commercial Agnibaan rocket, will be suborbital.
It thus appears that in 2024 India hopes to complete 14 orbital launches. If so, this would double that nation’s previous record of seven launches in a single year. This schedule is very aspirational, with those six entirely commercial launches likely not all happening as planned.

According to India’s space bureaucracy IN-SPACe, that nation has planned as many as 19 launches through March 2025.
The image to the right shows the manifest that IN-SPACe released. That agency is tasked with encouraging India’s private and independnt space industry, and it claims that 30 missions in total are planned, with half by commercial companies. This number however includes payloads and suborbital test missions, not just orbital launches. Based on the manifest to the right it appears that 19 of these missions are launches, with six being entirely private launches. One of those private launches, the first of Agnikul’s commercial Agnibaan rocket, will be suborbital.
It thus appears that in 2024 India hopes to complete 14 orbital launches. If so, this would double that nation’s previous record of seven launches in a single year. This schedule is very aspirational, with those six entirely commercial launches likely not all happening as planned.
