China accelerates its schedule for its upcoming Moon/Mars missions while admitting its lunar base will take longer

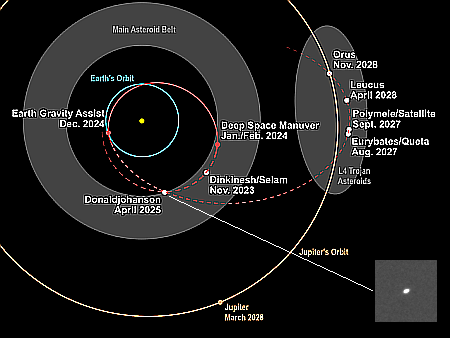
The original phase I plan of Chinese-Russian lunar
base plan, from June 2021.
The new colonial movement: In several different reports today in China’s state-run press — timed to coincide with the launch of three astronauts to Tiangong-3 — Chinese officials confirmed that it has moved up the planned launch dates for both its first lunar rover as well as its Mars sample return mission, and it is also expanding its offers to the international community to partner on those missions.
At the same time it let slip the fact that it will not be establishing its lunar base on the Moon in 2030, as previously claimed. Moreover, note how this so-called accelerated schedule of lunar missions is actually behind the announced timetable outlined by China and Russia in 2021, as shown on the right. None will fly by this year, as promised.
As for the news today, first China announced that its Tianwen-3 Mars sample return mission will launch in 2028.
» Read more

The original phase I plan of Chinese-Russian lunar
base plan, from June 2021.
The new colonial movement: In several different reports today in China’s state-run press — timed to coincide with the launch of three astronauts to Tiangong-3 — Chinese officials confirmed that it has moved up the planned launch dates for both its first lunar rover as well as its Mars sample return mission, and it is also expanding its offers to the international community to partner on those missions.
At the same time it let slip the fact that it will not be establishing its lunar base on the Moon in 2030, as previously claimed. Moreover, note how this so-called accelerated schedule of lunar missions is actually behind the announced timetable outlined by China and Russia in 2021, as shown on the right. None will fly by this year, as promised.
As for the news today, first China announced that its Tianwen-3 Mars sample return mission will launch in 2028.
» Read more