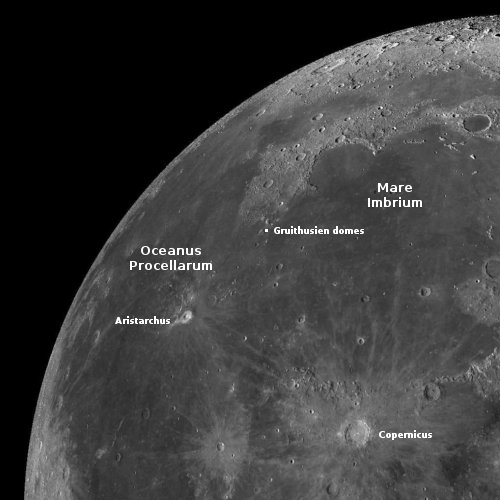
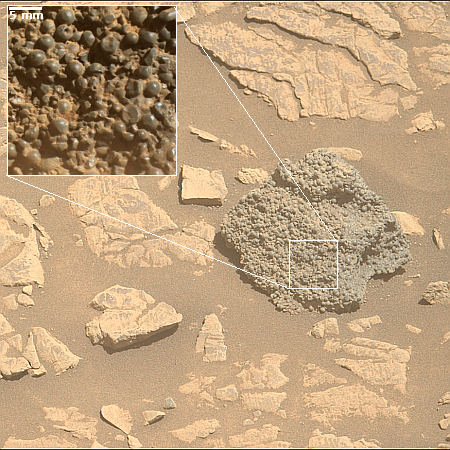
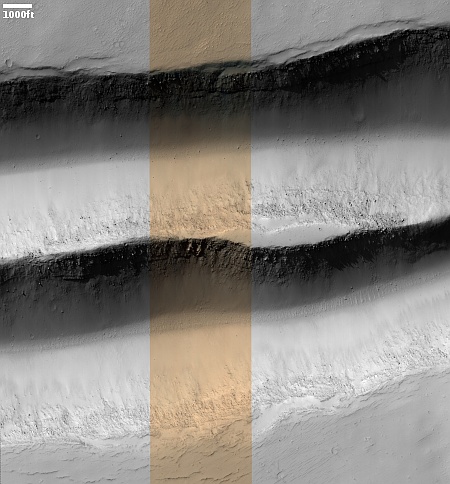
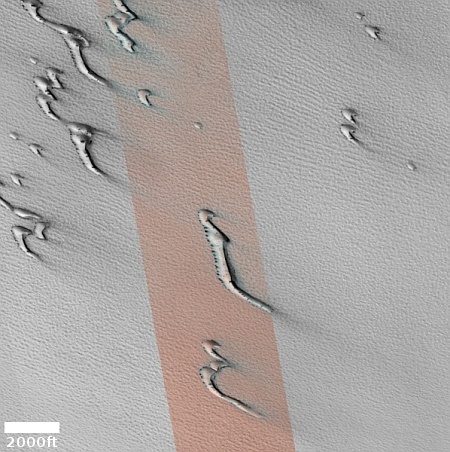
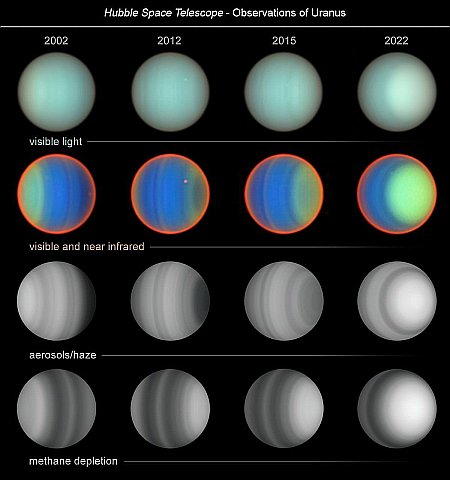
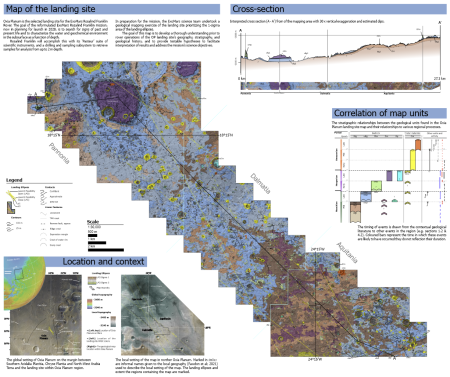
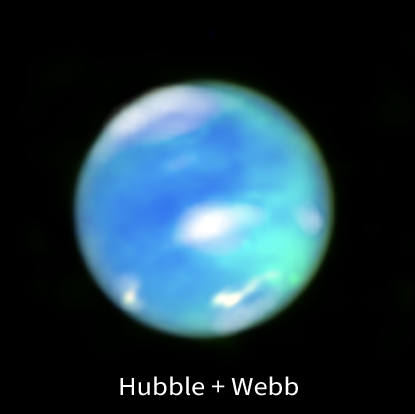
Webb infrared data increases odds asteroid 2024 YR4 will impact Moon in 2032
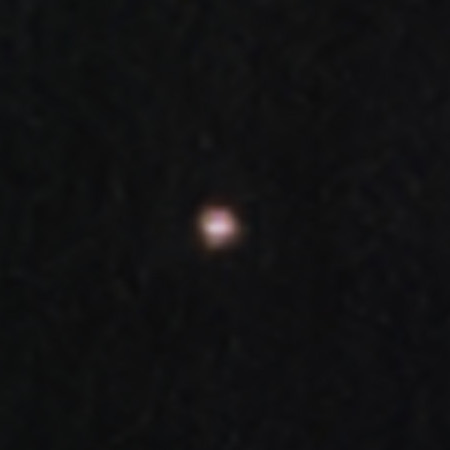

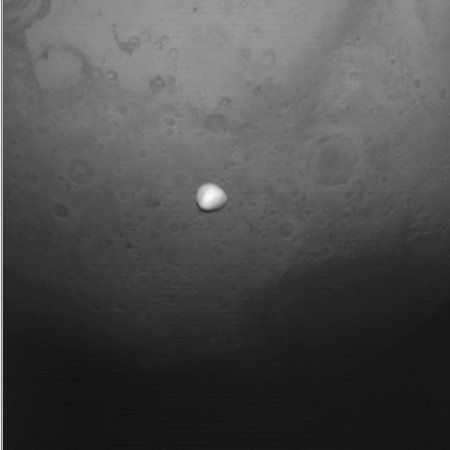
Asteroid 2024 YR4 as seen by Webb in the
mid-infrared. Click for original image.
Using new infrared images and data from the Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have further refined the orbit and size of the potentially dangerous asteroid 2024 YR4.
The image of 2024 YR4 to the right was taken by Webb’s mid-infrared camera, and provides information on its thermal surface characteristics.
First, the Webb data narrowed the uncertainty about the asteroid’s size, suggesting it is about 200 feet in diameter. You can read the paper outlining this result here. The data also suggested nature of the asteroid’s surface, which is important in determining its future path. The pressure from sunlight can change the orbits of small asteroids, but figuring out how much is extremely difficult without knowing the rotation of the asteroid and the reflective qualities of its entire surface.
Second, based on this new data, other astronomers are increasingly certain 2024 YR4 will not hit the Earth in 2032, but the odds of it impacting the Moon have now increased to 4%.

Asteroid 2024 YR4 as seen by Webb in the
mid-infrared. Click for original image.
Using new infrared images and data from the Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have further refined the orbit and size of the potentially dangerous asteroid 2024 YR4.
The image of 2024 YR4 to the right was taken by Webb’s mid-infrared camera, and provides information on its thermal surface characteristics.
First, the Webb data narrowed the uncertainty about the asteroid’s size, suggesting it is about 200 feet in diameter. You can read the paper outlining this result here. The data also suggested nature of the asteroid’s surface, which is important in determining its future path. The pressure from sunlight can change the orbits of small asteroids, but figuring out how much is extremely difficult without knowing the rotation of the asteroid and the reflective qualities of its entire surface.
Second, based on this new data, other astronomers are increasingly certain 2024 YR4 will not hit the Earth in 2032, but the odds of it impacting the Moon have now increased to 4%.