Astroforge names the target asteroid for its first commercial interplanetary mission
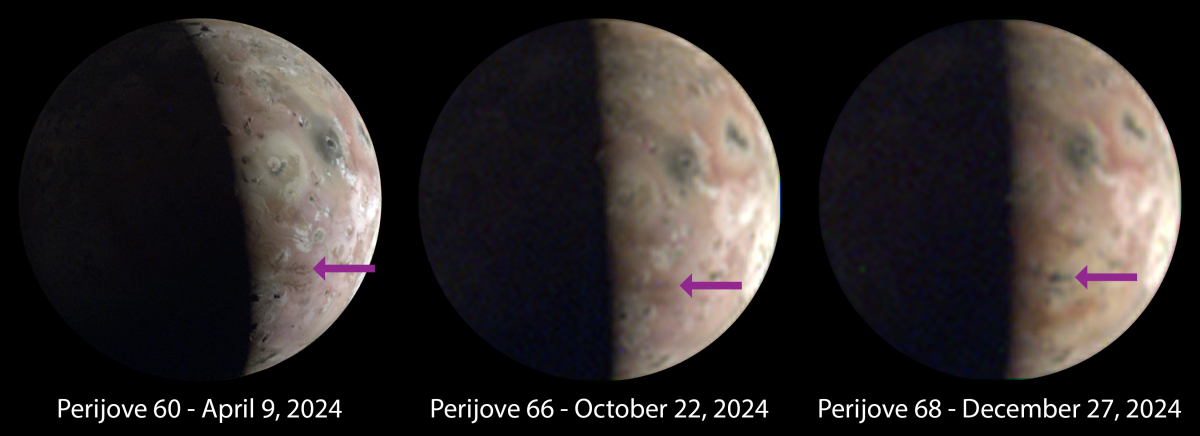
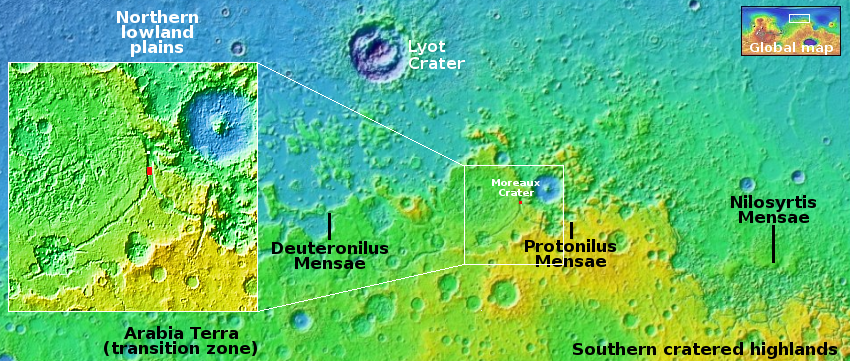
The asteroid mining startup Astroforge today finally named the asteroid that its first commercial interplanetary mission will do a close fly-by, set to launch as a secondary payload on a SpaceX Falcon 9 on February 26, 2025.
The mining startup is headed to asteroid 2022 OB5 as soon as Feb. 26, launching alongside Intuitive Machines’ second lunar mission. CEO Matt Gialich told Payload that they picked that asteroid for the initial mission for a few reasons:
- It’s under a kilometer wide.
- It could be a high-value, metal-filled M-type asteroid.
- AstroForge’s spacecraft will fly by the asteroid when it’s close to Earth, so imagery can be sent back quickly.
This will be Astroforge’s second mission, the first being an Earth-orbit demo flight to prove out its systems. The spacecraft, dubbed Odin, was quickly prepped when the planned satellite satellite failed vibration testing. The company quickly replaced it with the cubesat intended for the third mission.
The company is also proud that the entire cost for this asteroid mission is just $6.5 million. “Hopefully we’re going to show the world that NASA doesn’t need to be funded for $5B missions when we can do it for much less,” said Gialich. The company also announced it has signed a multi-launch contract with the rocket startup Stoke Space, though no specifics were released.
Hat tip BtB’s stringer Jay.
The asteroid mining startup Astroforge today finally named the asteroid that its first commercial interplanetary mission will do a close fly-by, set to launch as a secondary payload on a SpaceX Falcon 9 on February 26, 2025.
The mining startup is headed to asteroid 2022 OB5 as soon as Feb. 26, launching alongside Intuitive Machines’ second lunar mission. CEO Matt Gialich told Payload that they picked that asteroid for the initial mission for a few reasons:
- It’s under a kilometer wide.
- It could be a high-value, metal-filled M-type asteroid.
- AstroForge’s spacecraft will fly by the asteroid when it’s close to Earth, so imagery can be sent back quickly.
This will be Astroforge’s second mission, the first being an Earth-orbit demo flight to prove out its systems. The spacecraft, dubbed Odin, was quickly prepped when the planned satellite satellite failed vibration testing. The company quickly replaced it with the cubesat intended for the third mission.
The company is also proud that the entire cost for this asteroid mission is just $6.5 million. “Hopefully we’re going to show the world that NASA doesn’t need to be funded for $5B missions when we can do it for much less,” said Gialich. The company also announced it has signed a multi-launch contract with the rocket startup Stoke Space, though no specifics were released.
Hat tip BtB’s stringer Jay.