New gullies on Mars?
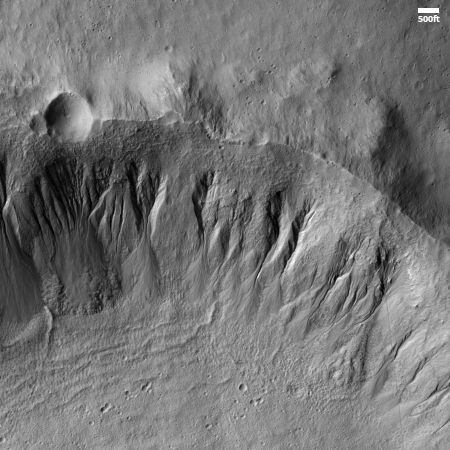
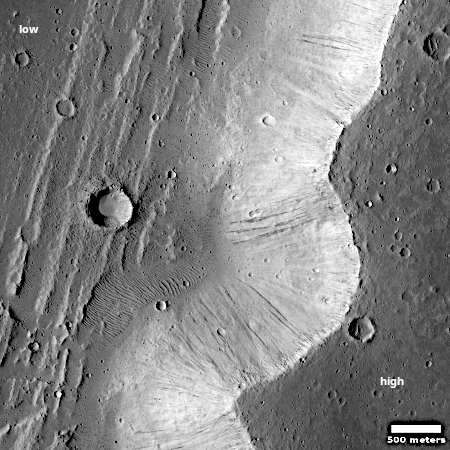
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on November 6, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
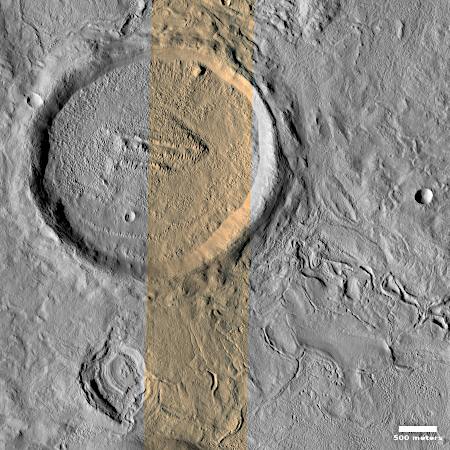
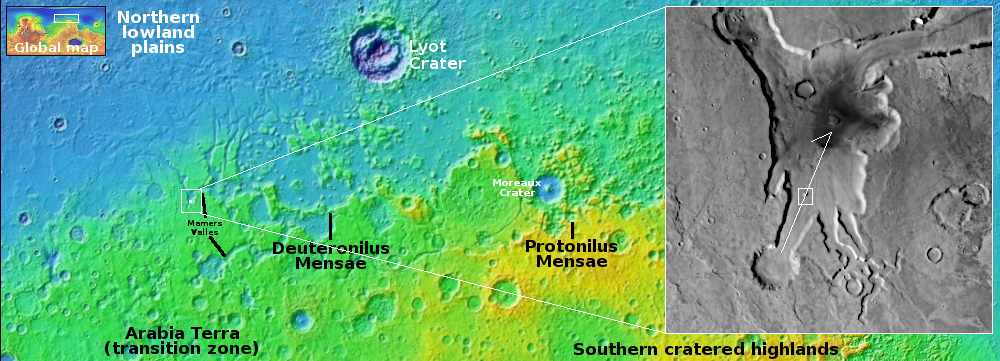
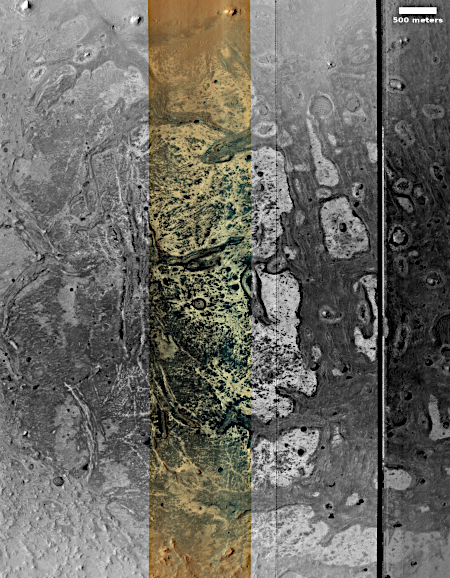
The science team labels this image “Fresh-Looking Gullies.” It was clearly taken to study the gullies flowing down the north interior crater wall of this 4.4 mile-wide unnamed crater, about 1,500 feet deep.
What causes these gullies remains an open question. They are found in many places in the Martian mid-latitudes. When first discovered scientists thought they might be related to the sublimation of underground ice. More recent research suggests they are formed by the seasonal dry ice frost cycle that in the high latitudes has carbon dioxide condense to fall as snow in autumn and then sublimate away in the spring.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on November 6, 2025 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The science team labels this image “Fresh-Looking Gullies.” It was clearly taken to study the gullies flowing down the north interior crater wall of this 4.4 mile-wide unnamed crater, about 1,500 feet deep.
What causes these gullies remains an open question. They are found in many places in the Martian mid-latitudes. When first discovered scientists thought they might be related to the sublimation of underground ice. More recent research suggests they are formed by the seasonal dry ice frost cycle that in the high latitudes has carbon dioxide condense to fall as snow in autumn and then sublimate away in the spring.
» Read more