A somewhat typical but strange crater in Mars’ Death Valley
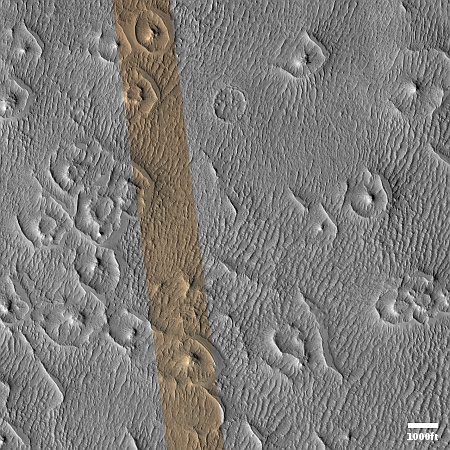
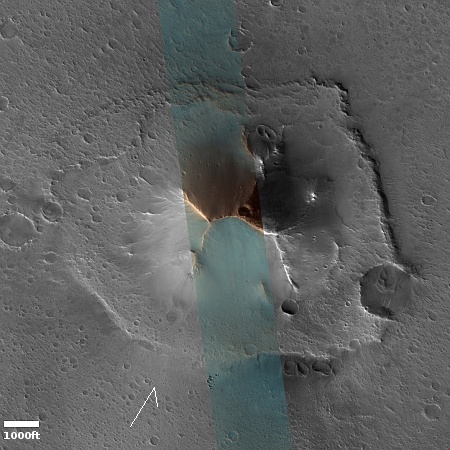
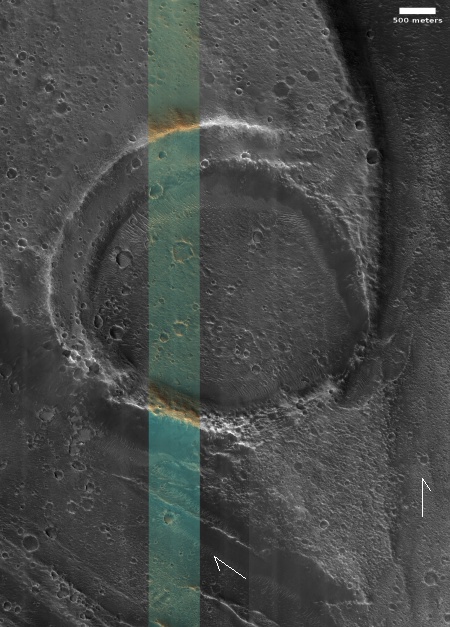
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on August 29, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
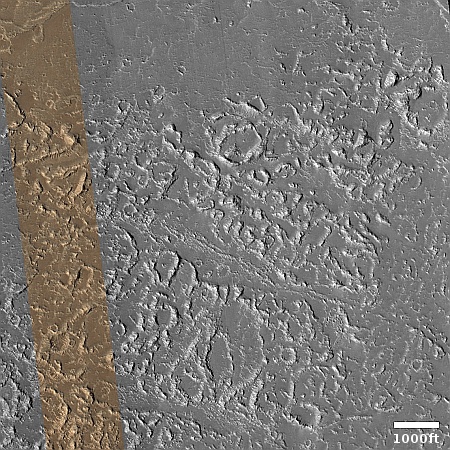
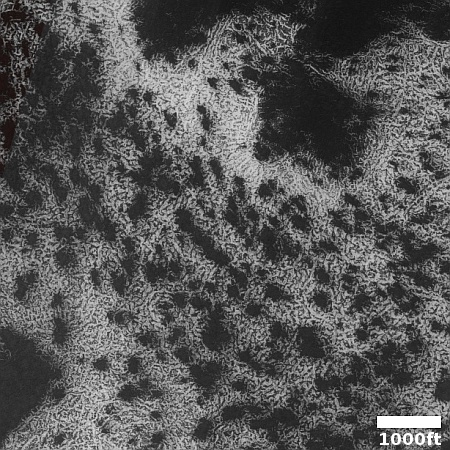
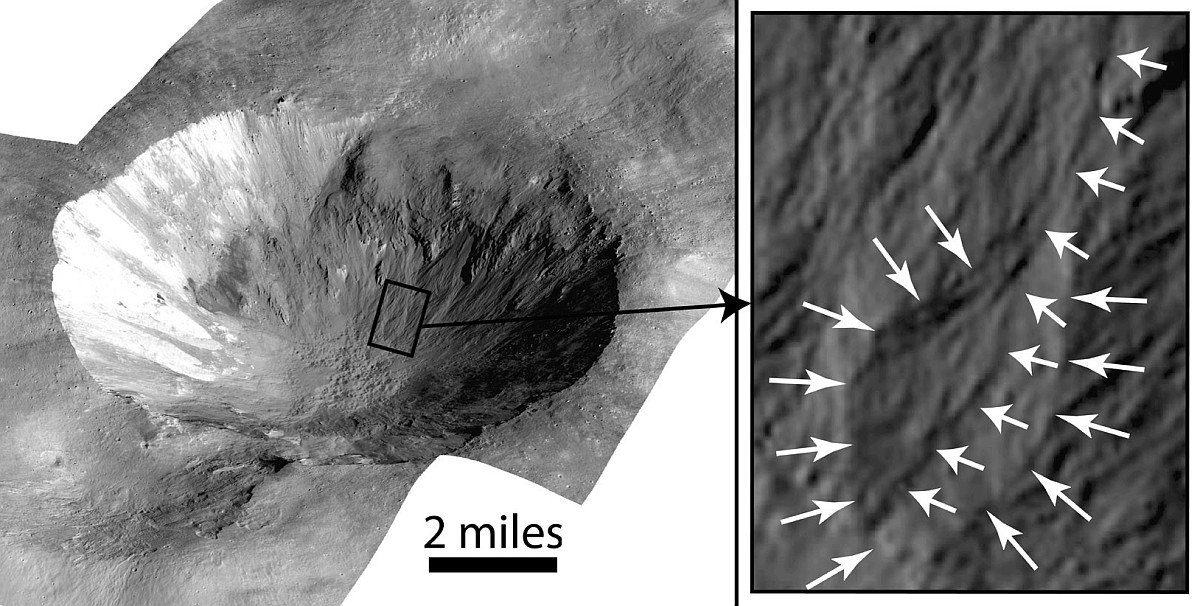
The camera team labels the primary feature in this picture as “ridges,” but what I see is a strange crater that at first glance appears to be impact-caused, but at closer inspection might be something else entirely.
This unnamed crater is about one mile wide. It is only about fifty feet deep, but sits above the surround landscape by about 200 feet. That high position suggests strongly that this crater was not formed by an impact by is instead a caldera from some sort of volcanic activity, with the splash apron around it simply examples of past magma flows erupting from within.
The ridges inside the crater might be glacial debris, as this location is at 35 degrees south latitude, making near surface ice possible.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on August 29, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The camera team labels the primary feature in this picture as “ridges,” but what I see is a strange crater that at first glance appears to be impact-caused, but at closer inspection might be something else entirely.
This unnamed crater is about one mile wide. It is only about fifty feet deep, but sits above the surround landscape by about 200 feet. That high position suggests strongly that this crater was not formed by an impact by is instead a caldera from some sort of volcanic activity, with the splash apron around it simply examples of past magma flows erupting from within.
The ridges inside the crater might be glacial debris, as this location is at 35 degrees south latitude, making near surface ice possible.
» Read more