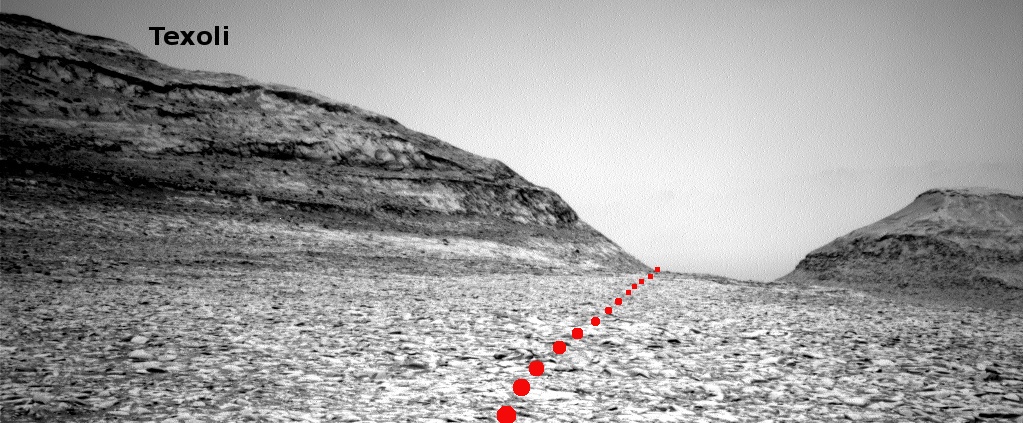
NASA assembles two new panels to review its Mars Sample Return mission plans
NASA yesterday announced that it has assembled two new panels to review its Mars Sample Return mission plans, dubbed the strategy review and the analysis team, to be done in conjunction with the proposals the agency has already received from the private sector.
The team’s report is anticipated by the end of 2024 and will examine options for a complete mission design, which may be a composite of multiple studied design elements. The team will not recommend specific acquisition strategies or partners.
The strategy review team has been chartered under a task to the Cornell Technical Services contract. The team may request input from a NASA analysis team that consists of government employees and expert consultants.
The analysis team also will provide programmatic input such as a cost and schedule assessment of the architecture recommended by the strategy review team.
The first panel contains a mixture of NASA officials and scientists, while the second is mostly made up of NASA managers.
Whatever these panels decide, it is very clear that major changes are required to this project in order to get the Perseverance core samples on Mars back to Earth within a reasonable amount of time and at an acceptable cost. The present project design is chaotic, confused, and running significantly overbudget and behind schedule, with no indication anything will change in the near future.
NASA yesterday announced that it has assembled two new panels to review its Mars Sample Return mission plans, dubbed the strategy review and the analysis team, to be done in conjunction with the proposals the agency has already received from the private sector.
The team’s report is anticipated by the end of 2024 and will examine options for a complete mission design, which may be a composite of multiple studied design elements. The team will not recommend specific acquisition strategies or partners.
The strategy review team has been chartered under a task to the Cornell Technical Services contract. The team may request input from a NASA analysis team that consists of government employees and expert consultants.
The analysis team also will provide programmatic input such as a cost and schedule assessment of the architecture recommended by the strategy review team.
The first panel contains a mixture of NASA officials and scientists, while the second is mostly made up of NASA managers.
Whatever these panels decide, it is very clear that major changes are required to this project in order to get the Perseverance core samples on Mars back to Earth within a reasonable amount of time and at an acceptable cost. The present project design is chaotic, confused, and running significantly overbudget and behind schedule, with no indication anything will change in the near future.