A preliminary copy of the next IPCC report has been leaked.
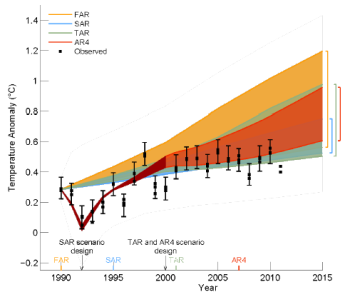
In the coming days there will be much discussion of this document — such as how it appears the IPCC has finally acknowledged the importance of the Sun’s variability to climate change — but for now, I post on the right what is probably its most important admission. This graph from the leaked report shows the rise in global temperatures as predicted by all the different climate models used by the IPCC, compared to actual observed temperatures. As you can see, since the late 1990s there has been no significant increase in global temperature. Moreover, the observed data now sits outside the predicted margin of error for all the models, making every single one of these models completely wrong.
But don’t worry, these facts aren’t important. In fact, any facts that contradict the religion of global warming must be ignored. It is far more important to shut down all industry and live like cavemen, just because we have faith in our belief in global warming.

