Curiosity spots a corroded weathered rock
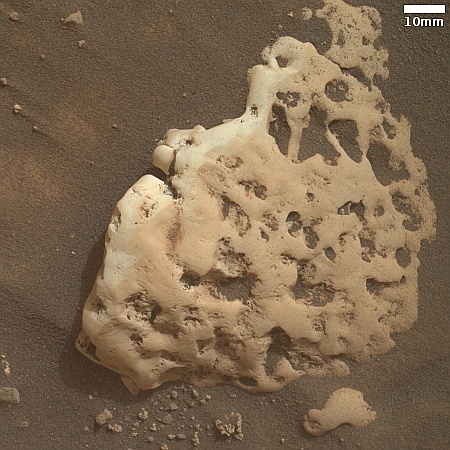
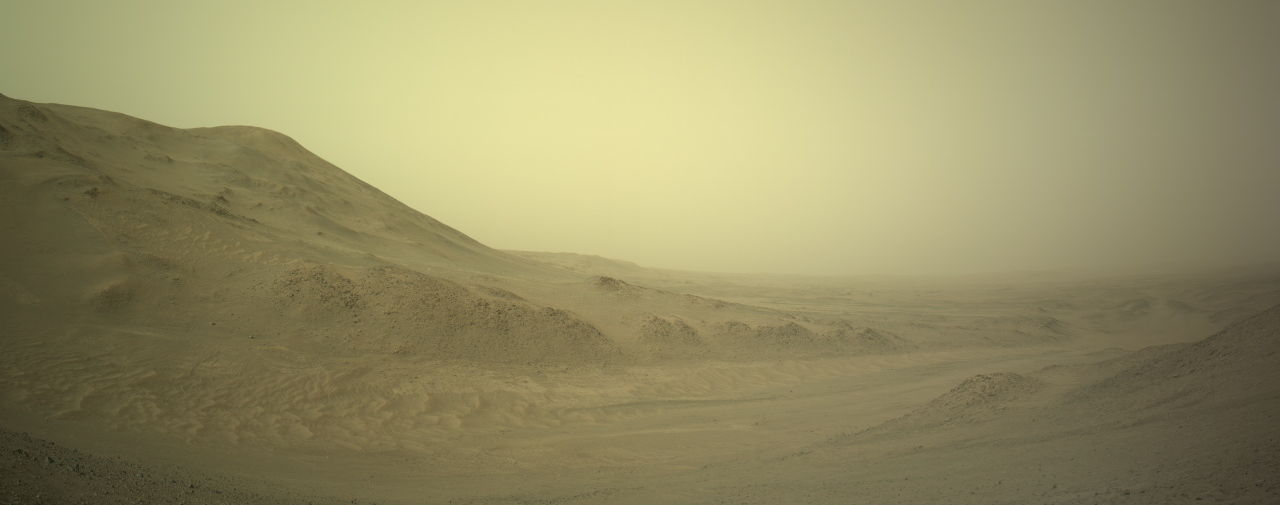
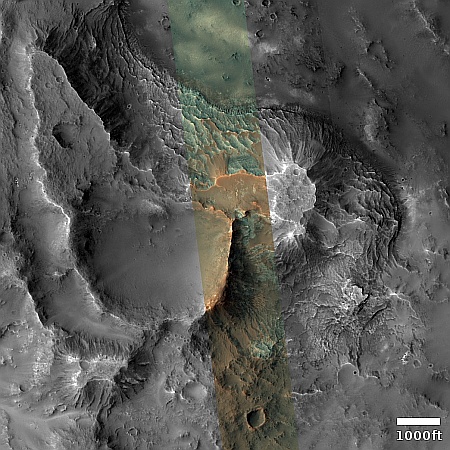
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on September 29, 2024 by the close-up camera mounted at the end of the robot arm of the rover Curiosity on Mars.
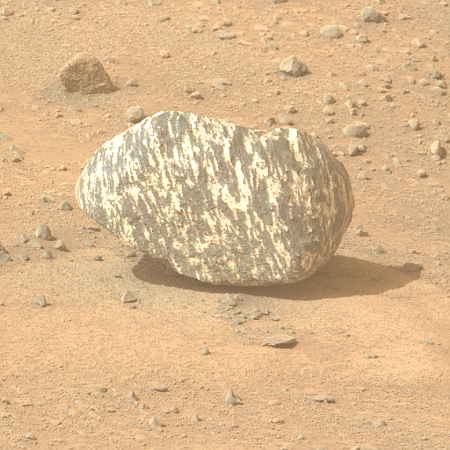
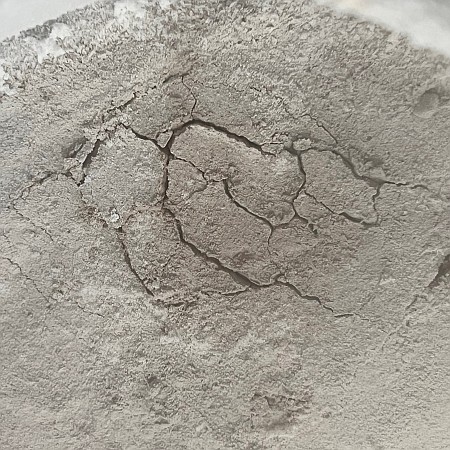
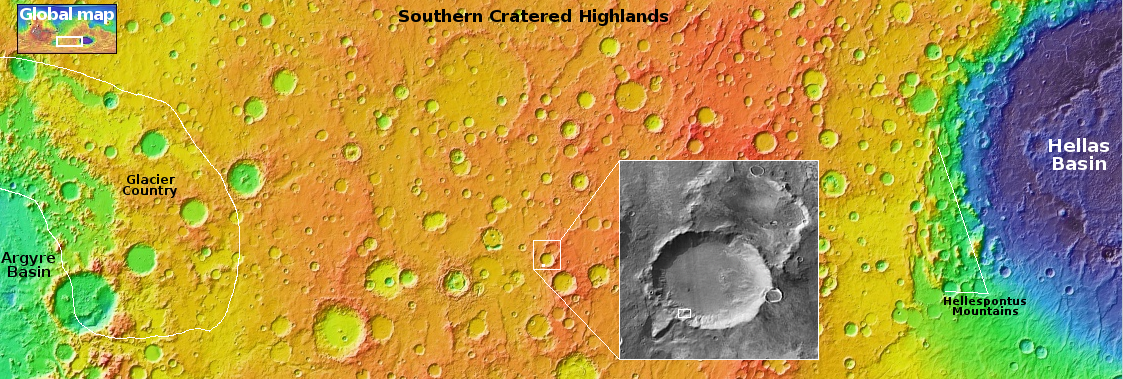
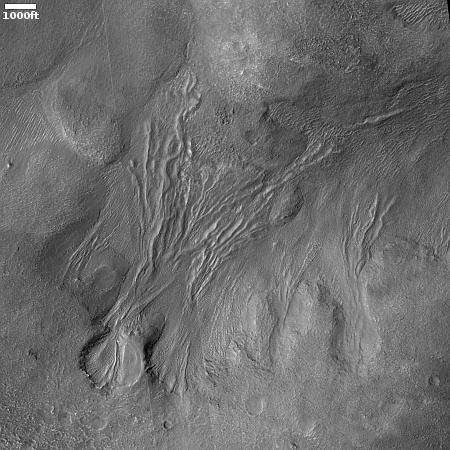
This is a small rock, less than three inches across. It is embedded in the sand and soil of Mars, its surface clearly weathered and smoothed by some process. The holes and gaps in the rock could have occurred prior to that smoothing, getting exposed by it. Or possibly the holes developed during the smoothing, with sections breaking off because the material was like sandstone, easily friable.
What caused the smoothing? The data from Curiosity as it climbs Mount Sharp suggests some water process, either flowing water or glacial ice. The scientists at present tend to prefer the liquid explanation, but that requires the Martian atmosphere to have once been much thicker and warmer, conditions that no model has yet demonstrated convincingly was ever possible.
The rock is also likely another example of sulfur, part of the sulfate-bearing unit of geology that Curiosity is presently traversing.
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken on September 29, 2024 by the close-up camera mounted at the end of the robot arm of the rover Curiosity on Mars.
This is a small rock, less than three inches across. It is embedded in the sand and soil of Mars, its surface clearly weathered and smoothed by some process. The holes and gaps in the rock could have occurred prior to that smoothing, getting exposed by it. Or possibly the holes developed during the smoothing, with sections breaking off because the material was like sandstone, easily friable.
What caused the smoothing? The data from Curiosity as it climbs Mount Sharp suggests some water process, either flowing water or glacial ice. The scientists at present tend to prefer the liquid explanation, but that requires the Martian atmosphere to have once been much thicker and warmer, conditions that no model has yet demonstrated convincingly was ever possible.
The rock is also likely another example of sulfur, part of the sulfate-bearing unit of geology that Curiosity is presently traversing.