Nine incredible places on Earth. With pictures.
Nine incredible places on Earth. With pictures.
Nine incredible places on Earth. With pictures.
Nine incredible places on Earth. With pictures.
Investment opportunity: Two Sandia National Laboratories researchers are seeking a partnership with a private company to market the self-guided bullet they developed.
The prototype design is a four-inch long bullet with a built-in optical sensor in its nose to detect a laser beam on the target. The sensor directs guidance and control information using an algorithm and a small central processing unit that helps steer tiny built-in fins to guide the bullet. According to the Sandia lab’s computer simulations, an unguided bullet in real world conditions can miss a target that is half a mile away by almost 10 yards. With this guided bullet, however, it could strike within eight inches of a target.
Duck! The orbit of a 150 foot wide asteroid that zipped past the Earth in February, has an orbit that will bring it past the Earth again on February 15, 2013 by less than 15,000 miles.
The team use several automated telescopes to scan the sky, and the discovery came somewhat serendipitously after they decided to search areas of the sky where asteroids are not usually seen. “A preliminary orbit calculation shows that 2012 DA14 has a very Earth-like orbit with a period of 366.24 days, just one more day than our terrestrial year, and it ‘jumps’ inside and outside of the path of Earth two times per year,” says Jaime.
While an impact with Earth has been ruled out on the asteroid’s next visit, astronomers will use that close approach for more studies and calculate the Earth and Moon’s gravitational effects on it.
Because this newly discovered asteroid passes so close and frequently to both the Earth and Moon, astronomers will need a lot more data before they can pin down its orbit precisely, and thus predict the chances of a collision in the near future.
Thank you Barack! Europe, dumped by Obama administration and NASA, has teamed up with Russia to build its ExoMars orbiter and lander.
Have researchers found Leonardo da Vinca’s lost “The Battle of Anghiari” fresco, hidden for the past six centuries behind a wall?
The painting, considered a masterpiece by contemporaries, had never been finished by da Vinci because he had used an experimental technique to paint it, and that technique had failed. Thus, the painting was painted over fifty years later. The only reason we have a good idea of what the painting looked like is that several artists were so impressed by it that they produced copies while it was still visible.
The research suggests the painting was not painted over, but that a false wall was built in front of it. If so, this would be truly exciting discovery. The painting would probably not be in very good shape, but to actually see it would be wonderful.
An artist’s conception of Martian weather. With pictures.
Research on ISS has found that prolonged spaceflight causes vision problems and might even damage the human eye.
There had been hints of this discovery in an earlier report, but today’s paper is the first published science on the subject.
The results are not only important for finding out the medical challenges of weightlessness. They illustrate once again the need to do long extended flights on ISS. Without that research we are never going to be able to fly humans to other planets.
The blistering hot exoplanet where it snows.
These results have led to a suggestion that [HD 189733b] could continually experience silicate snow. In the lower atmosphere of [the exoplanet], magnesium silicate sublimates, that is, it passes directly from a solid into a gas. But we know there are small silicate particulates in the upper atmosphere. Formation of these particulates requires that the temperature be lowered, and so must have been formed at a temperature inversion in the atmosphere. The generally windy conditions would help some of the tiny particulates grow into respectable snow crystals.
Venus Express was blinded for four days last week after being hit by a coronal mass ejection from the Sun.
Lord Monckton tries to educate a college professor and his students about the science of climate change.
This is why:
“We shall lose the West unless we can restore the use of reason to pre-eminence in our institutions of what was once learning. It was the age of reason that built the West and made it prosperous and free. The age of reason gave you your great Constitution of liberty. It is the power of reason, the second of the three great powers of the soul in Christian theology, that marks our species out from the rest of the visible creation, and makes us closest to the image and likeness of our Creator. I cannot stand by and let the forces of darkness drive us unprotesting into a new Dark Age.”
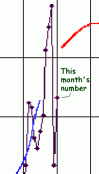
Late last week NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center released its monthly update of the ongoing solar cycle sunspot activity, covering February 2012. Though I am slightly late in posting it, as I do every month, you can now see the full graph below the fold. I have also created a close-up of the graph’s relevant area, shown on the left, because it is hard to decipher what is happening on the full graph.
Since the Sun began it ramp up to solar maximum back in 2009, the pattern has been consistent, two steps forward, one step back. First there are several months in a row in which the number of sunspots show a steep rise, followed immediately by several months in which the sunspot numbers decline just as steeply, though by not as much. All told, since 2009 we have seen this pattern repeat four times.
February’s numbers have continued that pattern.
» Read more
Researchers have completed the first comprehensive map of the entire ocean-floor debris field of the Titanic.
More Kepler results: From the abstract of a preprint paper published today on the Los Alamos astro-ph website:
The mean eccentricity of the Kepler candidates decreases with decreasing planet size indicating that smaller planets are preferentially found in low-eccentricity orbits.
In other words, the smaller a planet is, the more likely its orbit will be circular like the Earth’s. This result is encouraging news for the search for life on other worlds. Before Kepler, astronomers had found that the orbits of most exoplanets were far more eccentric than the orbits of the planets in our solar system, a condition that scientists thought was unfriendly for the development of life. These new results counter that conclusion. The orbits of the planets in our solar system might not be as unusual as first thought.
In a February 29 letter to NASA, House appropriators have challenged the Obama administration’s decision to shut down the agency’s Mars planetary program.
An evening pause: For anyone who has ever attended a science conference and listened to the presentations there, this presentation embodies that experience better than any I have ever seen. It was so good it won an Ig Noble award.
If you want to read the whole paper, you can find it here [pdf].
When a solar storm slammed into both the Earth and Mars in January 2008, scientists were able to directly measure the importance of the Earth’s magnetic field in protecting our atmosphere from oxygen loss.
They found that while the pressure of the solar wind increased at each planet by similar amounts, the increase in the rate of loss of martian oxygen was ten times that of Earth’s increase. Such a difference would have a dramatic impact over billions of years, leading to large losses of the martian atmosphere, perhaps explaining or at least contributing to its current tenuous state. The result proves the efficacy of Earth’s magnetic field in deflecting the solar wind and protecting our atmosphere.
Chinese physicists have discovered a key measurement that helps explain why and how neutrinos can magically oscillate between three different states. Moreover, the data
implies that there could be a slight asymmetry between neutrinos and antineutrinos—called CP violation—a slight asymmetry that might help explain why the universe evolved to contain so much matter and so little antimatter.
An analysis of the most recent Kepler data suggests that Earthlike planets in orbits like our own are extremely rare.
The USS Monitor gives up the faces of its dead.
Set your calendar: The last transit of Venus across the face of the Sun for the next century is only three months away.
Clouds inside a room. With pictures.
A scientist compares all the global warming climate models developed during the past twenty years with the actual data:
We’ve checked all the main predictions of the climate models against the best data. The climate models get them all wrong. … Therefore:
- The climate models are fundamentally flawed. Their assumed threefold amplification by feedbacks does not in fact exist.
- The climate models overestimate temperature rises due to CO2 by at least a factor of three.
Read the whole article. Not only does Evans outline the failures of all the climate models, he also clearly and distinctly describes the actual debate that has been going on in the climate field for the past three decades. It isn’t the effects of carbon dioxide that climate scientists have been arguing about, but, as Richard Lindzen explained to the UK Parliament last week, whether other climate factors, called feedbacks, will amplify or suppress the warming produced by CO2.
Dissecting the bad arguments on both sides of the climate debate.
What I find intriguing about Singer’s analysis is that the bad arguments from the global warming camp seem to come from noted scientists writing for the IPCC, while the bad arguments on the skeptical side mostly come from non-scientists on the fringes.
In either case, they remain bad arguments, but it is tragic that so many scientists participate in it.
New results from the Large Hadron Collider suggest that matter and anti-matter really are different.
JPL has issued a press release “reality check” on the impact possibilities of asteroid 2011 AG5 in 2040.
“In September 2013, we have the opportunity to make additional observations of 2011 AG5 when it comes within 91 million miles (147 million kilometers) of Earth,” said Don Yeomans, manager of NASA’s Near-Earth Object Program Office at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. “It will be an opportunity to observe this space rock and further refine its orbit. Because of the extreme rarity of an impact by a near-Earth asteroid of this size, I fully expect we will be able to significantly reduce or rule out entirely any impact probability for the foreseeable future.” Even better observations will be possible in late 2015.
In other words, we really will not know anything more about these possibilities until late next year.
Kepler today released an updated catalog of candidate exoplanets observed during the space telescope’s first sixteen months of observations. In this release, they list more than a thousand new exoplanet candidates, almost two hundred of which are Earth-sized. Among the new exoplanet candidates, twenty-five are in the habitable zone!
Now for some details.
» Read more