Tag: science
Five of the biggest unsolved mysteries of physics
The Great Moonbuggy Race
The Great Moonbuggy Race is an engineering competition that requires a team of six students to design a “proof-of-concept” wheeled rover that will race over a half mile of simulated lunar terrain. In April, two team members, one male and one female, will drive the completed vehicle in competition at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This contest will present design challenges that are similar to those encountered by the original lunar rover team. This is the 16th year of competition for high school teams, but it will be the first year for Chicago’s public high school students.
The Great Moonbuggy Race is an engineering competition that requires a team of six students to design a “proof-of-concept” wheeled rover that will race over a half mile of simulated lunar terrain. In April, two team members, one male and one female, will drive the completed vehicle in competition at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. This contest will present design challenges that are similar to those encountered by the original lunar rover team. This is the 16th year of competition for high school teams, but it will be the first year for Chicago’s public high school students.
White nose syndrome has been found in bats in Europe
White nose syndrome, the fungus that has been killing bats in the northeast United States these past five years, has now been definitively found on bats in Europe.
With this information, scientists now know that it is the differences between North American and European bats that can explain why European bat colonies can survive the fungus while North American bats cannot. Furthermore, this information should show us how future North American bats will adapt to the fungus.
White nose syndrome, the fungus that has been killing bats in the northeast United States these past five years, has now been definitively found on bats in Europe.
With this information, scientists now know that it is the differences between North American and European bats that can explain why European bat colonies can survive the fungus while North American bats cannot. Furthermore, this information should show us how future North American bats will adapt to the fungus.
Six former and current employees have sued the FDA agency under the Obama administration over its secret surveillance of their private emails.
How Obama encourages transparency: Six former and current employees have sued the FDA agency under the Obama administration over its secret surveillance of their private emails.
According to a release by the law firm representing the group, the FDA targeted the employees with a “covert spying campaign” that lasted for two years after it learned they had written a letter to President-Elect Obama in early 2009. … The plaintiffs allege the agency used spyware to read the their personal emails and take screenshots while they used government computers. But whether such reconnaissance is illegal is not quite clear. According to the Washington Post, “the startup screen on FDA computers warns employees, ‘you have no reasonable expectation of privacy,’ ” including any communication accessed or sent from the machine.”
According to the law firm representing the current and former FDA employees, the monitoring continued even after the Health and Human Services Office of Inspector General “denied the FDA’s request to take any criminal and/or administrative action against the whistleblowers” and noted the whistleblowers’ communications with Congress were protected under law.
How Obama encourages transparency: Six former and current employees have sued the FDA agency under the Obama administration over its secret surveillance of their private emails.
According to a release by the law firm representing the group, the FDA targeted the employees with a “covert spying campaign” that lasted for two years after it learned they had written a letter to President-Elect Obama in early 2009. … The plaintiffs allege the agency used spyware to read the their personal emails and take screenshots while they used government computers. But whether such reconnaissance is illegal is not quite clear. According to the Washington Post, “the startup screen on FDA computers warns employees, ‘you have no reasonable expectation of privacy,’ ” including any communication accessed or sent from the machine.”
According to the law firm representing the current and former FDA employees, the monitoring continued even after the Health and Human Services Office of Inspector General “denied the FDA’s request to take any criminal and/or administrative action against the whistleblowers” and noted the whistleblowers’ communications with Congress were protected under law.
Newt and Scientists: A Long, Complicated Love Affair
Newt and scientists: A long, complicated love affair.
The article gives you the science community’s take on Gingrich. And since that community is almost entirely Democratic in make-up and routinely hostile and almost bigoted in their hatred of Republicans, it is not surprising that this take has a certain schizophrenic air about it. They want to like him because of his passionate interest and support of science, but how can they? He’s a Republican (whispered softly like one was saying a curse word.)
Newt and scientists: A long, complicated love affair.
The article gives you the science community’s take on Gingrich. And since that community is almost entirely Democratic in make-up and routinely hostile and almost bigoted in their hatred of Republicans, it is not surprising that this take has a certain schizophrenic air about it. They want to like him because of his passionate interest and support of science, but how can they? He’s a Republican (whispered softly like one was saying a curse word.)
Identifying our galaxy’s next supernova
How crayons are made
Data issued last week without fanfare by both the UK’s Met Office and the University of East Anglia Climatic Research Unit has confirmed that the rising trend in world temperatures ended in 1997.
Data issued last week without fanfare by both the UK’s Met Office and the University of East Anglia Climatic Research Unit has confirmed that the rising trend in world temperatures ended in 1997.
The article also discusses at great length the additional influence the sun and its sunspot cycle might have on the climate, something I have discussed here at great length. However, the above factoid is the article’s most important data point.
Data issued last week without fanfare by both the UK’s Met Office and the University of East Anglia Climatic Research Unit has confirmed that the rising trend in world temperatures ended in 1997.
The article also discusses at great length the additional influence the sun and its sunspot cycle might have on the climate, something I have discussed here at great length. However, the above factoid is the article’s most important data point.
The Vintage Computer Festival
Want to play with some old computers? You can, at the Vintage Computer Festival East 8.0.
Want to play with some old computers? You can, at the Vintage Computer Festival East 8.0.
DNA research suggests that “Native Americans” actually came from a tiny mountain region in Siberia.
DNA research suggests that “Native Americans” actually came from a tiny mountain region in Siberia.
I added the quotes above. It is really hilarious to see the headline’s use of the politically correct term “Native Americans” while simultaneously describing proof that the American Indians were as much immigrants to the New World as everyone else.
DNA research suggests that “Native Americans” actually came from a tiny mountain region in Siberia.
I added the quotes above. It is really hilarious to see the headline’s use of the politically correct term “Native Americans” while simultaneously describing proof that the American Indians were as much immigrants to the New World as everyone else.
The Kepler team today announced the discovery of eleven new solar systems holding twenty-six planets.
Planets galore! The Kepler team today announced the discovery of eleven new solar systems holding twenty-six planets.
The planets orbit close to their host stars and range in size from 1.5 times the radius of Earth to larger than Jupiter. Fifteen of them are between Earth and Neptune in size, and further observations will be required to determine which are rocky like Earth and which have thick gaseous atmospheres like Neptune. The planets orbit their host star once every six to 143 days. All are closer to their host star than Venus is to our sun.
No Earths in the habitable zone quite yet, but we are circling in on our prey.
Planets galore! The Kepler team today announced the discovery of eleven new solar systems holding twenty-six planets.
The planets orbit close to their host stars and range in size from 1.5 times the radius of Earth to larger than Jupiter. Fifteen of them are between Earth and Neptune in size, and further observations will be required to determine which are rocky like Earth and which have thick gaseous atmospheres like Neptune. The planets orbit their host star once every six to 143 days. All are closer to their host star than Venus is to our sun.
No Earths in the habitable zone quite yet, but we are circling in on our prey.
A wiretap could exonerate the six seismologists on trial for manslaughter in Italy for not properly warning the public of an earthquake.
Scientists on trial: A wiretap conversation might exonerate the six seismologists on trial for manslaughter in Italy for not properly warning the public of an earthquake.
Scientists on trial: A wiretap conversation might exonerate the six seismologists on trial for manslaughter in Italy for not properly warning the public of an earthquake.
Roughly half of Vesta is cold enough for water ice to survive below the surface
New computer models suggest that roughly half of the asteroid Vesta is cold enough for ice to survive below the surface.
New computer models suggest that roughly half of the asteroid Vesta is cold enough for ice to survive below the surface.
Scouring the Aegean Sea for the world’s oldest shipwrecks.
Scouring the Aegean Sea for the world’s oldest shipwrecks.
A Bronze Age wreck called Ulu Burun shows how the remains of a single ship can transform archaeologists’ understanding of an era. Discovered in 1982, it lies about 9 kilometres southeast of Kaş in southern Turkey, and dates from around 1300 BC, a century or two after the Minoans disappeared.
Christos Agourides, secretary-general of the Hellenic Institute of Marine Archaeology in Athens, describes it as “the dream of every marine archaeologist”. It took ten years to excavate, and researchers are still studying the nearly 17 tonnes of treasures recovered. The vast cargo includes ebony, ivory, ostrich eggs, resin, spices, weapons, jewellery and textiles as well as ingots of copper, tin and glass.
But what really stunned archaeologists was that the artefacts on this one vessel came from at least 11 different cultures1 — from a gold scarab bearing the name of the Egyptian queen Nefertiti to copper from Cyprus and tin from central Asia.
The wreck provided tangible evidence of an astonishing array of contacts and trade between the different cultures of the Mediterranean and Near East in the late Bronze Age. The Ulu Burun ship sailed at around the time that Tutankhamun ruled Egypt, and “it is far more important than Tutankhamun’s tomb as a contribution to our understanding of the period”, according to Wachsmann. “This goes to the nitty gritty of the world. It’s Wall Street in a ship.”
Scouring the Aegean Sea for the world’s oldest shipwrecks.
A Bronze Age wreck called Ulu Burun shows how the remains of a single ship can transform archaeologists’ understanding of an era. Discovered in 1982, it lies about 9 kilometres southeast of Kaş in southern Turkey, and dates from around 1300 BC, a century or two after the Minoans disappeared.
Christos Agourides, secretary-general of the Hellenic Institute of Marine Archaeology in Athens, describes it as “the dream of every marine archaeologist”. It took ten years to excavate, and researchers are still studying the nearly 17 tonnes of treasures recovered. The vast cargo includes ebony, ivory, ostrich eggs, resin, spices, weapons, jewellery and textiles as well as ingots of copper, tin and glass.
But what really stunned archaeologists was that the artefacts on this one vessel came from at least 11 different cultures1 — from a gold scarab bearing the name of the Egyptian queen Nefertiti to copper from Cyprus and tin from central Asia.
The wreck provided tangible evidence of an astonishing array of contacts and trade between the different cultures of the Mediterranean and Near East in the late Bronze Age. The Ulu Burun ship sailed at around the time that Tutankhamun ruled Egypt, and “it is far more important than Tutankhamun’s tomb as a contribution to our understanding of the period”, according to Wachsmann. “This goes to the nitty gritty of the world. It’s Wall Street in a ship.”
A Japanese whistleblower is using the web and YouTube to document scientific fraud by a prominent Japanese researcher.
A Japanese whistleblower is using the web and YouTube to document scientific fraud by a prominent Japanese researcher.
Jigen has created separate Web sites for half a dozen cases in Japan in which he alleges scientific misconduct has occurred, and last week he posted details of what he believes is a case of image manipulation by researchers at a U.S. institution. The sites often include information about major grants and significant awards won by the scientist in question and any press releases from the institutions involved. The allegations against Kato are the first time Jigen has produced a video. He had previously used slide shows to make his point.
You can see his website here.
A Japanese whistleblower is using the web and YouTube to document scientific fraud by a prominent Japanese researcher.
Jigen has created separate Web sites for half a dozen cases in Japan in which he alleges scientific misconduct has occurred, and last week he posted details of what he believes is a case of image manipulation by researchers at a U.S. institution. The sites often include information about major grants and significant awards won by the scientist in question and any press releases from the institutions involved. The allegations against Kato are the first time Jigen has produced a video. He had previously used slide shows to make his point.
You can see his website here.
A new superconducting detector might supersede CCDs for astronomy
Good news: A new superconducting detector might supersede CCDs for large astronomical telescopes.
Ben Mazin, an astronomer at the University of California, Santa Barbara, believes that he is on the cusp of a camera breakthrough: his lab is working on a superconducting detector that could eventually replace the charge-coupled devices (CCDs) that have become de rigueur in both consumer and astronomical digital cameras. Mazin’s detectors, known as microwave kinetic inductance detectors (MKIDs), can simultaneously count photons, measure their energy and record each one’s time of arrival — something that CCDs can do only after the light is split with a prism or a grating, an extra step that adds to the loss of photons.
And you know that inevitably some variation of this technology is going to find its way into ordinary commercial products.
Good news: A new superconducting detector might supersede CCDs for large astronomical telescopes.
Ben Mazin, an astronomer at the University of California, Santa Barbara, believes that he is on the cusp of a camera breakthrough: his lab is working on a superconducting detector that could eventually replace the charge-coupled devices (CCDs) that have become de rigueur in both consumer and astronomical digital cameras. Mazin’s detectors, known as microwave kinetic inductance detectors (MKIDs), can simultaneously count photons, measure their energy and record each one’s time of arrival — something that CCDs can do only after the light is split with a prism or a grating, an extra step that adds to the loss of photons.
And you know that inevitably some variation of this technology is going to find its way into ordinary commercial products.
It doesn’t exist
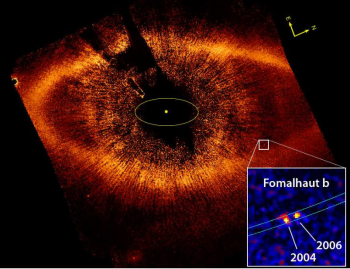
In a preprint paper published today on the Los Alamos astro-ph website, astronomers have concluded that the exoplanet orbiting the star Formalhaut might not exist. This planet, the first exoplanet ever thought to be directly imaged in visible light, was first described in a paper published in 2008, and was actually tracked in its orbit over several years, as shown in the image on the right.
The new research used the Spitzer Space Telescope to see if the planet’s heat could be detected in infrared wavelengths. Unfortunately, the scientists found nothing.
» Read more
A 33,000-year-old dog skull found in a Siberian cave, when compared with other ancient dog remains found in a Belgium cave, suggest to scientists that the domestication of dogs took place separately in many different places.
A 33,000-year-old dog skull found in a Siberian cave, when compared with other ancient dog remains found in a Belgium cave, suggest to scientists that the domestication of dogs took place separately in many different places.
A 33,000-year-old dog skull found in a Siberian cave, when compared with other ancient dog remains found in a Belgium cave, suggest to scientists that the domestication of dogs took place separately in many different places.
Cavers in West Virginia return a stalagmite to its original cave home after nearly fifty years
Cavers in West Virginia have returned a stalagmite to its original cave home after nearly fifty years above ground.
Cavers in West Virginia have returned a stalagmite to its original cave home after nearly fifty years above ground.
The biggest solar storm to be aimed at the Earth in seven years is expected to reach us by Tuesday.
The biggest coronal mass ejection to be aimed at the Earth in seven years is expected to reach us by Tuesday.
No need to panic. Not only is the storm still relatively mild compared to past eruptions, the airline and electrical industries are actually well prepared for this event. However, if you want to see the aurora, this will probably be a good opportunity.
The biggest coronal mass ejection to be aimed at the Earth in seven years is expected to reach us by Tuesday.
No need to panic. Not only is the storm still relatively mild compared to past eruptions, the airline and electrical industries are actually well prepared for this event. However, if you want to see the aurora, this will probably be a good opportunity.
This year’s hunt for meteorites in Antarctica bagged more than 300.
This year’s hunt for meteorites in Antarctica bagged more than 300.
This year’s hunt for meteorites in Antarctica bagged more than 300.
The dunes of Titan
A group of researchers have failed to reproduce the earlier NASA result that suggested arsenic-based life was possible.
A group of researchers have failed to reproduce the earlier NASA result that suggested arsenic-based life was possible.
One interesting aspect of this story is that the research results were discussed openly, with regular updates as the work was on-going, on one of the scientists blogs.
Redfield and her collaborators hope to submit their work to Science by the end of the month. She says that if Science refuses to publish the work because it has been discussed on blogs, it will become an important test case for open science.
A group of researchers have failed to reproduce the earlier NASA result that suggested arsenic-based life was possible.
One interesting aspect of this story is that the research results were discussed openly, with regular updates as the work was on-going, on one of the scientists blogs.
Redfield and her collaborators hope to submit their work to Science by the end of the month. She says that if Science refuses to publish the work because it has been discussed on blogs, it will become an important test case for open science.
Scientists have agreed to a sixty day voluntary pause in their research into the transmissibility of avian influenza, commonly called bird flu.
In a letter published jointly [pdf] in Science and Nature today, the researchers who have discovered how to easily transmit avian influenza — commonly called bird flu — have agreed to a sixty day voluntary pause in their research.
Despite the positive public health benefits these studies sought to provide, a perceived fear that the ferret-transmissible H5 HA viruses may escape from the laboratories has generated intense public debate in the media on the benefits and potential harm of this type of research. We would like to assure the public that these experiments have been conducted with appropriate regulatory oversight in secure containment facilities by highly trained and responsible personnel to minimize any risk of accidental release. Whether the ferret-adapted influenza viruses have the ability to transmit from human to human cannot be tested. We recognize that we and the rest of the scientific community need to clearly explain the benefits of this important research and the measures taken to minimize its possible risks. We propose to do so in an international forum in which the scientific community comes together to discuss and debate these issues. We realize that organizations and governments around the world need time to find the best solutions for opportunities and challenges that stem from the work. To provide time for these discussions, we have agreed on a voluntary pause of 60 days on any research involving highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 viruses leading to the generation of viruses that are more transmissible in mammals. In addition, no experiments with live H5N1 or H5 HA reassortant viruses already shown to be transmissible in ferrets will be conducted during this time.
The situation is difficult. This research is important as it helps scientists understand how flu is transmitted. At the same time, this research is very dangerous, as it could be used by evil people to kill millions.
In a letter published jointly [pdf] in Science and Nature today, the researchers who have discovered how to easily transmit avian influenza — commonly called bird flu — have agreed to a sixty day voluntary pause in their research.
Despite the positive public health benefits these studies sought to provide, a perceived fear that the ferret-transmissible H5 HA viruses may escape from the laboratories has generated intense public debate in the media on the benefits and potential harm of this type of research. We would like to assure the public that these experiments have been conducted with appropriate regulatory oversight in secure containment facilities by highly trained and responsible personnel to minimize any risk of accidental release. Whether the ferret-adapted influenza viruses have the ability to transmit from human to human cannot be tested. We recognize that we and the rest of the scientific community need to clearly explain the benefits of this important research and the measures taken to minimize its possible risks. We propose to do so in an international forum in which the scientific community comes together to discuss and debate these issues. We realize that organizations and governments around the world need time to find the best solutions for opportunities and challenges that stem from the work. To provide time for these discussions, we have agreed on a voluntary pause of 60 days on any research involving highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 viruses leading to the generation of viruses that are more transmissible in mammals. In addition, no experiments with live H5N1 or H5 HA reassortant viruses already shown to be transmissible in ferrets will be conducted during this time.
The situation is difficult. This research is important as it helps scientists understand how flu is transmitted. At the same time, this research is very dangerous, as it could be used by evil people to kill millions.
Scientists have postponed until 2015 the decision on whether clocks should be linked to the Earth’s rotation around the Sun.
Scientists have postponed until 2015 the decision on whether clocks should be linked to the Earth’s rotation around the Sun.
Scientists have postponed until 2015 the decision on whether clocks should be linked to the Earth’s rotation around the Sun.
Catching the death of a comet
Catching the death of a comet.
Catching the death of a comet.
A science journal for failed experiments
A new science journal for publishing the results of failed experiments.
A new science journal for publishing the results of failed experiments.
More cracks found in the wings of the Airbus A380
Not good: More cracks found in the wings of an Airbus A380.
Not good: More cracks found in the wings of an Airbus A380.
A meteorite that fell to Earth last July in Morocco has proven to be a rare chunk of Mars.
A meteorite that fell to Earth last July in Morocco has proven to be a rare chunk of Mars.
A meteorite that fell to Earth last July in Morocco has proven to be a rare chunk of Mars.
The hi-tech home of a British soccer star has become a threat to radio astronomy.
Who knew? The hi-tech home of a British soccer star has become a threat to radio astronomy.
Who knew? The hi-tech home of a British soccer star has become a threat to radio astronomy.
