The North Star has spots!
Astronomers using an array of six ground-based telescopes have obtained best new data of Polaris, the North Star, including the first rough image of its surface, and discovered sunspots on its surface.
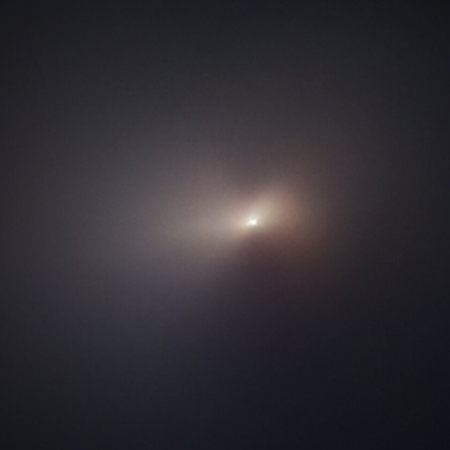
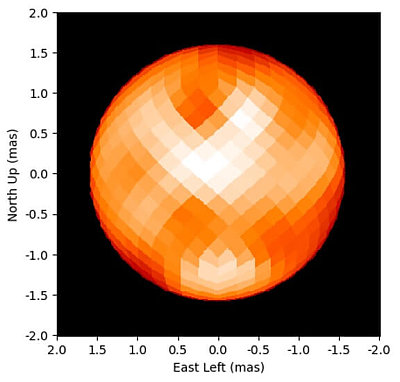
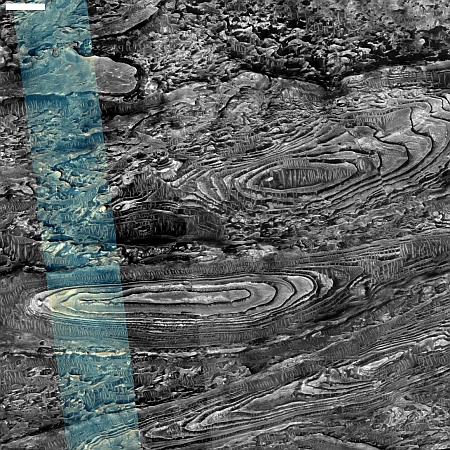
You can read the paper here [pdf]. The image to the right, taken from figure 4 of the paper, shows the surface as seen by the telescopes over two nights in April 2021. Polaris is what astronomers call a Cepheid variable star, which changes brightness on a very precise schedule as its diameter grows and shrinks. In the case of Polaris, that variation is four days long. The star’s brightness itself varies only slightly, and over the decades has even at times appeared to cease its variations.
As the true brightness of Cepheids is very predictable based on their pulse rate, these stars are one of the main tools astronomers use to determine distances to other galaxies. Knowing more about them thus has great importance to cosmological research.
The orbital motion showed that Polaris has a mass five times larger than that of the Sun. The images of Polaris showed that it has a diameter 46 times the size of the Sun.
The biggest surprise was the appearance of Polaris in close-up images. The CHARA observations provided the first glimpse of what the surface of a Cepheid variable looks like. “The CHARA images revealed large bright and dark spots on the surface of Polaris that changed over time,” said Gail Schaefer, director of the CHARA Array. The presence of spots and the rotation of the star might be linked to a 120-day variation in measured velocity.
The researchers plan to take regular images again of Polaris to better track the changes to its surface.
Astronomers using an array of six ground-based telescopes have obtained best new data of Polaris, the North Star, including the first rough image of its surface, and discovered sunspots on its surface.
You can read the paper here [pdf]. The image to the right, taken from figure 4 of the paper, shows the surface as seen by the telescopes over two nights in April 2021. Polaris is what astronomers call a Cepheid variable star, which changes brightness on a very precise schedule as its diameter grows and shrinks. In the case of Polaris, that variation is four days long. The star’s brightness itself varies only slightly, and over the decades has even at times appeared to cease its variations.
As the true brightness of Cepheids is very predictable based on their pulse rate, these stars are one of the main tools astronomers use to determine distances to other galaxies. Knowing more about them thus has great importance to cosmological research.
The orbital motion showed that Polaris has a mass five times larger than that of the Sun. The images of Polaris showed that it has a diameter 46 times the size of the Sun.
The biggest surprise was the appearance of Polaris in close-up images. The CHARA observations provided the first glimpse of what the surface of a Cepheid variable looks like. “The CHARA images revealed large bright and dark spots on the surface of Polaris that changed over time,” said Gail Schaefer, director of the CHARA Array. The presence of spots and the rotation of the star might be linked to a 120-day variation in measured velocity.
The researchers plan to take regular images again of Polaris to better track the changes to its surface.