The largest sunspot in years appears on the sun
The largest sunspot in years has appeared on the sun.
The largest sunspot in years has appeared on the sun.
The largest sunspot in years has appeared on the sun.
The global output of atmospheric carbon dioxide jumped in 2010 by the biggest amount on record, according to the U.S. Department of Energy.
In 2007 when the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change issued its last large report on global warming, it used different scenarios for carbon dioxide pollution and said the rate of warming would be based on the rate of pollution. Boden said the latest figures put global emissions higher than the worst case projections from the climate panel.
And yet, the global temperatures are not rising, as also predicted by those same IPCC models.
Finding ET by looking for their city lights.
With the end of the Mar500 simulated mission this coming Friday, the Russians are now proposing an eighteen month simulated Mars mission on board the International Space Station.
The Russians have been pushing to do this on ISS for years. Unfortunately, NASA has always resisted.
Yet, as I wrote in Leaving Earth, we will never be able to send humans to any other planets until we have flown at least one simulated mission, in zero gravity in Earth orbit, beforehand. Wernher von Braun pointed out this reality out back in the 1950s, and that reality has not changed in the ensuing half century. Not only will such a mission tell us a great deal about the medical issues of living in weightlessness for years at a time — issues that are far from trivial — it will give us the opportunity to find out the engineering problems of building a vessel capable of keeping humans alive during interplanetary flight, far from Earth.
» Read more
The law is such an inconvenient thing: White House officials held technology talks with China, despite a law banning such talks.
In [a General Accountability Office (GAO)] letter, Gibson said OSTP officials violated U.S. law by participating in May in bilateral discussions with Chinese officials in spite of a language included in a 2011 spending bill enacted in April that specifically prohibited such talks. GAO concluded that OSTP officials violated the Anti-Deficiency Act, which prohibits U.S. government employees from spending money that Congress has not appropriated. “If Congress specifically prohibits a particular use of appropriated funds, any obligation for that purpose is in excess of the amount available,” Gibson wrote in the Oct. 11 letter. In May, OSTP officials spent approximately $3,500 to participate in discussions and a dinner with Chinese government officials, according to the GAO letter.
[Congressman Frank] Wolf (R-Virginia), a vocal critic of China’s human rights policies who also testified at the hearing, inserted the language in the 2011 spending bill barring OSTP and NASA from participating in any bilateral activities with China. “Following the law is not voluntary for administration officials,” Wolf said. [emphasis mine]
Sadly, it appears that this administration does not agree with Wolf, and instead considers the law to be nothing more than vague advice they can ignore at will.
What could possibly go wrong? A National Research Council panel today proposed creating a massive data research network using the private health records of patients.
As a pilot project, the report recommends sequencing the whole genomes of 1 million Americans and combining the data with medical histories to look for genetic links to disease. That may sound expensive—even if sequencing costs drop to $1000 per genome, it would cost $1 billion—but $1000 is in the range of what a routine MRI scan costs, Desmond-Hellmann pointed out. Another pilot project would use metabolomic profiles of patients’ blood to help predict which patients with insulin resistance will go on to develop type II diabetes.
Creating the network over the next decade or two shouldn’t require new funding, the report says. “This is not the Human Genome Project,” said Sawyers. “It’s taking advantage of things happening anyway and bringing them together and doing it at the point of care.” NIH needs to redirect resources and push for more long-term studies that combine research with health care, the report says. Building the network might also require a revision of patient privacy rules and an “evolution” in the public’s attitudes about allowing researchers to use their medical data. [emphasis mine]
The last sentence, highlighted by me, was also the last sentence in the article, added almost as a minor aside. Yet, it is probably the most important aspect of this story, since the right of each of us to control our personal health records is directly threatened by this proposal.
Astronomers prepare for an asteroid fly-by on November 8, using the Earth as the spacecraft.
Large enough to cause regional devastation if it were to hit the Earth, 2005 YU55 is the closest pass by an asteroid this big since 1976, and there won’t be another until 2028. The near miss provides an unparallelled opportunity for radar, optical and infrared observations of a mysterious charcoal-black world similar to the type of asteroid that astronauts may one day set foot on.
Radar bonanza “It’s a bit like a spacecraft fly-by with the Earth being the spacecraft,” says astronomer Don Yeomans at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California. “It’s going to be an extraordinary target for radar.”
Sailing without a compass: the Viking’s sunstone revealed?
A series of technical problems have forced engineers to temporarily halt science operations on Mars Express.
Another scientist who doesn’t understand science: A former biologist at the Smithsonian National Zoo’s Migratory Bird Center has been found guilty of attempting to poison feral cats in Washington, DC.
It isn’t her crime here that disturbs me. It is her own research and testimony during her trial:
In addition to the videotaped evidence, prosecutors also introduced evidence that Dauphiné has a long history advocating in academic literature for the control of feral cat populations in order to protect native bird populations. In one paper, in the 2009 Proceedings of the Fourth International Partners in Flight Conference: Tundra to Tropics, Dauphiné and co-author Robert J. Cooper, a wildlife biologist at the University of Georgia in Athens, argue that feral cats kill upwards of 1 billion birds in the United States every year. They also argue that the “trap-neuter-release” model for population control, which is advocated by many animal rights organizations, does a poor job of managing feral cat populations.
Yesterday, Judge Truman A. Morrison III noted in his remarks that, during Dauphiné’s testimony during the trial, she declined to discuss whether she agreed with various academic papers on which she was listed as an author, and said she wasn’t familiar with many of their statements about the danger that feral cats pose to birds. In delivering his verdict, Morrison said that the notion that Dauphiné wouldn’t be familiar with papers she authored or co-authored “doesn’t have the ring of the truth.” He also “found that her inability, indeed her unwillingness to own up to her own professional writings … undermined her credibility.” [emphasis mine]
First, the claim that feral cats kill a billion birds a year in the U.S. seems extremely implausible. Second, for this scientist to then pretend she “wasn’t familiar” with this claim, written in her own work, tells us just how untrustworthy she and her work are.
Why even peer-reviewed research must always be questioned: An investigation has concluded that a fired Dutch researcher falsified data on dozens of papers.
[Diederik] Stapel’s work encompassed a broad range of attention-catching topics, including the influence of power on moral thinking and the reaction of psychologists to a plagiarism scandal. The committee, which interviewed dozens of Stapel’s former students, postdoctoral researchers, co-authors, and colleagues, found that Stapel alone was responsible for the fraud. The panel reported that he would discuss in detail experimental designs, including drafting questionnaires, and would then claim to conduct the experiments at high schools and universities with which he had special arrangements. The experiments, however, never took place, the universities concluded. Stapel made up the datasets, which he then gave the student or collaborator for analysis, investigators allege. In other instances, the report says, he told colleagues that he had an old dataset lying around that he hadn’t yet had a chance to analyze. When Stapel did conduct actual experiments, the committee found evidence that he manipulated the results.
I’m not sure which is worst about this scandal, that Stapel’s dishonesty has tainted the PhD’s of 21 innocent students, or that none of his fellow researchers ever had the brains, skepticism, or mental muscle to challenge his results.
Stapel’s fabrications weren’t particularly sophisticated, the committee says, and on careful inspection many of the datasets have improbable effect sizes and other statistical irregularities. His colleagues, when they failed to replicate the results, tended to blame themselves, the report says. Among Stapel’s colleagues, the description of data as too good to be true “was a heartfelt compliment to his skill and creativity,” the report says.
Update: I’d like to add one more addendum to this story, (covered today by Nature with its own long article). Unlike the climate field, where the scientists circled the wagons and protected the scientists who committed the frauds with whitewashed investigations, the field of social psychology and the scientists in the Netherlands have been refreshingly blunt and forthright in trying to clear the air by tracking down all Stapel’s corrupt papers. For this at least they deserve kudos.
Though it has been very clear for the past few months that the sun has finally transitioned from solar minimum and begun its ramp up to solar maximum, that ramp up has also been very slow and wimpy.
On October 9, 2011 the scientists at Physikalisch- Meteorologisches Observatorium Davos (PMOD) posted an updated summary of the satellite data that has been carefully measuring the variation of the sun’s total solar irradiance since 1978. The graph below, which can be found here [pdf], brings that data up through the present. (I had posted the previous update about a year ago.)
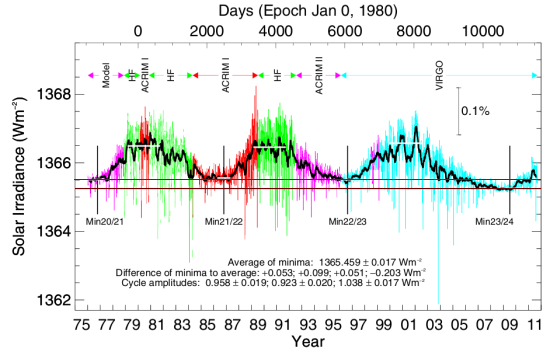
I have added a brown line to illustrate how deep the recently ended solar minimum was, compared to previous minimums. Note also that this most recent minimum would also be far below the minimum prior to 1975. I have also added a blue line to show that the sun has only very recently finally brightened enough to finally exceed the previous minimum. All told, the sun remained dimmer than the previous minimum for over five years!
» Read more
The lead scientist in a recent climate study has been accused of hiding the fact that the global temperature has been flat for more than a dozen years.
The new study, led by Richard Muller, had taken raw land data and re-analyzed it in an attempt to clear up the doubts caused by the climategate scandal. In an announcement last week, Muller claimed that their work had proven that the climate had been warming continuously since 1950.
Now, another climate scientist, Judith Curry, has accused Muller of failing to point out that his same re-analysis had also shown that climate temperatures have been totally flat for the past 13 years, even as carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere continue to rise. As Curry told the Daily Mail, “This is nowhere near what the climate models were predicting. Whatever it is that’s going on here, it doesn’t look like it’s being dominated by CO2.”
Curry is also accusing Muller of going to the press to spin the results in favor of global warming, before the research was complete.
» Read more
A team of scientists from Japan have found evidence that the human settlement of the Marshall Islands in the central Pacific Ocean occurred almost immediately after those islands emerged from beneath the sea. Though it had been previously believed that a thousand years had to pass until these newly emerged islands had developed sufficient vegetation for humans to occupy them, the evidence from this study shows that humans not only showed up almost immediately, they acted to vegetate the island themselves in order to make it habitable.
The scientists drilled four cores just off the western shore of Laura Island, the largest island of Majuro Atoll, as well as thirteen trenches on that same island, in order to determine when the island first emerged from under the sea. They also excavated a well-preserved bank at the center of Laura Island to study the human occupation of the island.
What they found was that the Atoll emerged from underwater approximately 2000 years ago, triggered by a fall in sea level. More surprising, the first evidence of human settlement appeared to occur at almost the same time.
» Read more
A giant sequoia has fallen in Giant Sequoia National Monument in California. You can see a very short video of the event, captured by a German tourist, here.
The Mars500 crew prepares to open the hatch after seventeen months of a simulated mission to Mars.
What could possibly go wrong? Automakers are developing technology to let cars drive themselves.
Chile’s powerful Cerro Hudson volcano has come back to life and is threatening a major eruption.
Patagonians are worried. Many remember Mount Hudson’s catastrophic eruptions of 1971 and 1991. The latter eruption was one of the most violent registered eruptions in Chile, and lasted for five months. At its peak it turned day into night, making the banks of nearby Huemules, Cupquelan and Ibáñez Rivers collapse with ash. Many areas in the region are still covered with ash, pumice and other volcanic rocks. “These are the characteristics of this highly explosive volcano,” said Juan Cayupi, a volcanologist at the National Emergency Office.
The first year’s hunt by the Large Hadron Collider for the Higgs particle is ending.
Vivek Sharma of the University of California, San Diego, who heads the search for the Higgs at [one experiment], points out that results . . . have already ruled out, with a confidence of 2 sigma, a Higgs mass of between about 145 and 400 gigaelectronvolts, and that the LHC’s predecessor, the Large Electron Positron collider, ruled out a Higgs mass below about 114 gigaelectronvolts. So the Higgs, if it exists, almost certainly lies in the gap between the two. According to Sharma, the extra data to be collected in 2012 once proton-proton collisions resume in March will allow the CERN scientists to “either find the Higgs in this mass range, or wipe it out”.
If the Higgs particle turns out not to exist, it will mean that physicists will have to go back to the drawing board to explain all the phenomenon seen in the subatomic world.
A congressional report today revealed that two American climate satellites were attacked by hackers in the past four years.
In October 2007 and July 2008, a NASA-managed Landsat-7 satellite experienced 12 or more minutes of interference, and a Terra AM-1 satellite was disrupted for two minutes in June 2008 and again that October for nine minutes, according to Bloomberg Businessweek’s analysis of the annual report by the U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission. The report says the hackers gained access to the satellites — both are used for Earth climate and terrain monitoring — through the Svalbard Satellite Station in Spitsbergen, Norway. It’s believed the attackers may have hijacked the Internet connection at the Norway ground station to interfere with the operation of the satellites.
According to Robert Zubrin, the Obama administration is planning to terminate all funding to NASA’s planetary program, while cutting back significantly on its astronomy program.
Word has leaked out that in its new budget, the Obama administration intends to terminate NASA’s planetary exploration program. The Mars Science Lab Curiosity, being readied on the pad, will be launched, as will the nearly completed small MAVEN orbiter scheduled for 2013, but that will be it. No further missions to anywhere are planned. After 2013, America’s amazing career of planetary exploration, which ran from the Mariner probes in the 1960s through the great Pioneer, Viking, Voyager, Pathfinder, Mars Global Surveyor, Mars Odyssey, Spirit, Opportunity, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, Galileo and Cassini missions, will simply end.
Furthermore, the plan from the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) also leaves the space astronomy program adrift and headed for destruction. The now-orbiting Kepler Telescope will be turned off in midmission, stopping it before it can complete its goal of finding other Earths. Even worse, the magnificent Webb Telescope, the agency’s flagship, which promises fundamental breakthroughs in our understanding of the laws of the universe, is not sufficiently funded to allow successful completion. This guarantees further costly delays, with the ensuing budgetary overruns leading inevitably to eventual cancellation.
I suspect these cuts have been leaked now, months before the budget is publicly released, in order to whip up support for funding these programs. I also find it distressing that these programs, which cost practically nothing, are targets, while others that cost many many more billions (in NASA and elsewhere) remain fully funded.
An international research team has diagnosed the oldest known case of prostate cancer in ancient Egypt and the second oldest case in the world, from a mummy 2250 years old.
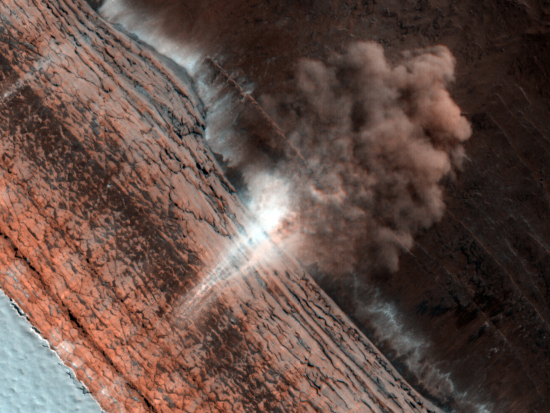
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter team today released this really cool image from Mars, showing an avalanche near the North Pole, in progress. The image looks directly down the cliff face from above. At the base of the cliff we can see the dust cloud from the crash of material billowing out away from the scarp.
What impresses me most about this image is that it was taken by an orbiting spacecraft approximately 200 miles above the planet’s surface, moving at thousands of miles an hour. Yet, the camera not only had the resolution to see the cloud of dust, it could snap the image fast enough to capture the actual fall of material (the white wisps down the side of the cliff that are reminiscent of a waterfall).
Also intriguing is the visible steep face of the cliff face itself. I know a lot of rock climbers who would love to literally get their hands (and chocks) on that rock face. And in Mars’s one-third gravity, rock climbing would surely be different.

Britain’s Royal Society has made its archive freely accessible online.
This covers everything published from 1665 to 1941.
Scientists today confirmed that the fungus, Geomyces destructans, causes white nose syndrome, the deadly killer that has been wiping out cave-hibernating bats throughout the eastern United States.
A science team led by David Blehert of the National Wildlife Health Center in Madison, Wisconsin captured healthy little brown bats and infected them with the fungus while they were in hibernation, some by direct application and others by putting them in contact with already infected bats. After 102 days, all of the first group had developed white nose on their muzzles and wings, while 16 of 18 of the second group had become infected as well.
» Read more
The battle in Congress over the EPA’s effort to regulate dust.
Not surprisingly, the Democrats all support the EPA’s effort, while there are Republicans who oppose. What I consider significant is that more than a hundred agricultural organizations oppose the regulations.
One of the agricultural groups that is supporting the bill [to block the EPA regulations], the National Association of Wheat Growers (NAWG), wrote a letter to the committee last month, saying that a slight raise in overall particulate matter standards would require the EPA to regulate farm dirt under the current standards. “And, for what purpose? Scientific studies have never shown rural dust to be a health concern at ambient levels,” said the NAWG letter. [emphasis mine]
NASA has ended its underwater mission early due to an approaching hurricane.