Tag: science
Tracing the Canals of Mars
“A good scientist is a humble and listening scientist and not one that is sure 100 percent in what he read in the textbooks.”
Water from comets
New results using the Herschel Space Telescope suggest that Earth’s water was brought here by comets.
New results using the Herschel Space Telescope suggest that Earth’s water was brought here by comets.
Astronomers have found a dozen supernovae taking place closer to the Big Bang than ever detected.
Astronomers have found a dozen supernovae taking place only a few billion years after the Big Bang.
[The results suggest that these types of supernovae] were exploding about five times more frequently 10 billion years ago than they are today. These supernovas are a major source of iron in the universe, the main component of the Earth’s core and an essential ingredient of the blood in our bodies.
Astronomers have found a dozen supernovae taking place only a few billion years after the Big Bang.
[The results suggest that these types of supernovae] were exploding about five times more frequently 10 billion years ago than they are today. These supernovas are a major source of iron in the universe, the main component of the Earth’s core and an essential ingredient of the blood in our bodies.
Aden Meinel, astronomer and innovator, has passed away
Aden Meinel, astronomer and innovator, has passed away.
Meinel, first director of the Kitt Peak Observatory, was the also first to conceive and try to build robotic telescopes that could be operated remotely. Many of his ideas were later incorporated both on the ground and in space.
Aden Meinel, astronomer and innovator, has passed away.
Meinel, first director of the Kitt Peak Observatory, was the also first to conceive and try to build robotic telescopes that could be operated remotely. Many of his ideas were later incorporated both on the ground and in space.
The sun’s activity goes boom
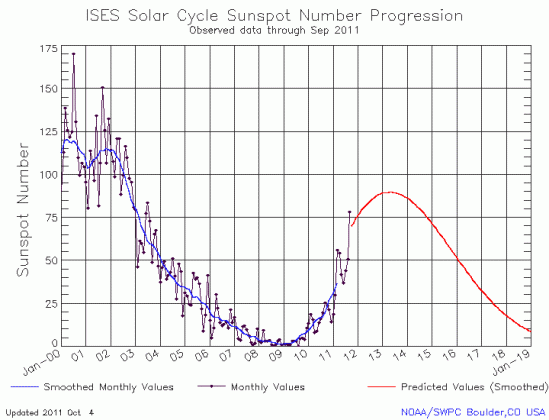
Today NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center released its monthly graph of the Sun’s solar cycle sunspot activity. Posted below, it shows the Sun’s activity finally leaping upward in September, after several months of less than expected performance.
It is interesting to see how the sun’s rising sunspot activity for the past year has followed a consistent fluctuating pattern, whereby a sudden monthly jump in sunspots is then followed by several months of decline. If this pattern repeats itself again, we should expect to see the numbers ease off again in October and November.
Regardless, the higher sunspot counts for September are more in line with past predictions. In fact, the solar scientists at the Marshall Space Flight Center have increased their prediction for the time and intensity for the peak of the sun’s maximum. Last month they had called for a peak in May 2013 with a sunspot number of 70. Now, they are predicting the peak will come in April 2013 with a number of 77. They note however that even this higher number will result in the weakest maximum in more than a hundred years.
A summary of Messenger’s first six months in orbit around Mercury
A summary of Messenger’s first six months in orbit around Mercury.
Though packed with lots of results, this strikes me as the most interesting discovery so far:
Orbital data reveal that Mercury’s magnetic field is offset far to the north of the planet’s center, by nearly 20% of Mercury’s radius. Relative to the planet’s size, this offset is much more than in any other planet, and accounting for it will pose a challenge to theoretical explanations of the field. . . . This finding has several implications for other aspects of Mercury, says Anderson, who co-authored several of the presentations in the MESSENGER session. “This means that the magnetic field in the southern hemisphere should be a lot weaker than it is in the north. At the north geographic pole, the magnetic field should be about 3.5 times stronger than it is at the south geographic pole.
A summary of Messenger’s first six months in orbit around Mercury.
Though packed with lots of results, this strikes me as the most interesting discovery so far:
Orbital data reveal that Mercury’s magnetic field is offset far to the north of the planet’s center, by nearly 20% of Mercury’s radius. Relative to the planet’s size, this offset is much more than in any other planet, and accounting for it will pose a challenge to theoretical explanations of the field. . . . This finding has several implications for other aspects of Mercury, says Anderson, who co-authored several of the presentations in the MESSENGER session. “This means that the magnetic field in the southern hemisphere should be a lot weaker than it is in the north. At the north geographic pole, the magnetic field should be about 3.5 times stronger than it is at the south geographic pole.
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Researcher Fired Amidst New Controversy
Office politics in science: Chronic fatigue syndrome researcher fired amidst new controversy.
I read this story and wonder if these scientists are as bad as politicians.
Office politics in science: Chronic fatigue syndrome researcher fired amidst new controversy.
I read this story and wonder if these scientists are as bad as politicians.
A global map of Titan, in color
The 2011 Nobel Prize for Physics has been awarded
The 2011 Nobel Prize for Physics has been awarded to the astronomers who discovered dark energy.
Saul Perlmutter from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and University of California, Berkeley, has been awarded half of this year’s prize for his work on the Supernova Cosmology Project, with the other half awarded to Brian P. Schmidt from the Australian National University and Adam G. Riess from the Johns Hopkins University and Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, for their work on the High-z Supernova Search Team.
The 2011 Nobel Prize for Physics has been awarded to the astronomers who discovered dark energy.
Saul Perlmutter from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and University of California, Berkeley, has been awarded half of this year’s prize for his work on the Supernova Cosmology Project, with the other half awarded to Brian P. Schmidt from the Australian National University and Adam G. Riess from the Johns Hopkins University and Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, for their work on the High-z Supernova Search Team.
For an extraterrestrial skiing experience, Enceladus is the place to go.
The strange hollows on the mountain tops of Mercury
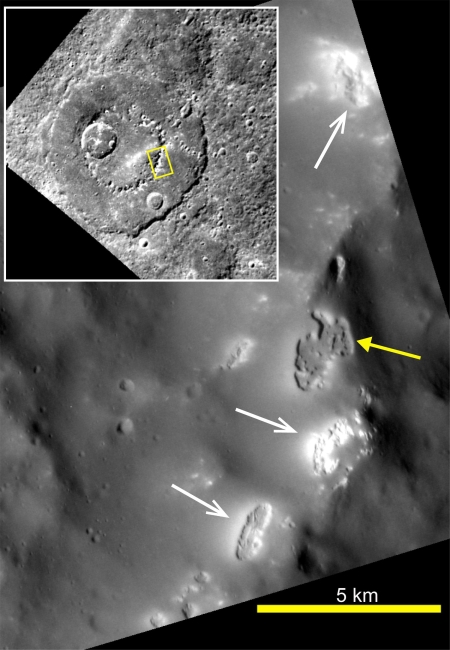
Another spectacular planetary science image, this time from Messenger orbiting Mercury. This close-up image of the hollows of Mercury only illustrates their mystery. The insert shows the context of the close-up image. These irregular sinks are here found on the mountain top ridge of an inner crater rim. Also, some but not all of the hollows have bright interiors.
Scientists have proposed that some form of impact melt process caused these hollows. At impact, the ground literally rippled like water when you toss a stone into a pool. Here, however, the molten ripples quickly froze, creating the inner and outer crater rim rings. To my untrained eye, the hollows look like collapse features where the surface hardened first, then collapsed when the molten inner material drained away as it became solid.
Why some hollows are bright, however, is not yet understood.
Dawn begins close-up orbit observations
Dawn begins close-up orbit observations of Vesta. More new results here.
In this orbit, the average distance from the spacecraft to the Vesta surface is 420 miles (680 kilometers), which is four times closer than the previous survey orbit.
Dawn begins close-up orbit observations of Vesta. More new results here.
In this orbit, the average distance from the spacecraft to the Vesta surface is 420 miles (680 kilometers), which is four times closer than the previous survey orbit.
The red cliffs of Mars
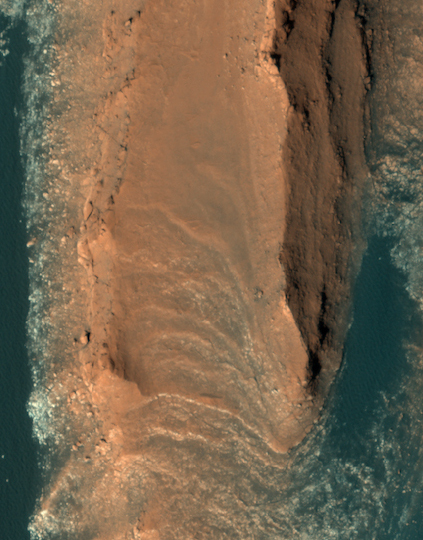

Last week the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter team released this beautiful image of what they call “layered yardangs” on Mars.
What creates these sharp ridges? This layered terrain has been sculpted by the wind. The aligned ridges are called yardangs, which are formed in areas where the dominant erosional force is the wind. Yardangs are also found on Earth, usually in very dry areas.
What I see are majestic red cliffs rising out of a aqua-colored sand desert. What a place to visit!
Scientist proposes that the superluminal neutrinos are merely measuring the true speed of light
On Thursday physicist Susan Gardner of the University of Kentucky proposed in a preprint on the Los Alamos astro-ph website that the neutrinos measured at CERN that appeared to be going faster than light were merely giving us a much more accurate measure of the speed of light.
This is only one of a plethora of papers published this last week on astro-ph discussing and attacking the CERN neutrino results. I expect the scientists will solve this mystery before too long.
On Thursday physicist Susan Gardner of the University of Kentucky proposed in a preprint on the Los Alamos astro-ph website that the neutrinos measured at CERN that appeared to be going faster than light were merely giving us a much more accurate measure of the speed of light.
This is only one of a plethora of papers published this last week on astro-ph discussing and attacking the CERN neutrino results. I expect the scientists will solve this mystery before too long.
Arctic ozone loss at record level
The ozone levels over the Arctic this past year were the lowest on record, caused by unusually cold temperatures.
No records for low temperature were set this year, but the air remained at its coldest for an unusually long period of time, and covered an unusually large area. In addition, the polar vortex was stronger than usual. Here, winds circulate around the edge of the Arctic region, somewhat isolating it from the main world weather systems.
“Why [all this] occurred will take years of detailed study,” said Dr. [Michelle] Santee [from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory]. “It was continuously cold from December through April, and that has never happened before in the Arctic in the instrumental record.”
The ozone levels over the Arctic this past year were the lowest on record, caused by unusually cold temperatures.
No records for low temperature were set this year, but the air remained at its coldest for an unusually long period of time, and covered an unusually large area. In addition, the polar vortex was stronger than usual. Here, winds circulate around the edge of the Arctic region, somewhat isolating it from the main world weather systems.
“Why [all this] occurred will take years of detailed study,” said Dr. [Michelle] Santee [from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory]. “It was continuously cold from December through April, and that has never happened before in the Arctic in the instrumental record.”
Science, Lies, and Videotape
Mars atmosphere has more water vapor than predicted
Data from Mars Express has found that the Martian upper atmosphere has far more water vapor than predicted.
“The vertical distribution of water vapour is a key factor in the study of Mars’ hydrological cycle, and the old paradigm that it is mainly controlled by saturation physics now needs to be revised,” said Luca Maltagliati [of the Laboratoire Atmosphères, Milieux, Observations Spatiales (LATMOS) in Guyancourt, France]. “Our finding has major implications for understanding the planet’s global climate and the transport of water from one hemisphere to the other.”
“The data suggest that much more water vapour is being carried high enough in the atmosphere to be affected by photodissociation,” added Franck Montmessin, also from LATMOS, who is the Principal Investigator for SPICAM and a co-author of the paper. “Solar radiation can split the water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen atoms, which can then escape into space. This has implications for the rate at which water has been lost from the planet and for the long-term evolution of the Martian surface and atmosphere.”
Data from Mars Express has found that the Martian upper atmosphere has far more water vapor than predicted.
“The vertical distribution of water vapour is a key factor in the study of Mars’ hydrological cycle, and the old paradigm that it is mainly controlled by saturation physics now needs to be revised,” said Luca Maltagliati [of the Laboratoire Atmosphères, Milieux, Observations Spatiales (LATMOS) in Guyancourt, France]. “Our finding has major implications for understanding the planet’s global climate and the transport of water from one hemisphere to the other.”
“The data suggest that much more water vapour is being carried high enough in the atmosphere to be affected by photodissociation,” added Franck Montmessin, also from LATMOS, who is the Principal Investigator for SPICAM and a co-author of the paper. “Solar radiation can split the water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen atoms, which can then escape into space. This has implications for the rate at which water has been lost from the planet and for the long-term evolution of the Martian surface and atmosphere.”
Scientists push for monitoring network to collect environmental and socioeconomic data from around the world
What could go wrong? Scientists push for a monitoring network to collect environmental and socioeconomic data from around the world.
Sandy Andelman, an ecologist with Conservation International in Arlington, Virginia, discussed her work setting up a pilot project that began two years ago in southern Tanzania. In addition to basic environmental data about soils, nutrients and land cover, the project tracks agricultural practices. It also incorporates data about income, health and education that is maintained by the government. Andelman says that all the data she collects can be broken down to the level of individual households, and that initial results from the project have already prompted the Tanzanian government to adjust the way it zones agricultural land in the area. [emphasis mine]
Lord help the farmers whose lives will be tracked by this network.
What could go wrong? Scientists push for a monitoring network to collect environmental and socioeconomic data from around the world.
Sandy Andelman, an ecologist with Conservation International in Arlington, Virginia, discussed her work setting up a pilot project that began two years ago in southern Tanzania. In addition to basic environmental data about soils, nutrients and land cover, the project tracks agricultural practices. It also incorporates data about income, health and education that is maintained by the government. Andelman says that all the data she collects can be broken down to the level of individual households, and that initial results from the project have already prompted the Tanzanian government to adjust the way it zones agricultural land in the area. [emphasis mine]
Lord help the farmers whose lives will be tracked by this network.
NASA has identified ninety percent of the largest near-Earth asteroids
Data from the infrared telescope WISE has now identified ninety percent of the largest near-Earth asteroids.
NASA researchers also downgraded their estimate of the number of medium-sized asteroids, saying there are 44 percent fewer than previously believed. The downside is that scientists have yet to find many of these mid-sized asteroids, which could destroy a metropolitan city.
Data from the infrared telescope WISE has now identified ninety percent of the largest near-Earth asteroids.
NASA researchers also downgraded their estimate of the number of medium-sized asteroids, saying there are 44 percent fewer than previously believed. The downside is that scientists have yet to find many of these mid-sized asteroids, which could destroy a metropolitan city.
Mercury is weirder than scientists thought.
Messenger’s data has found that Mercury is weirder than scientists thought.
Messenger’s data has found that Mercury is weirder than scientists thought.
Energy Department approves $737 million solar loan guarantee
More money wasted? The Energy Department has approved another solar power company loan guarantee, this for $737 million.
I’m not sure this project will go belly-up, as Solyndra did. I just find it questionable for this to be approved at this moment.
More money wasted? The Energy Department has approved another solar power company loan guarantee, this for $737 million.
I’m not sure this project will go belly-up, as Solyndra did. I just find it questionable for this to be approved at this moment.
A new report from the EPA Office of the Inspector General has said that EPA violated its own peer review process in determining that greenhouse gases endanger “the public health and welfare.”
A new report from the EPA Office of the Inspector General has said that EPA violated its own peer review process in determining that greenhouse gases endanger “the public health and welfare.”
A new report from the EPA Office of the Inspector General has said that EPA violated its own peer review process in determining that greenhouse gases endanger “the public health and welfare.”
The coming blindness of astronomy

The European Southern Observatory today released this infrared image today of what astronomers have named the Fried Egg Nebula. Taken by the Very Large Telescope in Chile, the picture shows the concentric dust shells surrounding a post-red supergiant star, thought to be transitioning to the next stage of stellar evolution called a yellow hypergiant. As the press release explains,
The monster star, known to astronomers as IRAS 17163-3907, has a diameter about a thousand times bigger than our Sun. At a distance of about 13 000 light-years from Earth, it is the closest yellow hypergiant found to date and new observations show it shines some 500 000 times more brightly than the Sun. . . . If the Fried Egg Nebula were placed in the centre of the Solar System the Earth would lie deep within the star itself and the planet Jupiter would be orbiting just above its surface. The much larger surrounding nebula would engulf all the planets and dwarf planets and even some of the comets that orbit far beyond the orbit of Neptune. The outer shell has a radius of 10 000 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun.
Yellow hypergiants are in an extremely active phase of their evolution, undergoing a series of explosive events — this star has ejected four times the mass of the Sun in just a few hundred years. The material flung out during these bursts has formed the extensive double shell of the nebula, which is made of dust rich in silicates and mixed with gas.
According to the science paper [pdf] describing this research, the stage of yellow hypergiants is a preliminary to the star evolving into a luminous blue variable, of which Eta Carinae is the most famous. In this next stage a star is thought to have a good chance of going supernova.
Though this image is truely spectacular, taken by a ground-based telescope of a star 13,000 light years away, what I find most significant about this image is its fuzziness. It reminds me of the kind of images astronomers and the public routinely accepted as the best possible, before the launch of the Hubble Space Telescope.
» Read more
NASA science administrator Ed Weiler is retiring after 33 years
Science administrator Ed Weiler is retiring after almost 33 years at NASA.
Among Weiler’s many achievements, he was crucial to getting the Hubble Space Telescope launched. Even more important, though others had conceived the idea of using the shuttle to maintain Hubble, he designed the maintenance schedule for the telescope. Seven years before it was launched, he insisted that a regular schedule of repair missions be placed on the shuttle manifest. He also insisted that a duplicate of the telescope’s main camera be built, so that if anything went wrong with the first a repaired unit could be launched quickly. It was his foresight here that made the first repair of Hubble in December 1993 go so smoothly. For this, astronomers will always be grateful.
Science administrator Ed Weiler is retiring after almost 33 years at NASA.
Among Weiler’s many achievements, he was crucial to getting the Hubble Space Telescope launched. Even more important, though others had conceived the idea of using the shuttle to maintain Hubble, he designed the maintenance schedule for the telescope. Seven years before it was launched, he insisted that a regular schedule of repair missions be placed on the shuttle manifest. He also insisted that a duplicate of the telescope’s main camera be built, so that if anything went wrong with the first a repaired unit could be launched quickly. It was his foresight here that made the first repair of Hubble in December 1993 go so smoothly. For this, astronomers will always be grateful.
The Accelerating Universe and Dark Energy Might Be Illusions
The uncertainty of science: A new theory posits that the accelerating universe and dark energy might be illusions caused by motion of our galaxy through space.
The uncertainty of science: A new theory posits that the accelerating universe and dark energy might be illusions caused by motion of our galaxy through space.
Sunspot 1302 Continues to Turn Toward Earth
Giant sunspot 1302 turns its aim towards Earth.
Giant sunspot 1302 turns its aim towards Earth.
Virtual monkeys typing Shakespeare
A computer programmer has created a legion of virtual monkeys programmed to randomly type until the works of Shakespeare are reproduced.
If the nine-letter sequence appears anywhere in one of Shakespeare’s writings, it is matched against the relevant passage in a copy of the Bard’s complete works, and is checked off the list. The monkeys, which started typing on August 21, have already completed more than five trillion of the 5.5 trillion possible nine-letter combinations, but have so far only finished one whole work.
They appear to be doing better than Congress’s attempt to balance the federal budget.
A computer programmer has created a legion of virtual monkeys programmed to randomly type until the works of Shakespeare are reproduced.
If the nine-letter sequence appears anywhere in one of Shakespeare’s writings, it is matched against the relevant passage in a copy of the Bard’s complete works, and is checked off the list. The monkeys, which started typing on August 21, have already completed more than five trillion of the 5.5 trillion possible nine-letter combinations, but have so far only finished one whole work.
They appear to be doing better than Congress’s attempt to balance the federal budget.
Anthropologists have uncovered what appears to be the first and only evidence of preserved flesh from an early pre-human ancestor nearly 2 million years old
Anthropologists have uncovered what appears to be the first and only evidence of preserved flesh from an early pre-human ancestor nearly 2 million years old.
Anthropologists have uncovered what appears to be the first and only evidence of preserved flesh from an early pre-human ancestor nearly 2 million years old.
Obama: “You’ve got a governor whose state is on fire denying climate change.”
Obama on Sunday at a fundraiser, attacking Rick Perry: “You’ve got a governor whose state is on fire denying climate change.”
Here is another example of a politician making a fool of himself. The wildfires in Texas have nothing to do with climate change. And if Obama thinks they do, he immediately shows himself to be completely ignorant of the science behind the Earth’s climate.
Obama on Sunday at a fundraiser, attacking Rick Perry: “You’ve got a governor whose state is on fire denying climate change.”
Here is another example of a politician making a fool of himself. The wildfires in Texas have nothing to do with climate change. And if Obama thinks they do, he immediately shows himself to be completely ignorant of the science behind the Earth’s climate.
