The sun, cosmic rays, and the politics of climate change
The sun, cosmic rays, and the politics of climate change.
The sun, cosmic rays, and the politics of climate change.
The sun, cosmic rays, and the politics of climate change.
Archeologists may have found King Arthur’s round table in Scotland.
The new survey — funded by Historic Scotland and Stirling City Heritage Trust — used the latest scientific techniques to showing lost structures and features up to a metre below the ground. It also revealed a series of ditches south of the main mound, as well as remains of buildings, and more recent structures, including modern drains which appear at the northern end of the gardens.
Mr Harrison, who has studied the King’s Knot for 20 years, said: “It is a mystery which the documents cannot solve, but geophysics has given us new insights. “Of course, we cannot say that King Arthur was there, but the feature which surrounds the core of the Knot could explain the stories and beliefs that people held.”
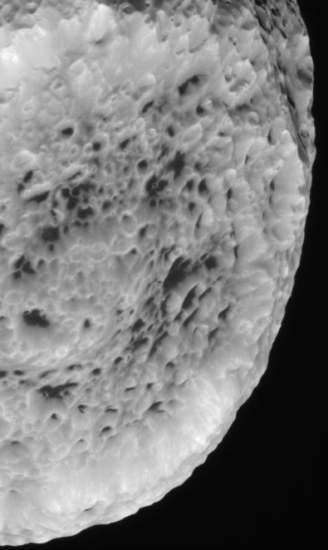
On August 25 Cassini did a close fly-by of the small Saturn moon Hyperion, getting as close as 15,500 miles. The mission has just released images from that fly-by.
Looks like a sponge, doesn’t it? This moon is small, only 168 miles across, which makes it about half the size of the asteroid Vesta that Dawn is presently orbiting. Why it is so peppered with craters is of course the big science question. I would guess this has something to do with the environment around Saturn, with its rings and the innumerable particles that come from it. Yet, other moons of Saturn are not as crater-filled, so there is obviously more to this than meets the eye.
This fly-by was the second closest of Hyperion that Cassini has done, the first passing over the the moon’s surface by only 310 miles. Because the irregularly-shaped moon’s rotation is more like a chaotic tumble, scientists could not predict what part of the surface they would see. To their luck the new images captured new territory.
Another fly-by is scheduled in only three weeks, on September 16, 2011. This time, however, the spacecraft won’t get as close, passing at a distance of about 36,000 miles.
Get out those binoculars! Two comets, Elenin and Garradd, are now showing in the night sky.
It’s not just space where we are dependent on the Russians: The National Science Foundation has just hired a Russian icebreaker “to escort resupply and refueling ships into McMurdo Station,” the hub of U.S. activities on Antarctica.
Astronomers have spotted the closest supernovae in almost 25 years, only 21 million light years away.
The supernova, dubbed PTF 11kly, occurred in the Pinwheel Galaxy, located in the “Big Dipper,” otherwise known as the Ursa Major constellation. It was discovered by the Palomar Transient Factory (PTF) survey, which is designed to observe and uncover astronomical events as they happen. “We caught this supernova very soon after explosion. PTF 11kly is getting brighter by the minute. It’s already 20 times brighter than it was yesterday,” said Peter Nugent, the senior scientist at Berkeley Lab who first spotted the supernova. Nugent is also an adjunct professor of astronomy at UC Berkeley. “Observing PTF 11kly unfold should be a wild ride. It is an instant cosmic classic.”
Astronomers expect the supernova to continue to brighten over the next two weeks, when it should be visible to anyone using binoculars.
If you are on the east coast, this post is for you: Preparing for Hurricane Irene.
Asteroid dust from Hayabusa have been linked to the origin of the most common meteorite types found on Earth.
The science team of Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter released an intriguing picture yesterday of what scientists call a granular flow down the side of a five mile wide crater on the far side of the moon. Looking at the image, one would swear that the darker material flowing down the slope of the crater rim is a lava flow frozen in place.

However, according to the scientists, that is not what it is. Instead, this is merely debris left behind from an avalanche.
» Read more
Divers have recovered the telegraph and some of the steering equipment from the Lusitania.
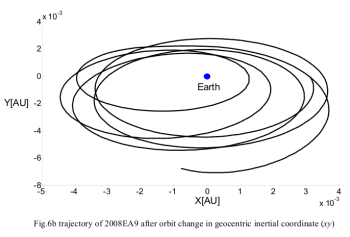
Want to mine an asteroid? Rather than travel to it with all their mining equipment, three Chinese scientists have proposed a better way. In a paper published today on the Los Alamos astro-ph preprint website, they have calculated the energy required to shift the orbits of the six thousand near-Earth asteroids and place them in Earth orbit for later mining. Of these, they found 46 asteroids that had the potential for such an operation, and two likely candidates for a space mission. One 30-foot-wide asteroid, 2008EA9, will actually be in the right place for this technique in 2049. As they write,
It can be seen that the velocity increment of the 2008EA9 is relatively small (-1.00km/s) and it will very close approach [approximately 645,000 miles] to the Earth in [February] 2049. Moreover the size of the NEO 2008EA9 is very small so that the capturing of it is relatively easy.
The real problem, of course, is adding that small “velocity increment” to the asteroid.
» Read more
Watching a black hole devour a star, 3.9 billion light years away.
The geology behind the Virginia earthquake of August 23. And an even better analysis, with maps, can be found here.
A 5.9 magnitude earthquake hit Virginia at about 1:51 pm (Eastern).
I am in Maryland, just outside the beltway, and felt something like an earthquake about five minutes ago. The house started to shake, then settled, then shook again. Quite startling. I opened the front door the same time a neighbor did. She had felt the same thing.
The above quake was more than 90 miles away. I wonder how bad it is there, considering the eastern U.S. rarely experiences quakes and has made no preparations for such a thing.
For updates:
» Read more
A super-Earth has been identified orbiting its star on the edge of the habitable zone.
Below the fold are two images released today, one from Dawn at Vesta and the other from Messenger at Mercury. What makes them interesting to me is that, though the surfaces of both Vesta and Mercury are crater-packed, there are definitely distinct differences between them that one can spot if you look closely, all highlighting the fundamentally different environments of both worlds.
First, the Vesta photograph. The image looks out past the asteroid’s horizon, showing clearly that this dwarf planet is not spherical, with the south pole depression that puzzles scientists just on the planet’s limb. The parallel long deep grooves that are associated with this depression can be seen on the right. Notice also that the inside walls of all the craters slope downward in a very shallow manner. This gives the impression that the impacts that formed these craters smashed into an almost beachlike sandy surface. Note too the that the center of some craters have what appear to be flat small “ponds,” a phenomenon seen by the spacecraft NEAR when it orbited the asteroid Eros. These ponds are not liquid, but are actually made up of fine-grained particles that settle in the hollows of the asteroid.
» Read more
Feeling the pinch: A Florida university has shuttered its manned submersible research program after forty years of operation due to lack of funds.
NASA pushes for funds to save the James Webb Space Telescope.
NASA has announced three awards for technology demonstration space missions, all set to fly within four years. More details here.
The three missions are:
I especially like the solar sail mission because of its long range possibilities, though the other technologies would probably be put to practical use more quickly.
Early hints that scientists had found the Higgs boson at CERN have faded with fresh data.
New data presented today at the Lepton Photon conference in Mumbai, India, show the signal fading. It means that “this excess is probably just a statistical fluctuation”, says Adam Falkowski, a theorist at the University of Paris-South in Orsay, France.
Researchers have found what could be the oldest microbial fossils yet, discovered in 3.4-billion-year-old Australian rocks
Europe and Russia talk of joint manned mission to Mars.
I’m not sure how seriously to take this story, though its implications are intriguing regardless. More than any other country, Russia knows how to build the kind of spaceship necessary for the journey. What Europe will contribute more than anything else would be money.
An evening pause: In honor of the 100th anniversary of the sending of the first round-the-world telegram on August 20, 1911, here is the story of the real inventor of the telegraph. And it ain’t what you think.
A reindeer herder in Russia’s Arctic has stumbled on the pre-historic remains of a baby woolly mammoth.
Opportunity begins exploring the rim of Endeavour Crater, taking a bunch of new images . I especially like this one, of which I’ve posted a cropped scaled-down version below. The image looks across the 13-mile-wide Endeavour Crater to its far rim on the horizon. Note the haze. Mars very clearly has an atmosphere, even though it is far thinner than Earth’s. In the foreground are scattered rocks, ejecta produced from the impact that formed a smaller nearby crater now named Opportunity Crater.

The Pioneer anomaly is fading.
The analysis shows that the anomaly is not constant, as researchers had believed, but is decreasing with time. The finding points toward a conventional explanation of the phenomenon, most likely asymmetric radiation of heat, and against some of the more exotic proposals.
Archeologists reap treasures from a newly-discovered POW camp from the Civil War.
Camp Lawton’s obscurity helped it remain undisturbed all these years. Built about 50 miles south of Augusta, the Confederate camp imprisoned about 10,000 Union soldiers after it opened in October 1864 to replace the infamous Andersonville prison. But it lasted barely six weeks before Sherman’s army arrived and burned it during his march from Atlanta to Savannah.
Barely a footnote in the war’s history, Camp Lawton was a low priority among scholars. Its exact location was never verified. While known to be near Magnolia Springs State Park, archaeologists figured the camp was too short-lived to yield real historical treasures. That changed last year when Georgia Southern archaeology student Kevin Chapman seized on an offer by the state Department of Natural Resources to pursue his master’s thesis by looking for evidence of Camp Lawton’s stockade walls on the park grounds.
New research has shown that humans, not rats, spread the Black Death in the plague of 1348-1349. Also,
Sloane, who was previously a field archaeologist with the Museum of London, working on many medieval sites, is now attached to English Heritage. He has concluded that the spread of the 1348-49 plague, the worst to hit the capital, was far faster, with an impact far worse than had been estimated previously. While some suggest that half the city’s population of 60,000 died, he believes it could have been as high as two-thirds. Years later, in 1357, merchants were trying to get their tax bill cut on the grounds that a third of all property in the city was lying empty. [emphasis mine]