Webb takes infrared image of exoplanet
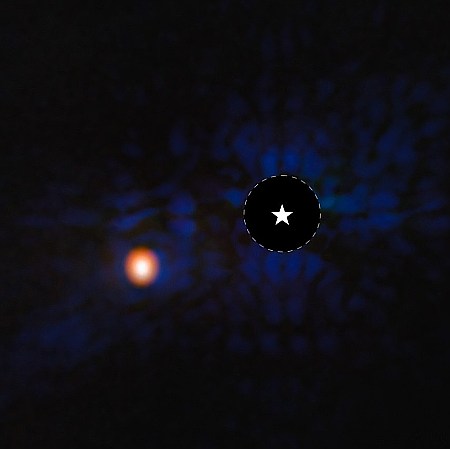
Cool image time! Using the Webb Space Telescope, scientists have taken an infrared false color image of a multi-Jupiter-sized exoplanet located only twelve light years away and orbiting the K-type star Epsilon Indi A.
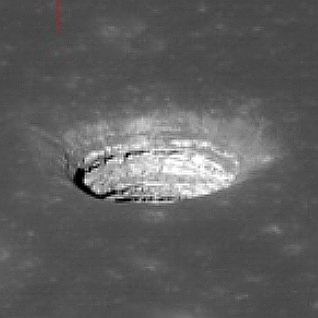
That picture, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, is to the right. The light of the star, indicated by the star symbol, has been blocked by Webb’s coronagraph, the size of which is shown by the dashed circle. The exoplanet is the orange blob to the left.
[This exoplanet] is one of the coldest exoplanets to be directly detected, with an estimated temperature of 35 degrees Fahrenheit (2 degrees Celsius) — colder than any other imaged planet beyond our solar system, and colder than all but one free-floating brown dwarf. The planet is only around 180 degrees Fahrenheit (100 degrees Celsius) warmer than gas giants in our solar system. This provides a rare opportunity for astronomers to study the atmospheric composition of true solar system analogs.
The data also revealed that the exoplanet is twice as massive as expected and has a slightly different orbit than expected based on previous less precise data.
Cool image time! Using the Webb Space Telescope, scientists have taken an infrared false color image of a multi-Jupiter-sized exoplanet located only twelve light years away and orbiting the K-type star Epsilon Indi A.
That picture, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, is to the right. The light of the star, indicated by the star symbol, has been blocked by Webb’s coronagraph, the size of which is shown by the dashed circle. The exoplanet is the orange blob to the left.
[This exoplanet] is one of the coldest exoplanets to be directly detected, with an estimated temperature of 35 degrees Fahrenheit (2 degrees Celsius) — colder than any other imaged planet beyond our solar system, and colder than all but one free-floating brown dwarf. The planet is only around 180 degrees Fahrenheit (100 degrees Celsius) warmer than gas giants in our solar system. This provides a rare opportunity for astronomers to study the atmospheric composition of true solar system analogs.
The data also revealed that the exoplanet is twice as massive as expected and has a slightly different orbit than expected based on previous less precise data.