A Martian lava flow so strong it eats mountains
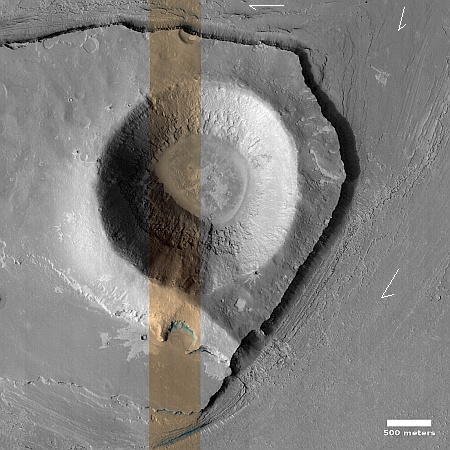
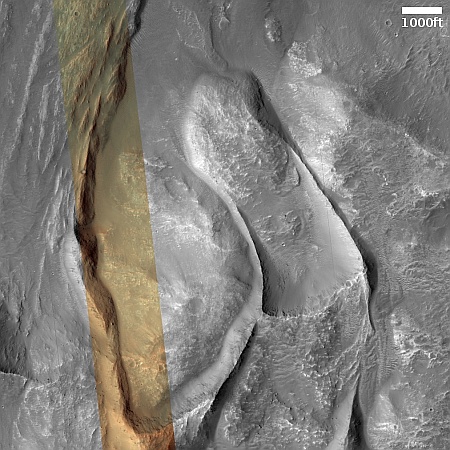
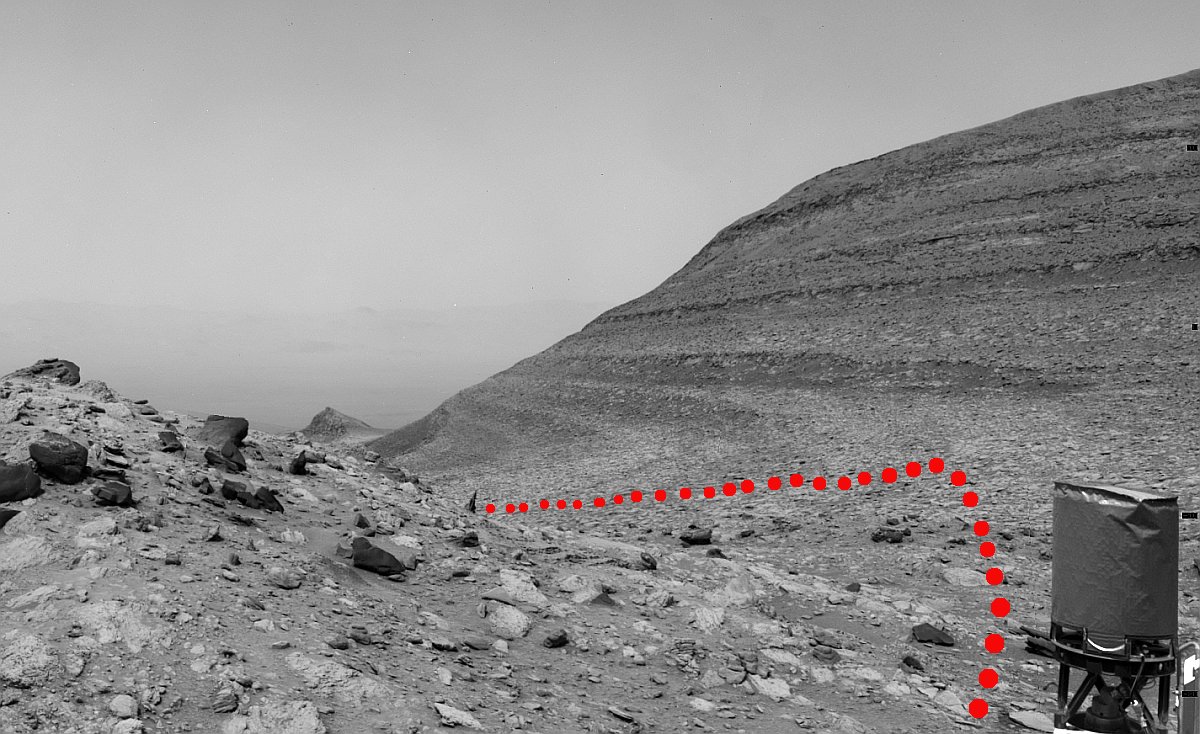
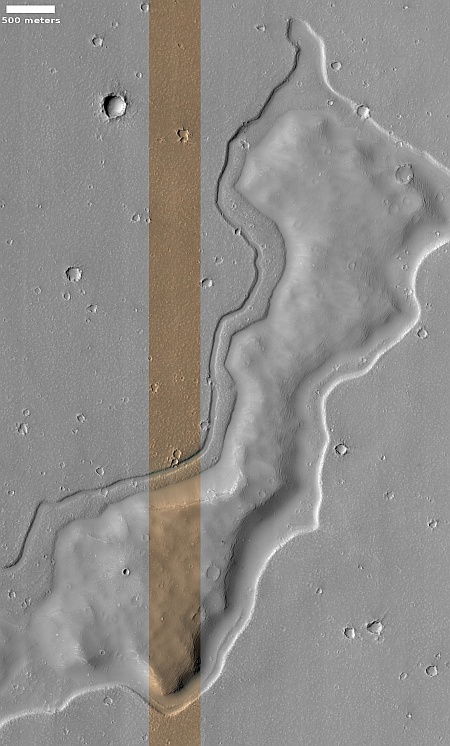
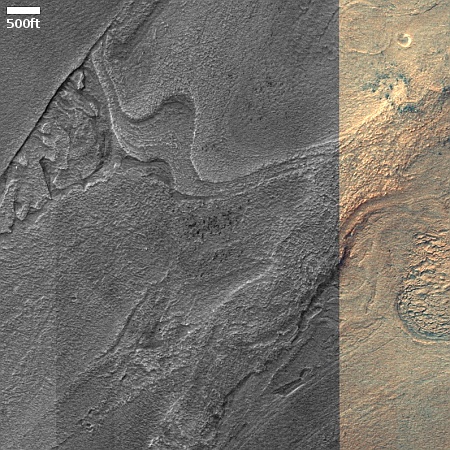
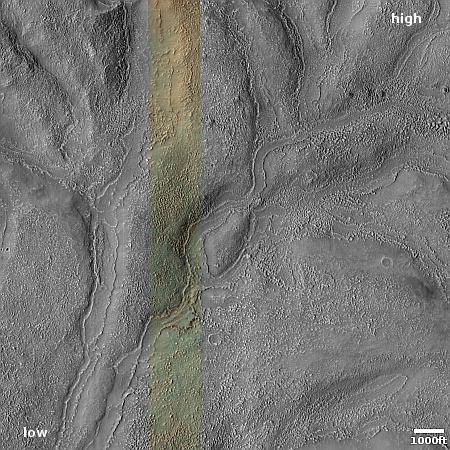
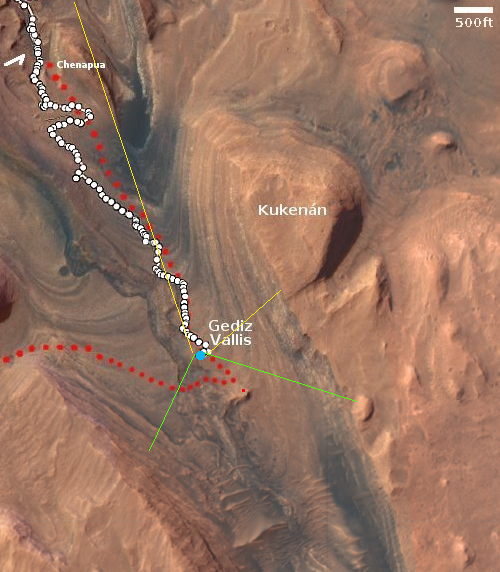
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, sharpened, and annotated to post here, was taken on March 19, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a crater that appears to sit on top of a plateau that was created by a flow of material coming from the northeast that — as the flow divided to get around that crater — it wore away the ground to leave the crater sitting high and dry.
What was the material in that flow? The location is at 9 degrees north latitude, in Mars’ dry tropics, so it is highly unlikely that the flows here are glaciers, even though they have some glacier-like features.
Instead, this is frozen lava, but Martian in nature in that its ability to push the ground out of its way suggests it was moving very fast, far faster than lava on Earth.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, rotated, cropped, reduced, sharpened, and annotated to post here, was taken on March 19, 2024 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows a crater that appears to sit on top of a plateau that was created by a flow of material coming from the northeast that — as the flow divided to get around that crater — it wore away the ground to leave the crater sitting high and dry.
What was the material in that flow? The location is at 9 degrees north latitude, in Mars’ dry tropics, so it is highly unlikely that the flows here are glaciers, even though they have some glacier-like features.
Instead, this is frozen lava, but Martian in nature in that its ability to push the ground out of its way suggests it was moving very fast, far faster than lava on Earth.
» Read more