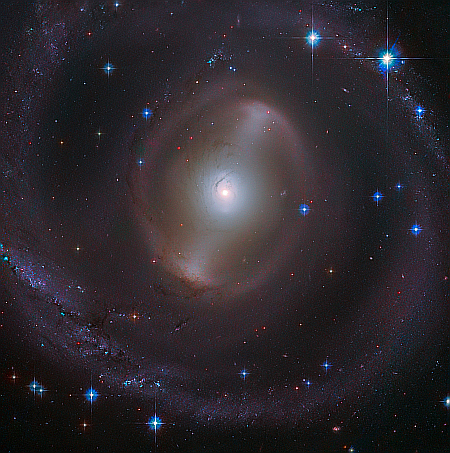
Hubble out of safe mode and resumed science observations
According to the Hubble website, engineers have corrected the gyro issue that put the Hubble Space Telescope into safe mode on April 23, 2024.
On April 30, 2024, NASA announced it restored the agency’s Hubble Space Telescope to science operations April 29. The spacecraft is in good health and once again operating using all three of its gyros. All of Hubble’s instruments are online, and the spacecraft has resumed taking science observations.
No other information was released. The safe mode was initiated by faulty readings from one of those gyros. Was the problem in the gyro itself, or were the readings merely incorrect? This matters because when one of those gyros finally fails, the telescope will go to one-gyro mode, saving its second gyro in reserve. At that point Hubble will no longer be able to take sharp images, though it will still be able to some science.
According to the Hubble website, engineers have corrected the gyro issue that put the Hubble Space Telescope into safe mode on April 23, 2024.
On April 30, 2024, NASA announced it restored the agency’s Hubble Space Telescope to science operations April 29. The spacecraft is in good health and once again operating using all three of its gyros. All of Hubble’s instruments are online, and the spacecraft has resumed taking science observations.
No other information was released. The safe mode was initiated by faulty readings from one of those gyros. Was the problem in the gyro itself, or were the readings merely incorrect? This matters because when one of those gyros finally fails, the telescope will go to one-gyro mode, saving its second gyro in reserve. At that point Hubble will no longer be able to take sharp images, though it will still be able to some science.