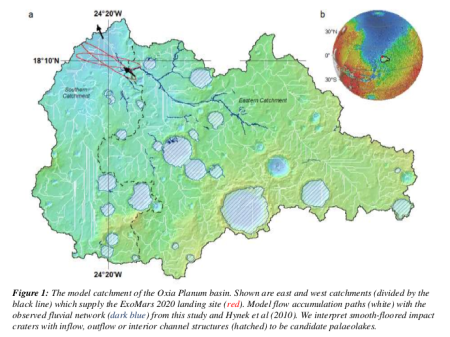
Japan to sign deal with NASA to fly two Japanese astronauts to Moon
According to story in the Japanese press yesterday, a deal between Japan and NASA will be signed next week whereby Japan will have two astronauts go on Moon missions in exchange for providing cargo to the Lunar Gateway station as well as a manned lunar rover.
The report today is unclear whether those Japanese astronauts will land on the Moon, but I expect they will. The rover project is being led by Toyota. It will include a airtight cabin where spacesuits will not be necessary and passengers can also sleep, allowing for very long exploratory traverses from the landing site.
Reports of this deal have been appearing in the press since 2022, when NASA said it would involve flying one Japanese astronaut to the Moon. In December 2023 it was reported that the deal would be signed within a month. It is now April. It appears the extended negotiations have gotten Japan a second astronaut Moon walker.
NASA’s Artemis program is beginning to shape up as an international program for getting almost everyone to the Moon but Americans. I am exaggerating, but I think in the future Americans will find it easier to go on a private mission to the Moon than depend on NASA, especially because of all the international deals NASA will have to honor.
According to story in the Japanese press yesterday, a deal between Japan and NASA will be signed next week whereby Japan will have two astronauts go on Moon missions in exchange for providing cargo to the Lunar Gateway station as well as a manned lunar rover.
The report today is unclear whether those Japanese astronauts will land on the Moon, but I expect they will. The rover project is being led by Toyota. It will include a airtight cabin where spacesuits will not be necessary and passengers can also sleep, allowing for very long exploratory traverses from the landing site.
Reports of this deal have been appearing in the press since 2022, when NASA said it would involve flying one Japanese astronaut to the Moon. In December 2023 it was reported that the deal would be signed within a month. It is now April. It appears the extended negotiations have gotten Japan a second astronaut Moon walker.
NASA’s Artemis program is beginning to shape up as an international program for getting almost everyone to the Moon but Americans. I am exaggerating, but I think in the future Americans will find it easier to go on a private mission to the Moon than depend on NASA, especially because of all the international deals NASA will have to honor.