The tangled view of astronomers
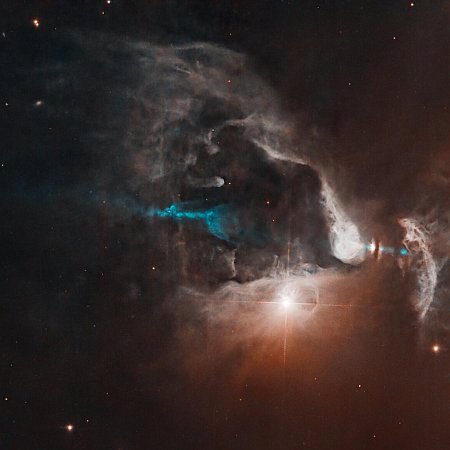
The uncertainty of science: The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope as part of a survey of young stars surrounded by an edge-on dust disk. From the caption:
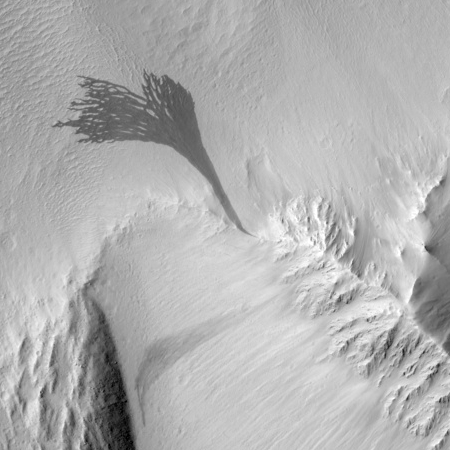
FS Tau is a multi-star system made up of FS Tau A, the bright star-like object near the middle of the image, and FS Tau B (Haro 6-5B), the bright object to the far right that is partially obscured by a dark, vertical lane of dust. The young objects are surrounded by softly illuminated gas and dust of this stellar nursery. The system is only about 2.8 million years old, very young for a star system. Our Sun, by contrast, is about 4.6 billion years old.
The blue lines on either side of that vertical dust lane are jets moving out from FS Tau B. The caption says their asymetrical lengths are likely due to ” mass is being expelled from the object at different rates,” but it just as easily be caused by the angle in which we see this object, making the nearer jet seem longer than the one behind.
That astronomers cannot move around such an object and see it from many angles explains the headline of this post. We can only see astronomical objects from one angle, and when they are complex objects such as this one, a large part of the research problem is disentangling the shapes we see into a coherent picture. Spectroscopy helps a lot, as it provides information about the speed and direction of different parts of the object, but even this can be enormously complicated and difficult to interpret.
Remember these facts when you read news reports about astronomical research. No matter how certain the press release sounds, its certainty is always tempered by many unknowns, some very pedestrian but fundamental.
The uncertainty of science: The picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here, was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope as part of a survey of young stars surrounded by an edge-on dust disk. From the caption:
FS Tau is a multi-star system made up of FS Tau A, the bright star-like object near the middle of the image, and FS Tau B (Haro 6-5B), the bright object to the far right that is partially obscured by a dark, vertical lane of dust. The young objects are surrounded by softly illuminated gas and dust of this stellar nursery. The system is only about 2.8 million years old, very young for a star system. Our Sun, by contrast, is about 4.6 billion years old.
The blue lines on either side of that vertical dust lane are jets moving out from FS Tau B. The caption says their asymetrical lengths are likely due to ” mass is being expelled from the object at different rates,” but it just as easily be caused by the angle in which we see this object, making the nearer jet seem longer than the one behind.
That astronomers cannot move around such an object and see it from many angles explains the headline of this post. We can only see astronomical objects from one angle, and when they are complex objects such as this one, a large part of the research problem is disentangling the shapes we see into a coherent picture. Spectroscopy helps a lot, as it provides information about the speed and direction of different parts of the object, but even this can be enormously complicated and difficult to interpret.
Remember these facts when you read news reports about astronomical research. No matter how certain the press release sounds, its certainty is always tempered by many unknowns, some very pedestrian but fundamental.