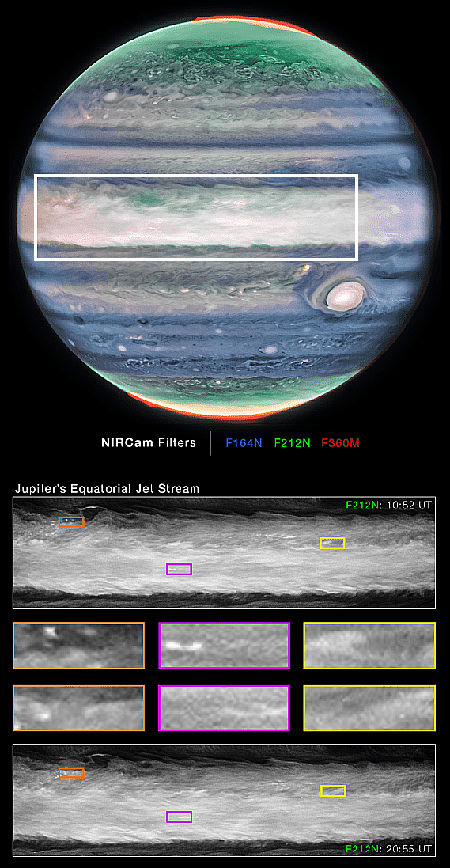
Ingenuity completes 64th flight on Mars
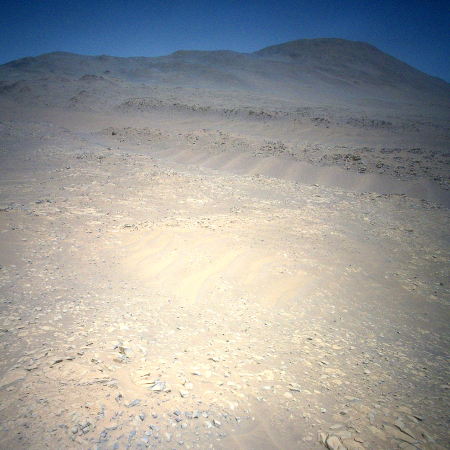
In a pattern that is beginning to be almost routine, on October 27, 2023 the Mars helicopter Ingenuity completed its 64th flight on Mars, flying 1,348 feet at a speed of 13 mph for 139 seconds at an altitude of 39 feet.
As with most of its recent flights, the distance and time was slightly longer than the flight plan, likely because the helicopter took extra time finding a good landing spot.
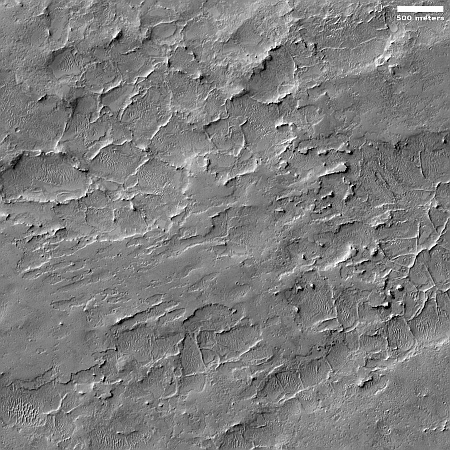
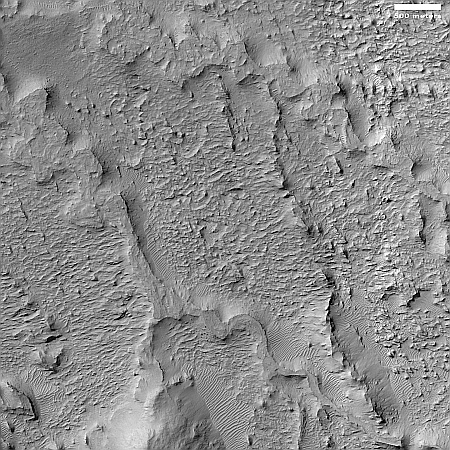
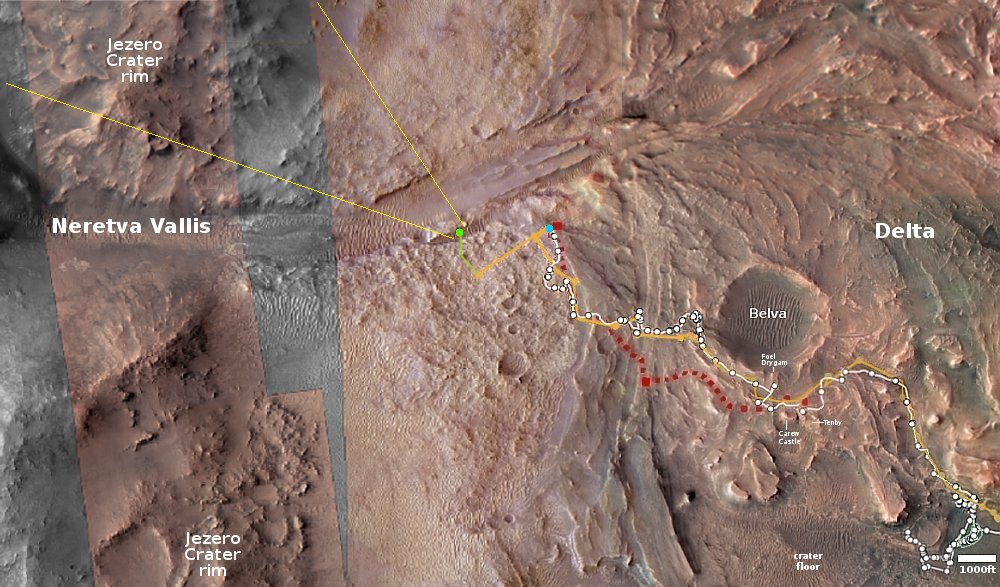
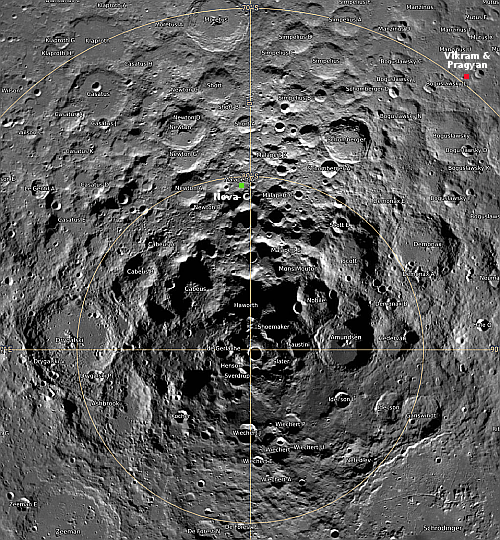
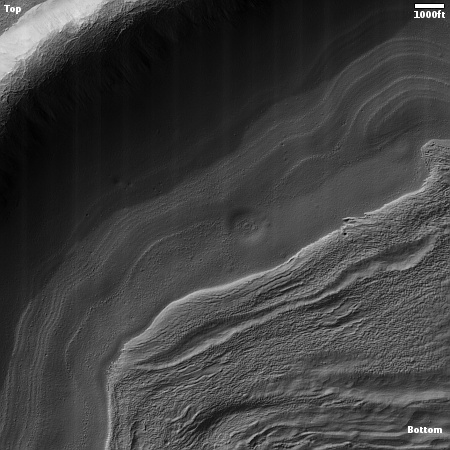
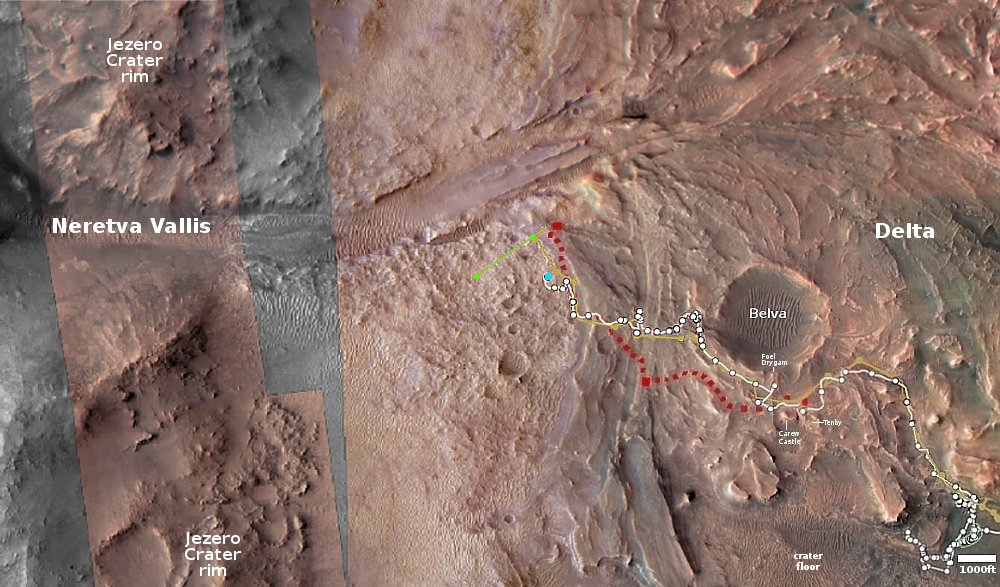
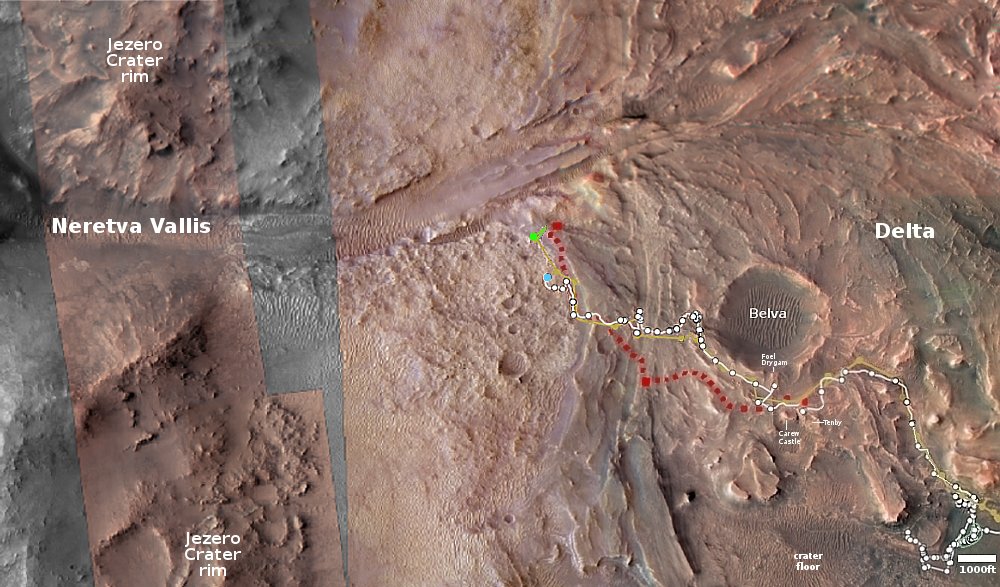
On the overview map above, the green line marks the flight path, and the green dot the helicopter’s present position. The blue dot marks Perseverance’s present position. The yellow lines indicate the area covered by the color image to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here. This image was taken by Ingenuity just a few seconds before landing, and looks across the floor of Neretva Vallis, where Perseverance will soon be traveling.
In a pattern that is beginning to be almost routine, on October 27, 2023 the Mars helicopter Ingenuity completed its 64th flight on Mars, flying 1,348 feet at a speed of 13 mph for 139 seconds at an altitude of 39 feet.
As with most of its recent flights, the distance and time was slightly longer than the flight plan, likely because the helicopter took extra time finding a good landing spot.
On the overview map above, the green line marks the flight path, and the green dot the helicopter’s present position. The blue dot marks Perseverance’s present position. The yellow lines indicate the area covered by the color image to the right, cropped, reduced, and enhanced to post here. This image was taken by Ingenuity just a few seconds before landing, and looks across the floor of Neretva Vallis, where Perseverance will soon be traveling.