Intuitive Machines delays launch of its Nova-C lunar lander two months
Intuitive Machines yesterday announced that it has decided to delay the launch of its Nova-C lunar lander from in November launch window to a new window beginning on January 12, 2023.
The company did not elaborate on the reasons for the delay. However, executives warned at a media event Oct. 3 that “pad congestion” at LC-39A could delay their launch. The mission has to launch from that pad, rather than nearby Space Launch Complex 40, because only LC-39A is equipped to fuel the lander with methane and liquid oxygen propellants on the pad shortly before liftoff.
That pad is used for Falcon 9 crew and cargo missions to the International Space Station as well as Falcon Heavy launches. The pad is scheduled to host the Falcon 9 launch of the CRS-29 cargo mission Nov. 5 followed by a Falcon Heavy mission for the Space Force in late November. Converting the pad between Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launches can take up to three weeks.
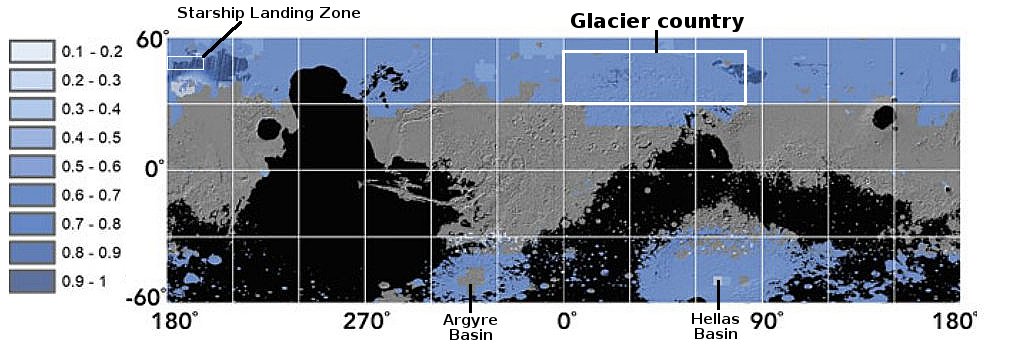
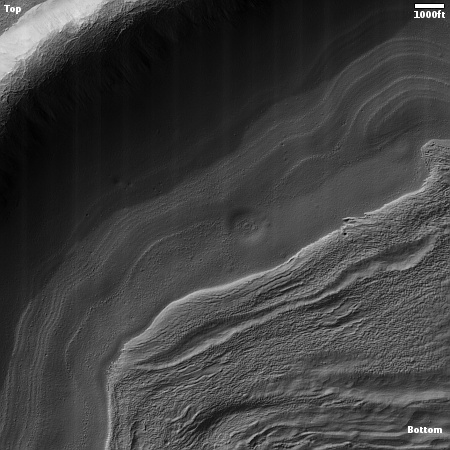
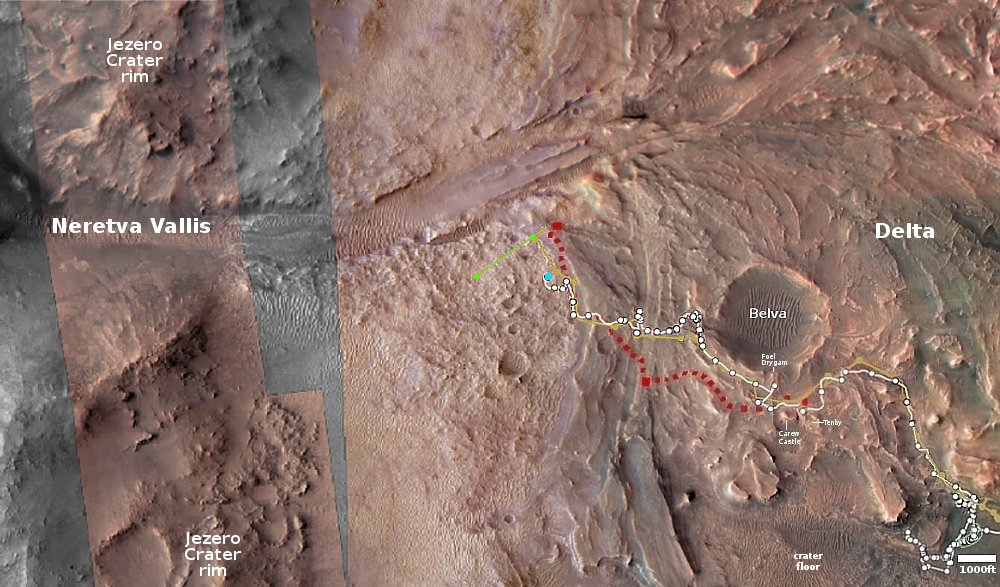
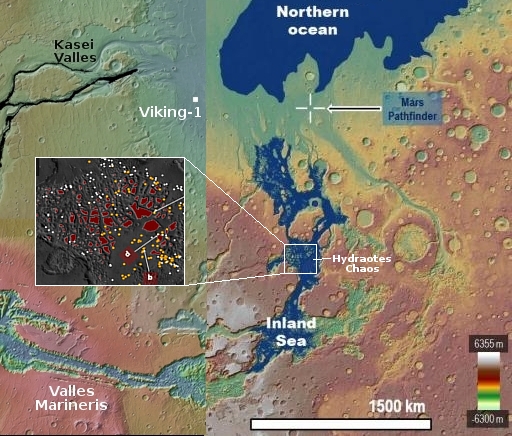
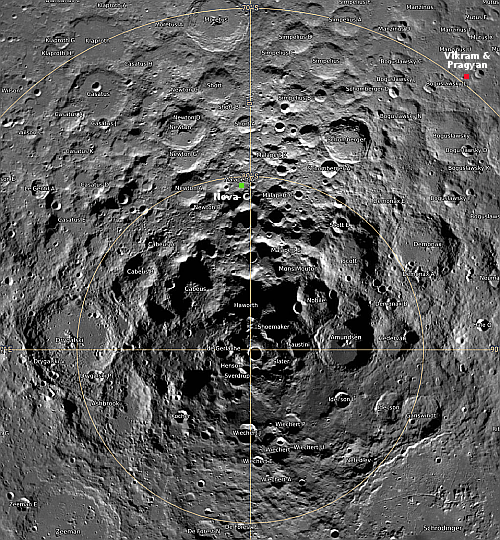
The landing site is indicated by the green dot on the map of the south pole to the right. Note that this landing will be the closest to the south pole yet, though not at the south pole. It will also be the first to land next to a crater that has a permanently shadowed interior, though Nova-C will not be able to enter it because it carries no rover and is only designed to last through the first lunar day.
Based on the present launch schedule, Astrobotic now gets the first chance to successfully land a privately built lunar lander. It is scheduled to launch on December 24, 2023 on a Vulcan rocket. The Japanese company Ispace attempted and failed to land its Hakuto-R1 spacecraft in April.

Intuitive Machines yesterday announced that it has decided to delay the launch of its Nova-C lunar lander from in November launch window to a new window beginning on January 12, 2023.
The company did not elaborate on the reasons for the delay. However, executives warned at a media event Oct. 3 that “pad congestion” at LC-39A could delay their launch. The mission has to launch from that pad, rather than nearby Space Launch Complex 40, because only LC-39A is equipped to fuel the lander with methane and liquid oxygen propellants on the pad shortly before liftoff.
That pad is used for Falcon 9 crew and cargo missions to the International Space Station as well as Falcon Heavy launches. The pad is scheduled to host the Falcon 9 launch of the CRS-29 cargo mission Nov. 5 followed by a Falcon Heavy mission for the Space Force in late November. Converting the pad between Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launches can take up to three weeks.
The landing site is indicated by the green dot on the map of the south pole to the right. Note that this landing will be the closest to the south pole yet, though not at the south pole. It will also be the first to land next to a crater that has a permanently shadowed interior, though Nova-C will not be able to enter it because it carries no rover and is only designed to last through the first lunar day.
Based on the present launch schedule, Astrobotic now gets the first chance to successfully land a privately built lunar lander. It is scheduled to launch on December 24, 2023 on a Vulcan rocket. The Japanese company Ispace attempted and failed to land its Hakuto-R1 spacecraft in April.