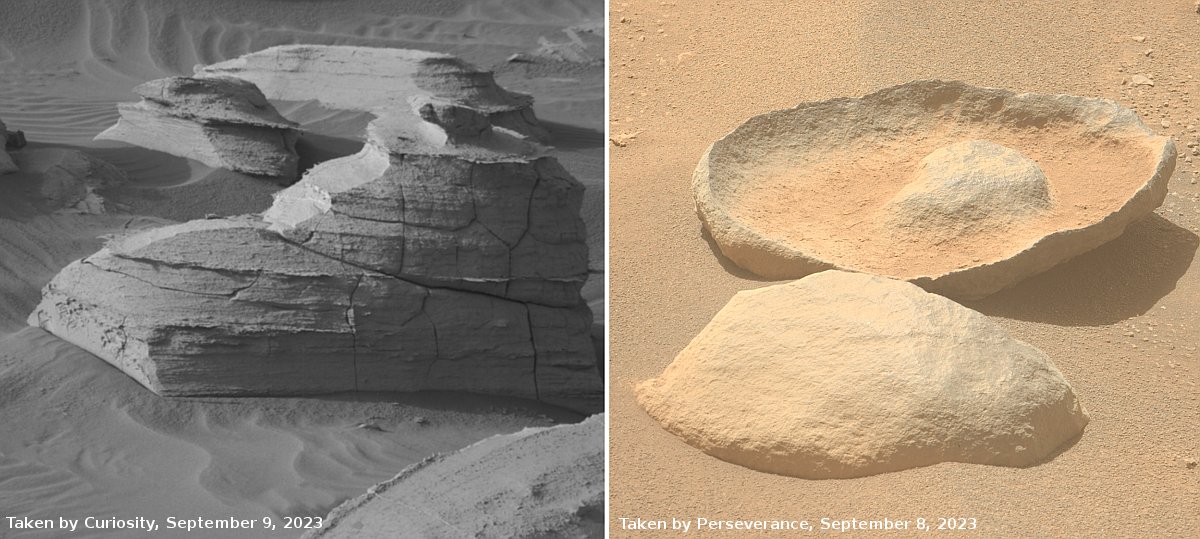
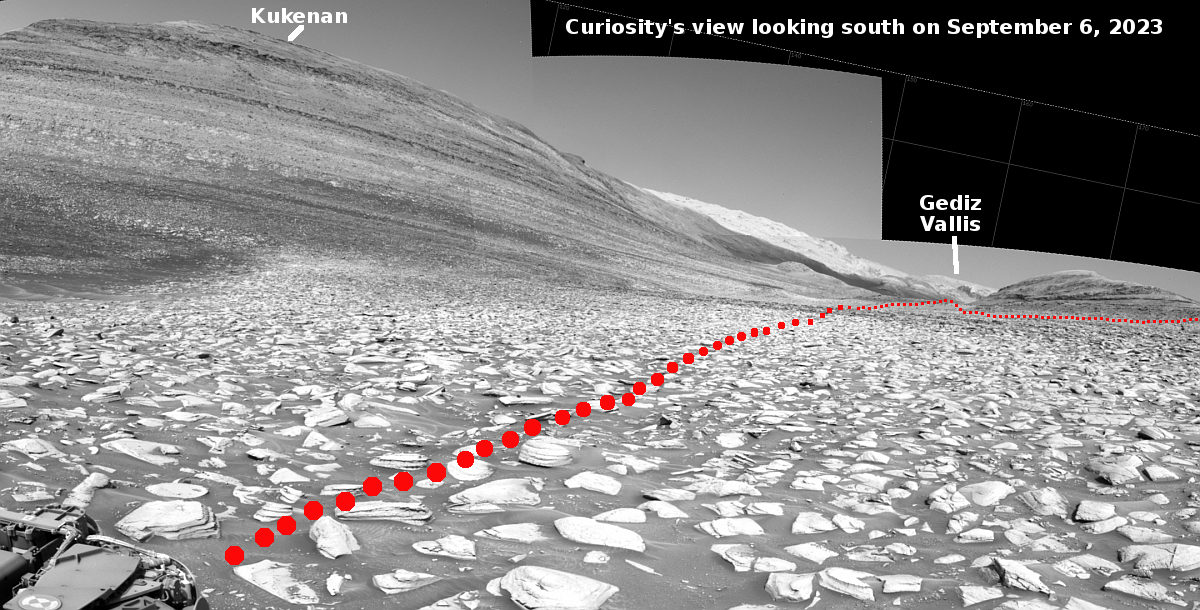
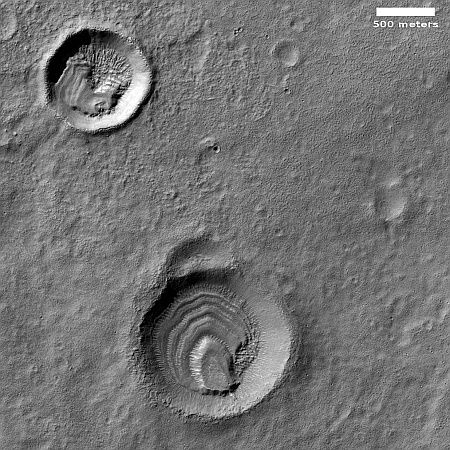
Strange wormlike tube features on slopes of Martian shield volcano
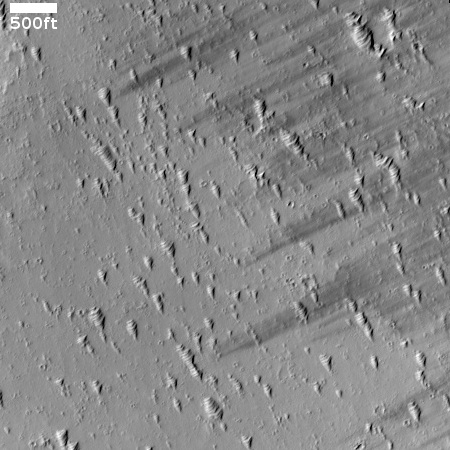
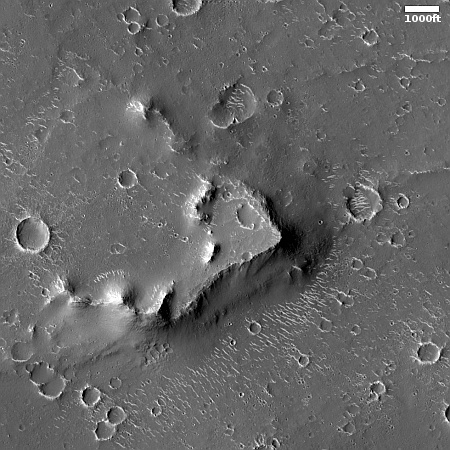
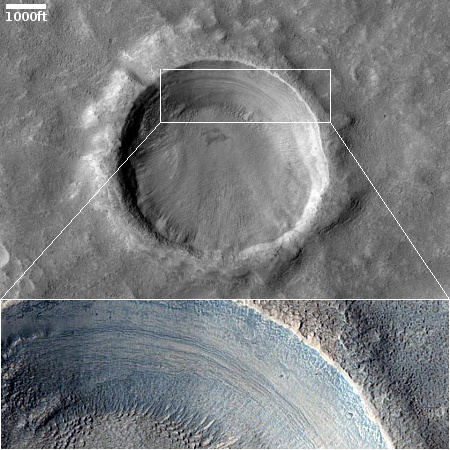
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped to post here, was taken on June 21, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
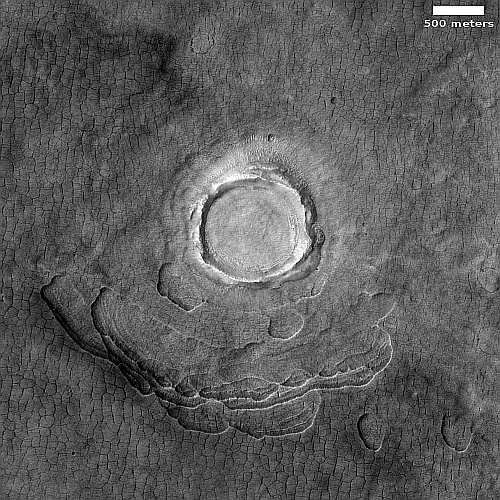
The scientists label the strange tubelike features that are scattered throughout this picture as “landforms,” which is correctly vague because their origin is utterly inexplicable. The ground here is on the eastern slope of a small 20-mile-wide very flat shield volcano located about 150 miles northwest of the giant volcano Ascraeus Mons. The dark wind streaks point down that grade to the east, away from the shield volcano’s peak about 1,000 feet away. (If you look at the full image this indistinct peak is at dead center, with a linear depression (the volcano’s vent) beginning there and heading to the northeast for about four miles.)
Why these many tubes are all oriented in a northwest-southwest direction, at right angles to the slope, is baffling, especially because they hold to that same orientation all across the shield volcano, no matter the downward direction of the slope.
» Read more
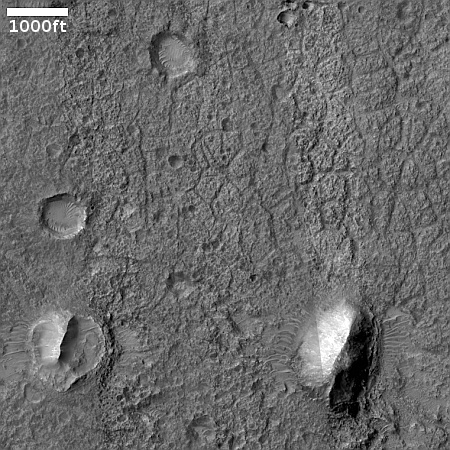
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped to post here, was taken on June 21, 2023 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
The scientists label the strange tubelike features that are scattered throughout this picture as “landforms,” which is correctly vague because their origin is utterly inexplicable. The ground here is on the eastern slope of a small 20-mile-wide very flat shield volcano located about 150 miles northwest of the giant volcano Ascraeus Mons. The dark wind streaks point down that grade to the east, away from the shield volcano’s peak about 1,000 feet away. (If you look at the full image this indistinct peak is at dead center, with a linear depression (the volcano’s vent) beginning there and heading to the northeast for about four miles.)
Why these many tubes are all oriented in a northwest-southwest direction, at right angles to the slope, is baffling, especially because they hold to that same orientation all across the shield volcano, no matter the downward direction of the slope.
» Read more