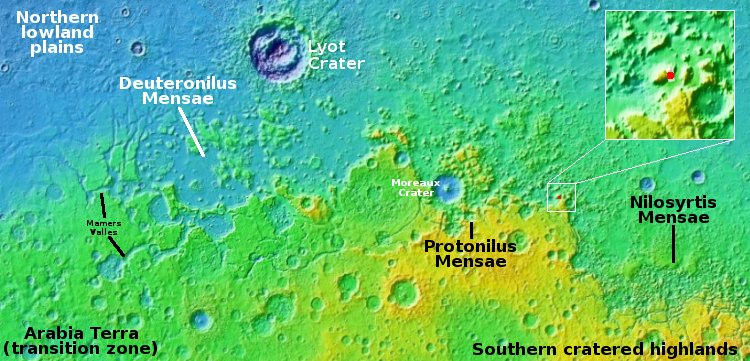
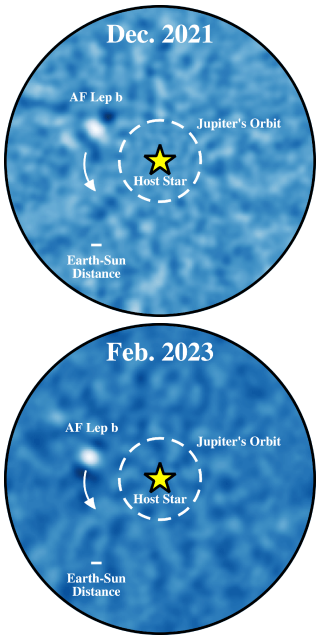
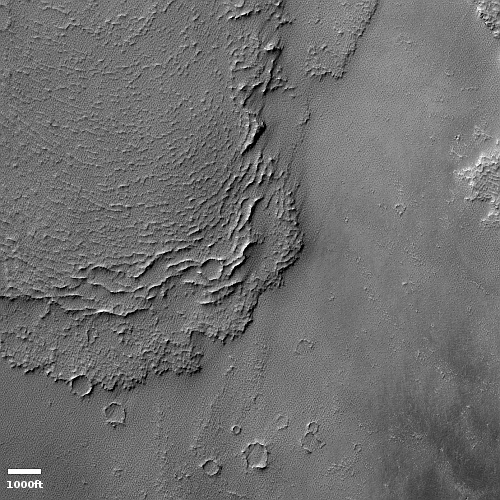
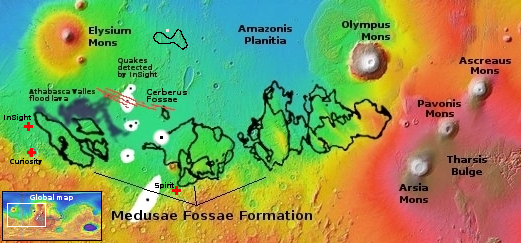
Galaxies at the dawn of time
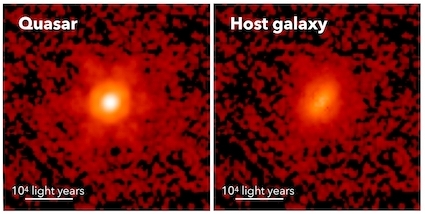
Link here. The article takes a quick look at six galaxies found by Webb’s infrared view that all less than 650 million years after the Big Bang is thought to have occurred.
None disprove the Big Bang. All however raise serious questions about the cosmological theories that posit that event and the subsequent evolution of the universe. Take a look. It is worthwhile reading.
Link here. The article takes a quick look at six galaxies found by Webb’s infrared view that all less than 650 million years after the Big Bang is thought to have occurred.
None disprove the Big Bang. All however raise serious questions about the cosmological theories that posit that event and the subsequent evolution of the universe. Take a look. It is worthwhile reading.