More direct images released of exoplanet 87.5 light years away
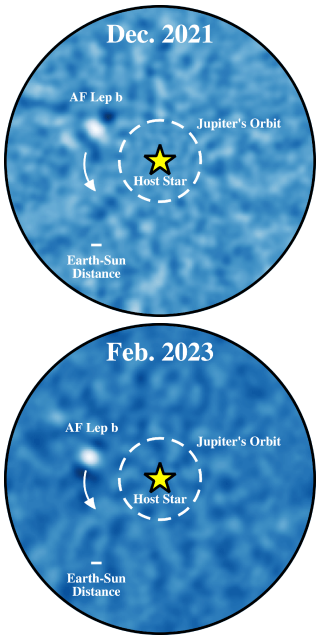
The Keck Observatory in Hawaii has now released its own image of the exoplanet AF Leporis b, following up the images produced by the Very Large Telescope (VLT) released in February.
The direct images Franson’s team captured revealed that AF Lep b is about three times the mass of Jupiter and orbits AF Leporis, a young Sun-like star about 87.5 light-years away. They took a series of deep images of the planet starting in December 2021; two other teams also captured images of the same planet since then.
What make the Keck observations most interesting is that they captured over time the motion of the exoplanet as it orbited its star. The two images to the right show this motion.
The paper, available here, was published today in Astrophysical Journal Letters. This particular star also has a debris disk surrounding it, suggesting it is a young solar system still in the process of forming. From the paper’s conclusion:
AF Lep joins other young planet hosts with debris disks such as β Pic, HR 8799, HD 206893, and HD 95086, reinforcing indications of a higher frequency of long-period planets orbiting stars hosting debris disks.

The Keck Observatory in Hawaii has now released its own image of the exoplanet AF Leporis b, following up the images produced by the Very Large Telescope (VLT) released in February.
The direct images Franson’s team captured revealed that AF Lep b is about three times the mass of Jupiter and orbits AF Leporis, a young Sun-like star about 87.5 light-years away. They took a series of deep images of the planet starting in December 2021; two other teams also captured images of the same planet since then.
What make the Keck observations most interesting is that they captured over time the motion of the exoplanet as it orbited its star. The two images to the right show this motion.
The paper, available here, was published today in Astrophysical Journal Letters. This particular star also has a debris disk surrounding it, suggesting it is a young solar system still in the process of forming. From the paper’s conclusion:
AF Lep joins other young planet hosts with debris disks such as β Pic, HR 8799, HD 206893, and HD 95086, reinforcing indications of a higher frequency of long-period planets orbiting stars hosting debris disks.