Hubble snaps picture of another jellyfish galaxy
Astronomers today released another picture of a jellyfish galaxy taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, with that picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here. From the caption:
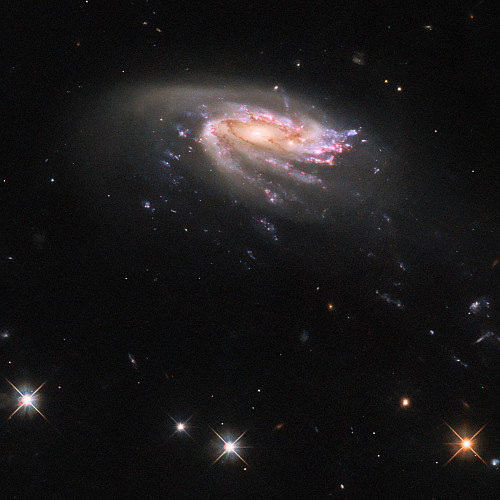
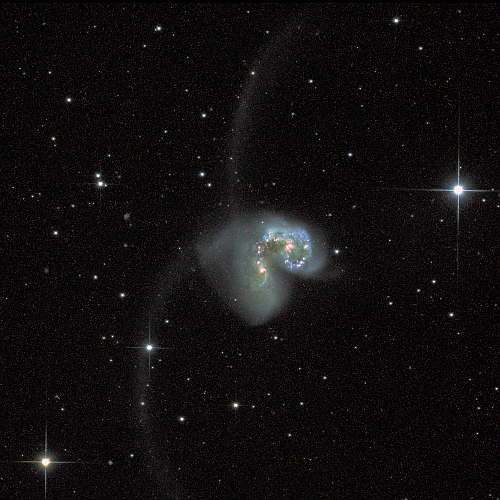
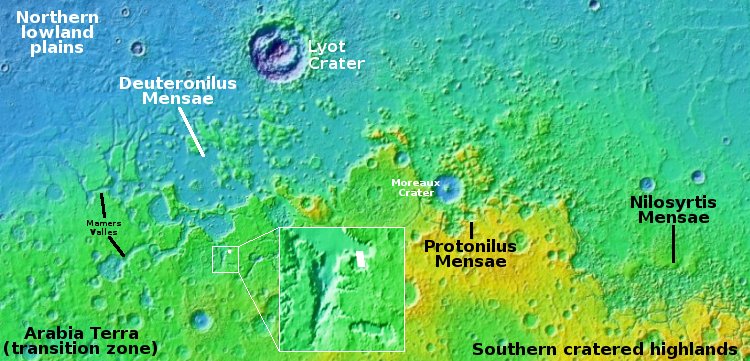
The jellyfish galaxy JO206 trails across this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, showcasing a colourful star-forming disc surrounded by a pale, luminous cloud of dust. A handful of bright stars with criss-cross diffraction spikes stand out against an inky black backdrop at the bottom of the image. JO206 lies over 700 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Aquarius.
This image is the sixth and final such photograph in this survey. You can view all of these images here. The study has found that star formation does not seem to be significantly different inside the galaxy versus the tentacles that stretch out beyond due to pressure from the intergalactic material. This suggests that the influence of this intergalactic material on the formation of stars is relatively minor.
Astronomers today released another picture of a jellyfish galaxy taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, with that picture to the right, cropped, reduced, and sharpened to post here. From the caption:
The jellyfish galaxy JO206 trails across this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, showcasing a colourful star-forming disc surrounded by a pale, luminous cloud of dust. A handful of bright stars with criss-cross diffraction spikes stand out against an inky black backdrop at the bottom of the image. JO206 lies over 700 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Aquarius.
This image is the sixth and final such photograph in this survey. You can view all of these images here. The study has found that star formation does not seem to be significantly different inside the galaxy versus the tentacles that stretch out beyond due to pressure from the intergalactic material. This suggests that the influence of this intergalactic material on the formation of stars is relatively minor.