A journey into Martian chaos
With today’s cool image, we shall begin with the overview map, and drill our way down until we get a close look at another example of truly alien Martian terrain, with only a hint of similarity to comparable geology on Earth.
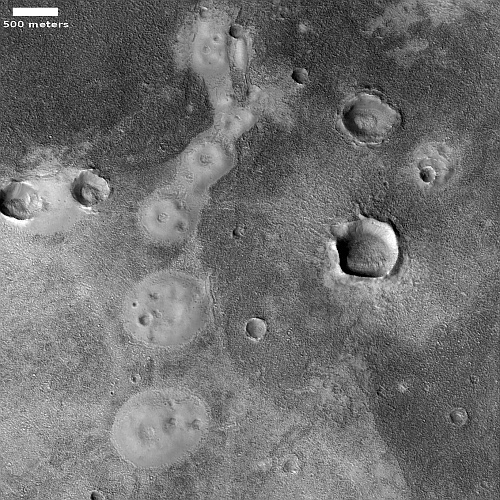
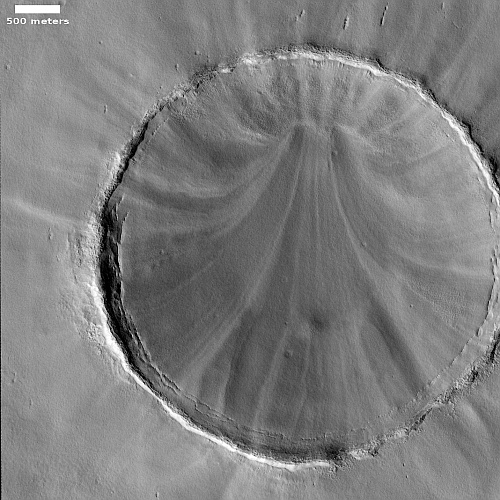
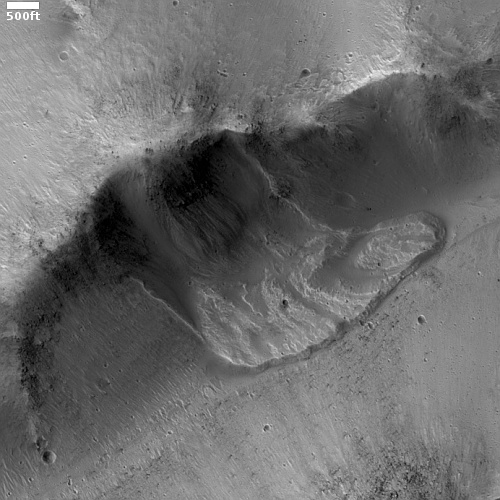
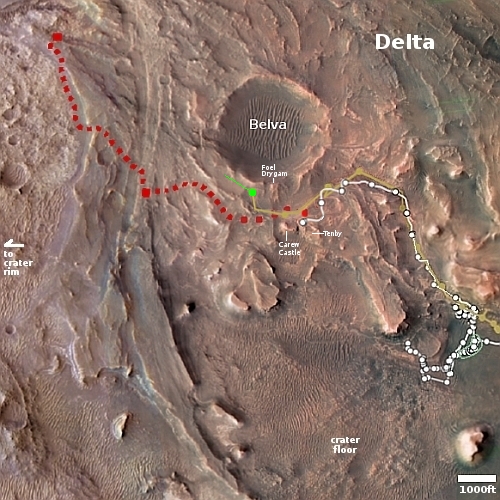
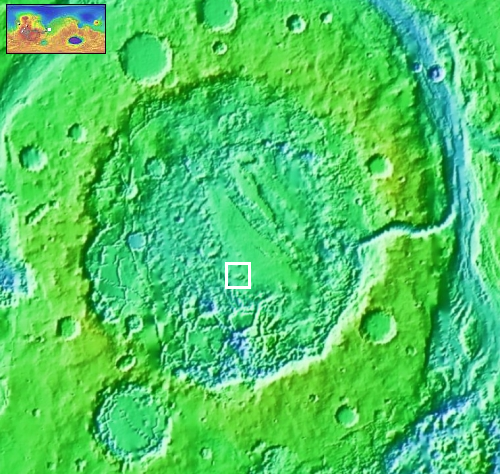
The overview map to the right shows us Aram Chaos, an ancient 170-mile-wide impact crater that has gone through such complex geology that it is difficult, maybe impossible, to unravel it based on data obtained from orbit. As I wrote in a detailed December 2020 post describing the confusing geology of this crater,
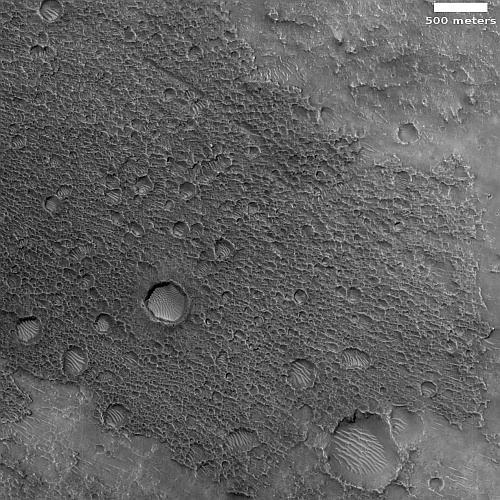
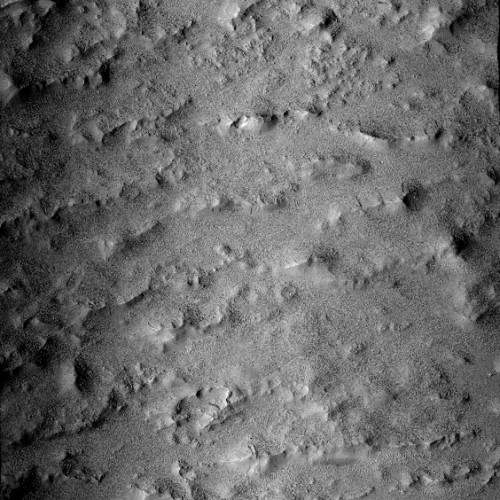
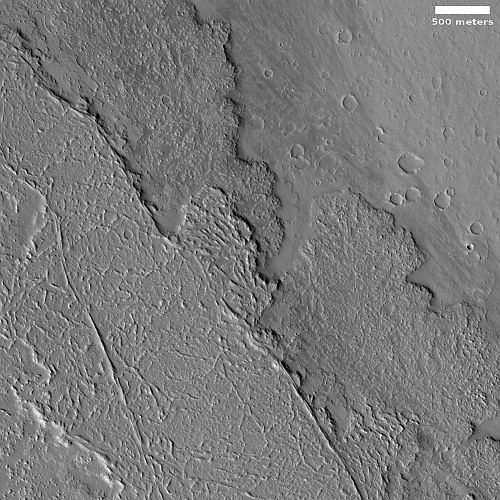
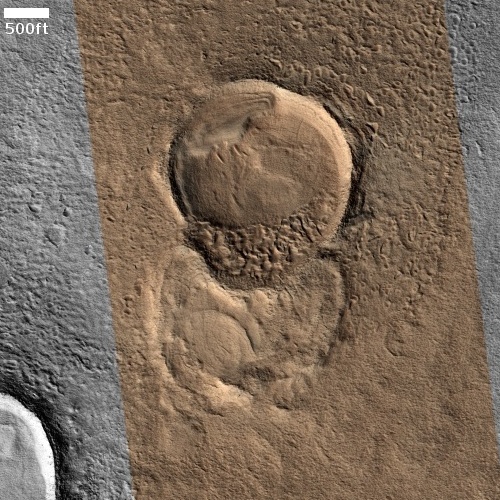
The floor of Aram Chaos is a place of great puzzlement to planetary geologists. The geology there is incredibly complex, and includes chaos terrain overlain by several sedimentary layers of sulfate minerals. The chaos terrain is most obvious in the southern part of the crater’s floor. The flat areas near the eastern center are those overlaying sedimentary layers.
When we zoom into the white box we can see a good example of this complexity.
» Read more

With today’s cool image, we shall begin with the overview map, and drill our way down until we get a close look at another example of truly alien Martian terrain, with only a hint of similarity to comparable geology on Earth.
The overview map to the right shows us Aram Chaos, an ancient 170-mile-wide impact crater that has gone through such complex geology that it is difficult, maybe impossible, to unravel it based on data obtained from orbit. As I wrote in a detailed December 2020 post describing the confusing geology of this crater,
The floor of Aram Chaos is a place of great puzzlement to planetary geologists. The geology there is incredibly complex, and includes chaos terrain overlain by several sedimentary layers of sulfate minerals. The chaos terrain is most obvious in the southern part of the crater’s floor. The flat areas near the eastern center are those overlaying sedimentary layers.
When we zoom into the white box we can see a good example of this complexity.
» Read more