A half-mile high Martian cliff on the verge of collapse
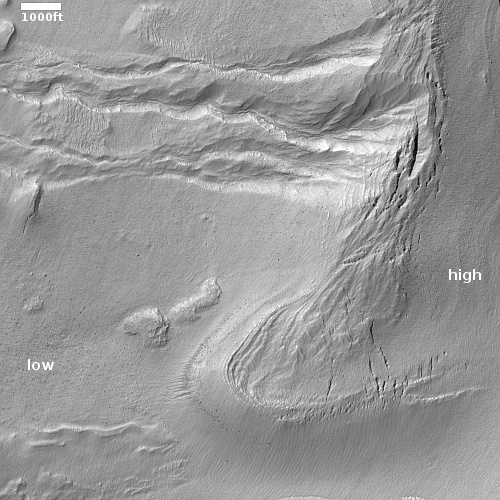
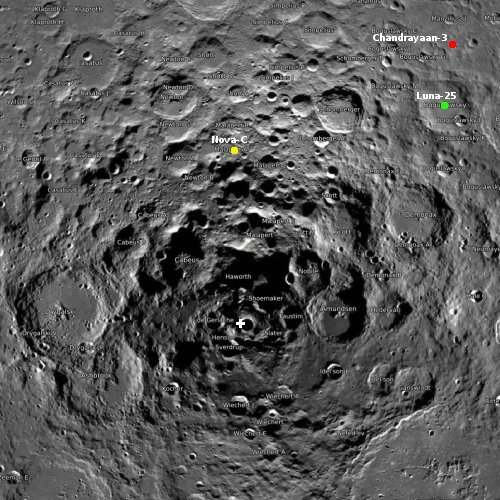
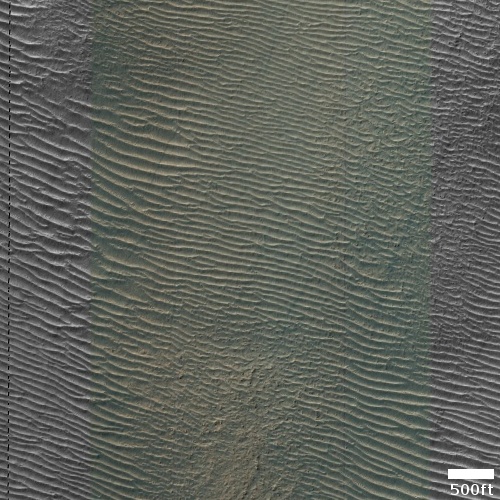
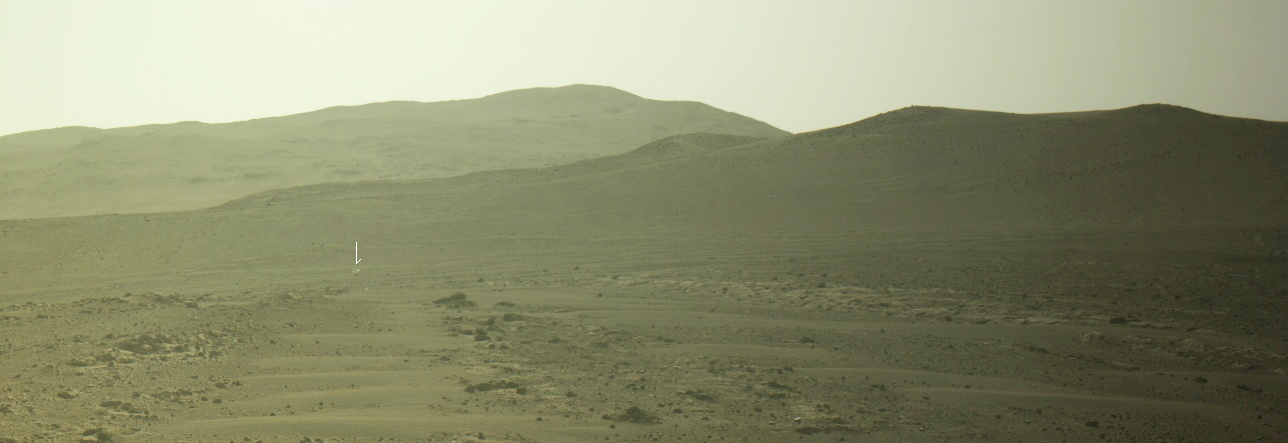
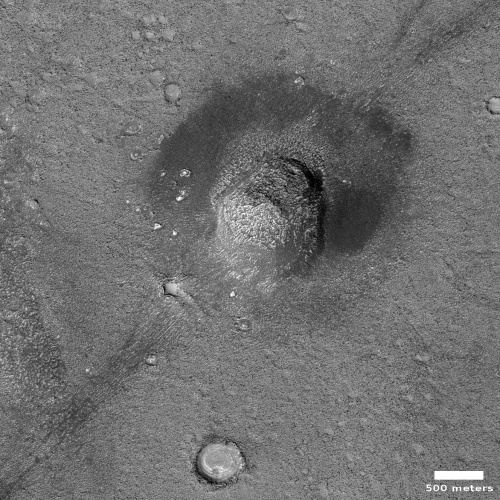
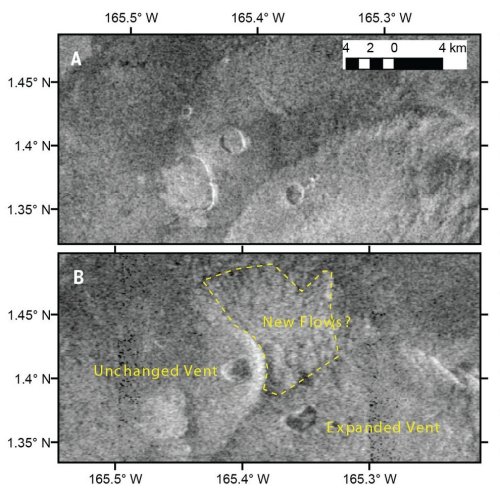
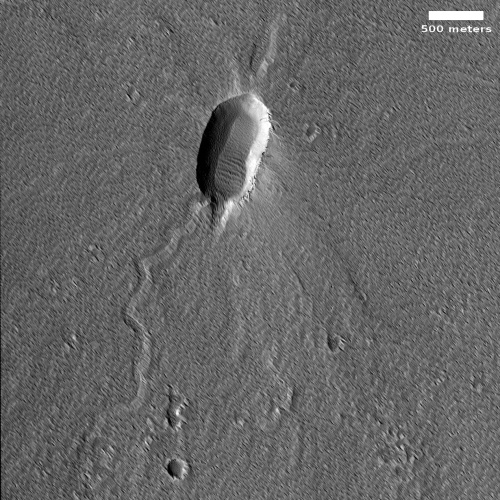
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on December 24, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows erosion gullies coming down off a mountain side, just north of a massive cliff that I estimate to be around 2,000 to 3,000 feet high.
Note the north-south-trending cracks. These suggest that this entire half-mile-high cliff face is slumping downward, cracking as it does so. The cracks at the start of the high flat-topped thumb-shaped mesa near the image bottom are especially intriguing. They suggest that this entire mesa might eventually separate and give way.
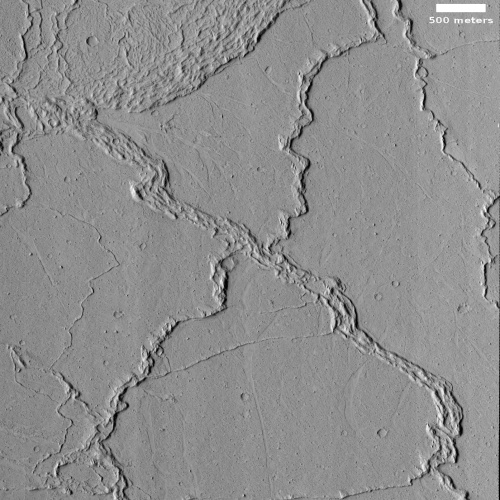
There is a specific reason this cliff face is slumping, as shown in the overview map below.
» Read more
Cool image time! The picture to the right, cropped and reduced to post here, was taken on December 24, 2022 by the high resolution camera on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). It shows erosion gullies coming down off a mountain side, just north of a massive cliff that I estimate to be around 2,000 to 3,000 feet high.
Note the north-south-trending cracks. These suggest that this entire half-mile-high cliff face is slumping downward, cracking as it does so. The cracks at the start of the high flat-topped thumb-shaped mesa near the image bottom are especially intriguing. They suggest that this entire mesa might eventually separate and give way.
There is a specific reason this cliff face is slumping, as shown in the overview map below.
» Read more